Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080401-12
- Publication
- Ignatius et al., 2008 - colgate/hdac1 repression of foxd3 expression is required to permit mitfa-dependent melanogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
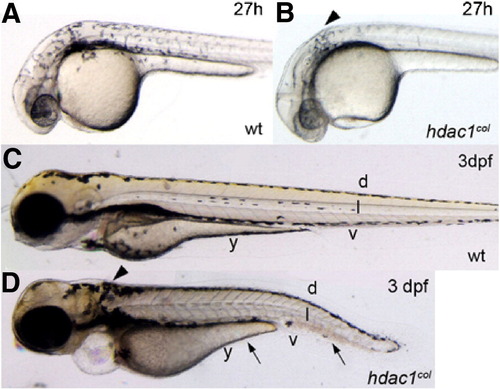
Melanophore development is defective in hdac1col mutants. Lateral views of live embryos at 27 hpf (A, B) and 3 dpf (C, D). (A, B) At 27 hpf in wild-type embryos melanophores are present posterior to the eye and otic vesicle and are migrating over the flank of the embryo. In hdac1col mutants, there are fewer melanophores and most of the melanophores are located posterior to the otic vesicle (arrowhead). There are no migrating melanophores in hdac1col mutants. (C, D) By 3 dpf, melanophores are present in four stripes in wild-type: dorsal (d), lateral (l), ventral (v) and yolk (y). In hdac1col mutants melanophore numbers do not recover. Melanophores present in hdac1col fail to migrate and are mainly localized to the dorsal stripe and a patch of melanophores posterior to the otic vesicle (arrows, arrowhead). Melanophores that do migrate ventrally in hdac1 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 313(2), Ignatius, M.S., Moose, H.E., El-Hodiri, H.M., and Henion, P.D., colgate/hdac1 repression of foxd3 expression is required to permit mitfa-dependent melanogenesis, 568-583, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.