- Title
-
Complex expression of the zp-50 pou gene in the embryonic zebrafish brain is altered by overexpression of sonic hedgehog
- Authors
- Hauptmann, G. and Gerster, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
In situ hybridization analysis of zp-50 expression during embryogenesis. All pictures are side views with the anterior part of the embryos oriented towards the left. In some cases the yolk has been removed for better visibility. Wild-type (A-F) and cyclops mutant (G,H) embryos were hybridized with a zp-50 probe. (A) bud (10 hpf). The asterisk marks the earliest expression domain in the forming posterior diencephalon (dorsal thalamus). (B) 5 somites (12 hpf). Rhombomeres r3 and r5 are indicated, as well as the early transverse zp-50 expression domain in the diencephalon (asterisk). The longitudinal expression domain in the ventral forebrain (arrowheads) is absent in cyc-/- embryos (cf. G). (C) 10 somites (14.5 hpf). Alternating high levels of zp-50 expression are found in odd-numbered rhombomeres r1, r3, r5 and r7. Expression begins in the telencephalon. (D) 20 somites (19 hpf). The asterisk marks the initial zp-50 expression domain in the dorsal thalamus. The initially contiguous longitudinal expression along the forebrain is subdivided into several domains. (E) 26 hpf. Open triangles indicate the lateral arches in rhombomeres r3 and r5. The lower part of these arches coincide with rhombomere boundaries. The arrow points to the forming ventral flexure. (F) 34 hpf. Hindbrain expression is observed in paired stripes along the rhombomere boundaries. (G) 5 somite cyc-/- embryo. zp-50 is expressed in rhombomeres r3 and r5 and the transverse domain in the posterior diencephalon (asterisk). Arrowheads indicate missing zp-50 expression in the ventroanterior brain. (H) 30 hpf cyc-/- embryo. Diencephalic zp-50 expression is found only in the dorsal thalamus in the area derived from the initial expression site visible after the bud stage (asterisk). c, cerebellum; d, diencephalon; dt, dorsal thalamus; e, eye; h, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; m, mesencephalon; sc, spinal cord; t, telencephalon; tc, tectum; tg, tegmentum; vt, ventral thalamus. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Characterization of zp-50 expression by doublelabeling. In all side and dorsal views anterior is to the left. (A-D) 2 color in situ hybridization for zp-50 (purple) and pax-2 transcripts (red). (A) Dorsal view of flat mounted bud stage embryo with zp-50 staining in the posterior diencephalon and pax-2 expression along the future midbrain/hindbrain junction. (B) Side view of the mid-/hindbrain border region of a 10 somite stage embryo. Arrows indicate a zone of overlapping zp-50 and pax-2 expression. (C) Dorsal view of 26 hpf embryo. zp-50-expressing cells in the tegmentum are separated by a gap of 2-3 cell diameters (arrowheads) from the pax-2 domain at the midbrain/hindbrain boundary. (D) Frontal view of 27 hpf embryo: pax-2 stains the optic stalks emerging next to the anteriormost position of diencephalic zp-50 expression. (E) Dorsal view of 34 hpf anterior diencephalon hybridized with zp-50 (purple). Axons are immunostained with an antibody to acetylated tubulin (red). The anteriormost zp-50 expression site is surrounded (arrows) by the axons of the postoptic commissure and its associated longitudinal tract (TPOC). (F) Dorsal view of 36 hpf telencephalon hybridized with zp-50 (purple). The zp-50-expressing cells are more medial but partially overlap with neural cells positive for the zn-12 epitope (red) projecting axons into the tract of the anterior commissure. (G) Side view of 34 hpf embryo hybridized with zp-50 (purple). Axons are stained with the acetylated tubulin antibody (red). The eyes have been removed. The small arrow in the anterior diencephalon indicates zp-50 expression located in the immediate vicinity of the junction between the telencephalic (or supraoptic) axon tract with the tract of the postoptic commissure. The white arrow shows the nucMLF which is surrounded ventrally, anteriorly and dorsally by the zp-50 expression domains. Large arrows in the area of the hindbrain indicate reticulospinal neurons in the rhombomere centers flanked by zp-50-expressing double stripes at