Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-060824-9
- Publication
- Gulati-Leekha et al., 2006 - A reporter-assisted mutagenesis screen using α1-tubulin-GFP transgenic zebrafish uncovers missteps during neuronal development and axonogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
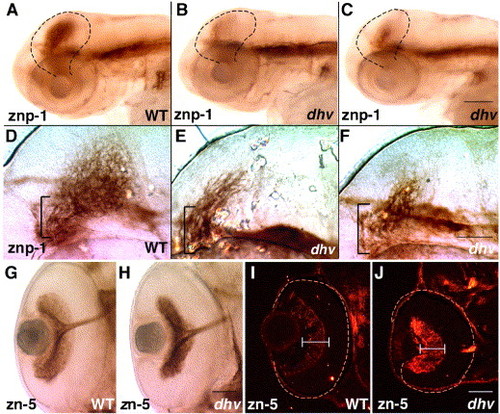
Mutation in dhruva disrupts the retinotectal architecture without affecting RGC differentiation and optic nerve formation. znp-1 immunostaining of 3-day-old embryos highlights tectal innervation, which is dramatically reduced in mutants (A–C). Higher magnification images indicate unbranched (E) or stalled retinal axons (F) in mutant tecta whereas the wild-type tectum displays an intricate arborization pattern (D). Brackets mark the fasciculated segments of the optic tract as it approaches the tectum. Immunostaining using zn-5 antibody in panels G and H confirms that RGCs elaborate axons and form a normal optic tract in dhv mutants at 57 hpf. Subsequently, impaired arborization and innervation probably leads to loss of DM-GRASP down-regulation in 3-day-old dhv retinas (zn-5 immunostaining of retinal sections; I, J). All images are oriented such that anterior is towards left. Scale bar: 100 μm in panels A–C, 50 μm in panels D–F, G and H, and I and J. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 296(1), Gulati-Leekha, A., and Goldman, D., A reporter-assisted mutagenesis screen using α1-tubulin-GFP transgenic zebrafish uncovers missteps during neuronal development and axonogenesis, 29-47, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.