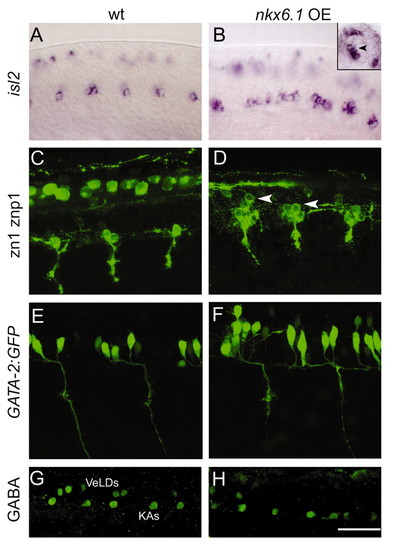
nkx6.1 is sufficient to induce zebrafish motoneurons and repress interneurons. (A) isl2-positive CaPs and VaPs at 18 hpf. Wild-type embryos have 1.3±0.7 isl2-positive cells per spinal hemisegment (n=5). (B) Embryos injected with nkx6.1 mRNA (Nkx6.1 OE) display supernumerary isl2-positive cells (2.3±0.5 per spinal hemisegment; n=7). These numbers are significantly different (P<0.001). Most RBs are not in focus in these images. Inset is a cross-section indicating the more dorsal position of supernumerary PMNs (arrowhead). (C) 24 hpf wild type labeled with zn1 and znp1 antibodies reveals 1 or 2 CaP/VaP cell bodies and axons as well as RBs. (D) Embryos injected with nkx6.1 RNA have 3-4 CaP/VaPs with normal axons, but some are more dorsally located (arrowheads). RBs are out of focus. (E) Wild-type 24 hpf GATA-2:GFP embryo has clusters of 3.0±1.7 SMNs in each rostral spinal cord hemisegment (8 hemisegments in 2 embryos). (F) nkx6.1 RNA-injected embryos have 4.0±2.8 SMNs per cluster (n=4; numbers are significantly different, P<0.009). All views are lateral, rostral to left. Scale bar: 50 μm for A,B; 33 μm for C-H.
|