the interrhombomeric boundaries. (H) Side view of a 5 somite embryo double labeled with zp-50 (purple) and krx-20 (red) expressed in rhombomeres r3 and r5. (I) Dorsal view of 36-40 hpf hindbrain hybridized with zp-50 (purple) and hlx-1 (red) showing similar expression domains along medial rhombomere borders. The numbers indicate the corresponding rhombomere centers. (J) Dorsal view of 36-40 hpf hindbrain doublestained for zp-50 (purple) and krx-20 (red). At this stage, krx-20 is only strongly expressed in r5 whose borders are indicated by open triangles. AC, anterior commissure; c, cerebellum; d, diencephalon; e, eye; h, hindbrain; m, mesencephalon; nMLF, nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle; OS, optic stalk; PC, posterior commissure; POC, postoptic commissure; r1, r3, r5, rhombomeres 1, 3 and 5; t, telencephalon; TAC, tract of the anterior commissure; TPC, tract of the posterior commissure; TPOC, tract of the postoptic commissure; TT, telencephalic (or supraoptic) tract. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Alterations of gene expression in 10-12 somite stage shh-injected embryos. Embryos injected (inj) with 25 ng/ml shh RNA (D,F,H,J) or control embryos (A,B,C,E,G,I) fixed at the 10-12 somite stage were analyzed by in situ hybridization. (A) shh staining in the ventral CNS. (B) The longitudinal expression domains of shh (red) and zp-50 (purple) occupy very similar territories in the ventral diencephalon. (C,D) zp-50 expression is dorsally expanded in the ventral diencephalon and the midbrain of shh-injected embryos. The beginning expression in the telencephalon (cf. B) is reduced in injected embryos. (E,F) axial expression is extended dorsally in the posterior diencephalon. (G,H) hlx-1 expression in the prechordal plate and the ventralmost midline ectoderm is not significantly altered by shh overexpression. However, expression (asterisks) in the mid- and hindbrain is shifted to more dorsal locations. (I,J) Crossections through the middiencephalon of double-labeled embryos show the dorsal expansion (arrowheads) of zp-50 expression (purple), whereas hlx-1 expression in the mesoderm and in the ventralmost ectodermal tissue is unaltered (red). d, diencephalon; h, hindbrain; m, mesencephalon; pcp, prechordal plate. |
|
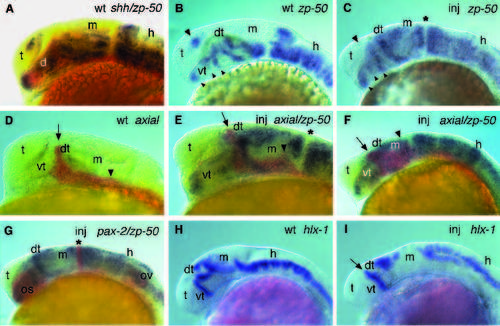
Ectopic gene expression in 1-day old shh injected embryos. Embryos injected with capped shh RNA at 25 or 50 ng/μl (inj; C,E,F,G,I) or controls (wt; A,B,D,H) were analyzed by in situ hybridization. Embryos were fixed at 24-26 hpf (A-G) or at 30 hpf (H,I). (A) Double hybridization with zp-50 (purple) and shh (red) shows close proximity of expression in the ventroanterior brain. (B,C) shh injection causes disorganized and elongated zp- 50 expression domains in the ventroanterior diencephalon (small arrowheads). Prominent ectopic expression is visible in the dorsal thalamus and the midbrain. No aberrant zp-50 expression is observed along the midbrain/hindbrain boundary of injected embryos (asterisk). zp-50 expression is reduced in the telencephalon of injected embryos (large arrowheads). (D) Uninjected embryo stained for axial. (E,F) Two different examples of shh-injected embryos double labeled for zp-50 (purple) and axial (red). Besides ectopic zp- 50 expression, axial expression shows in these embryos a dorsal expansion of the finger-like domain in the dorsal thalamus (arrow). The relatively modest axial overexpression in the midbrain seen in E is more frequently seen than the more widespread expression in the midbrain tegmentum (arrowhead) visible in F. (G) shh-injected embryo double labeled for zp-50 (purple) and pax-2 (red). pax-2 expression in the otic vesicle and in the zp- 50-free gap at the midbrain/hindbrain boundary (asterisk) is not obviously affected by shh misexpression. However, pax-2 expression is dramatically widened in the optic stalk (cf. Fig. 3D). (H,I) Injection of shh RNA eliminates several hlx-1 expression domains in the midbrain. Residual hlx-1 midbrain expression is shifted dorsally like the expression domains in the hindbrain. d, diencephalon; dt, dorsal thalamus; h, hindbrain; m, mesencephalon; os, optic stalk; ov, otic vesicle; t, telencephalon; vt, ventral thalamus. |

Unillustrated author statements |