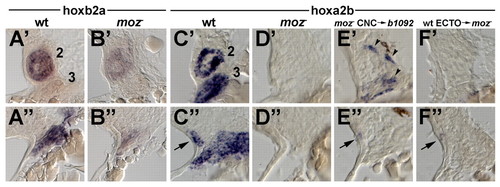
Moz is required for Hox expression in multiple facial tissues. Horizontal sections were taken at 34 hpf at dorsal (A'-F') and ventral (A"-F") levels of the pharyngeal segments and stained with probes against hoxb2a (A,B) or hoxa2b (C-F). The second and third segments (numbered) from individual sides are shown with anterior to the top and lateral (ectoderm) to the left. (A',A") In the wild-type pharynx, hoxb2a is expressed exclusively in CNC of the second segment. (B',B") hoxb2a expression is very reduced inmoz mutants. (C',C") In wild types, hoxa2b is strongly expressed in the CNC of the second and more posterior segments but not in the mesoderm core of the second segment. Ventral sections show additional expression in a small amount of surface ectoderm (arrows). In other sections, hoxa2b expression is seen in the endoderm of the second and more posterior pouches (data not shown). (D',D") In moz mutants, hoxa2b expression is absent or very reduced in CNC, surface ectoderm and endoderm. (E',E") In b1092 mutant sides that received moz- CNC transplants (see text), hoxa2b expression is lost in CNC. In this example, a small amount of CNC expression persists (arrowheads). However, weak expression of hoxa2b in the ectoderm is still seen (arrow). (F',F") In moz- sides that received wild-type ectoderm transplants (see text), hoxa2b expression is present in the ectoderm (arrow) but absent in CNC.
|

