Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090520-1
- Publication
- Thisse et al., 1994 - Goosecoid expression in neurectoderm and mesendoderm is disrupted in zebrafish cyclops gastrulas
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
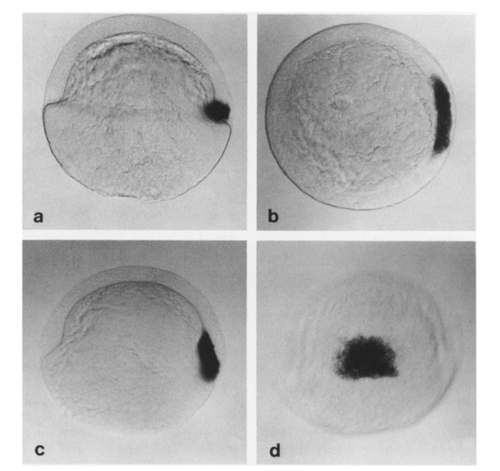
Localization of gsc transcripts by in situ hybridization in wild-type late blastula and early gastrula. (a) Lateral view of an embryo at 45% epiboly (late blastula) showing gsc transcripts restricted to a group of deep cells at the dorsal margin of the embryo (animal pole up; dorsal, right). (b) Animal pole view of the same embryo. The territory of goosecoid expression occupies about 60° of the circumference of the embryo at the dorsal margin (dorsal, right; ventral, left). (e) Lateral view of an embryo at 60% epiboly (early gastrula). All goosecoid-expressing cells have involuted and the territory has begun to extend toward the animal pole. (d) Dorsal view of the same embryo showing that the gsc-expression territory now occupies the central part of the embryonic shield, the precursor of the prechordal plate (animal pole, up). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 164, Thisse, C., Thisse, B., Halpern, M.E., and Postlethwait, J.H., Goosecoid expression in neurectoderm and mesendoderm is disrupted in zebrafish cyclops gastrulas, 420-429, Copyright (1994) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.