Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-060706-12
- Publication
- Crump et al., 2006 - Moz-dependent Hox expression controls segment-specific fate maps of skeletal precursors in the face
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
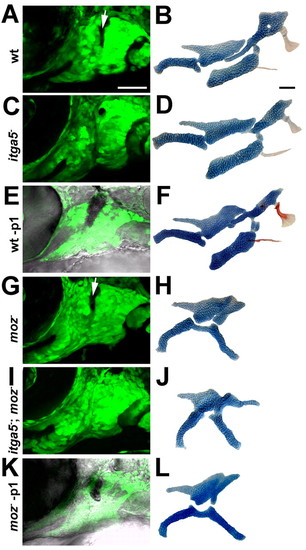
The development of moz- second-segment cartilage does not depend on p1 endoderm. CNC segments at 36 hpf (A,C,E,G,I,K) and facial skeletons at 4 dpf (B,D,F,H,J,L) from wild-type fli1:GFP (A,B,E,F), itga5b926; fli1:GFP (C,D), moz-; fli1:GFP (G,H,K,L), and moz-; itga5b926; fli1:GFP (I,J) animals. In E and K, inclusion of the Normarski channel shows that p1 endoderm has been selectively ablated by laser irradiation, as evinced by the dark pyknotic nuclei. When p1 is eliminated in either itga5b926; fli1:GFP (C) or p1 ablated (-p1) (E) animals, the anterior portion of the Hm cartilage is lost and Sy cartilage is variably reduced (D,F). However, removal of p1 in moz-; itga5b926; fli1:GFP (I) or p1 ablated moz- (K) animals does not affect the shape of Pq' (J,L). For p1 laser ablations, 13/14 wild-type animals had reduced Hm cartilage and 0/5 moz mutants had reduced Pq'. Arrows denote p1. Scale bars: 50 µm. |