- Title
-
Prpf4 sequentially regulates the expansion and maturation of erythrocyte through distinct mechanisms
- Authors
- Deng, Z., Huang, S., Pei, Y., Li, H., Dong, Y., Li, Y., Ran, Q., Liu, X., Feng, Y., Wang, Q., Guo, Z., Huang, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell Death Discov
|
The |
|
|
|
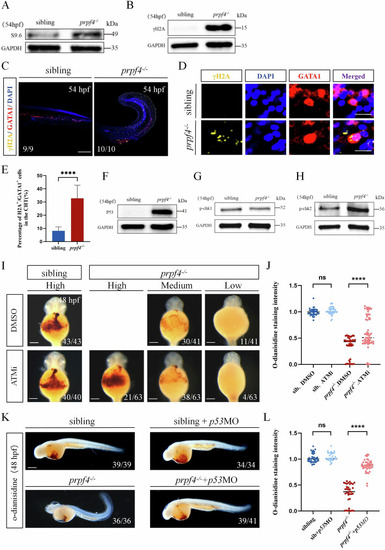
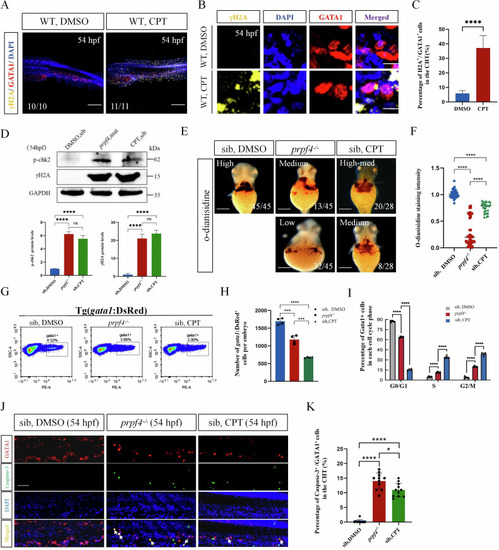
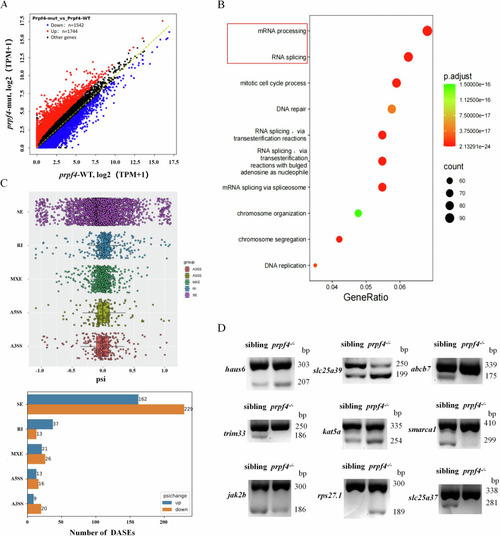
Activating of the DDR-ATM/Chk2-p53 signaling pathway disrupts erythropoiesis in |
|
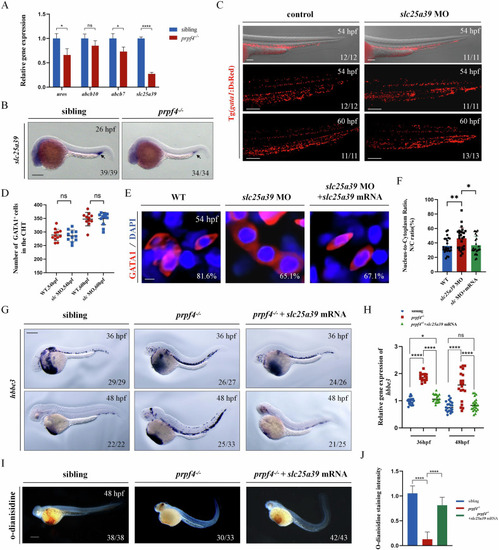
DNA damage-induced ATM/Chk2-p53 pathway partially mediates erythrocyte defects in |
|
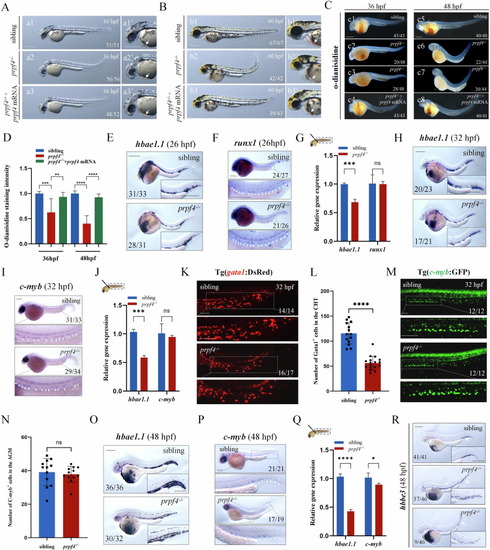
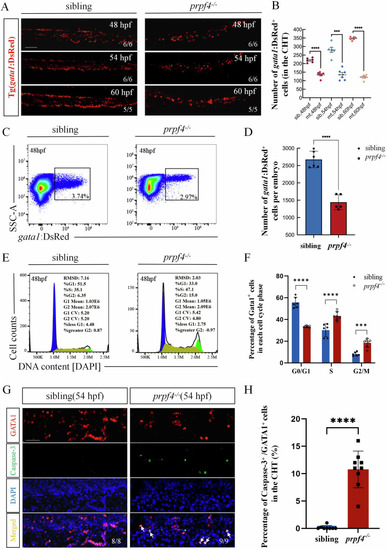
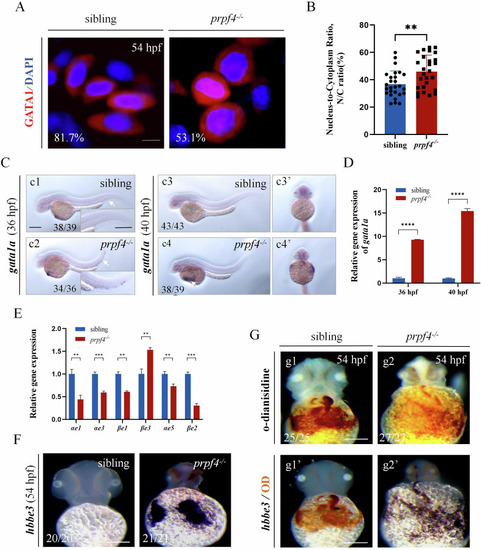
The maturation of erythrocytes is disturbed in |
|
|
|
|