- Title
-
The Neuroprotective Effects of the Crinoid Natural Compound Rhodoptilometrin in Parkinson's Disease Experimental Models: Implications for ER Stress and Autophagy Modulation
- Authors
- Wen, Z.H., Chiu, Y.J., Yang, S.N., Guo, B.L., Feng, C.W., Chunag, J.M., Chen, N.F., Chen, W.F.
- Source
- Full text @ ACS Chem. Neurosci.
|
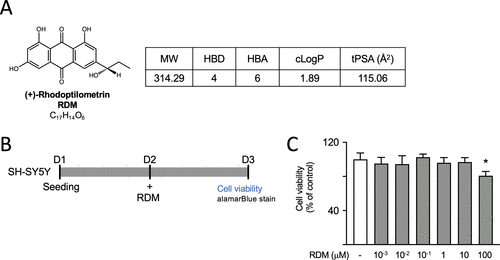
RDM properties and its impact on cell viability. (A) Structure, formula, molecular weight (MW), hydrogen bond donor (HBD), hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA), calculated octanol–water partition coefficient (cLogP), and topological polar surface area (tPSA) of RDM. (B, C) The cytotoxicity of RDM against SH-SY5Y cells was assessed by using the alamarBlue assay. Cells were plated on day 1 and treated with RDM at concentrations ranging from 10–3 to 100 μM for 16 h on day 2, and cell viability was assessed using alamarBlue stain on day 3. The relative viability of control cells is presented as 100% for normalization. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group. RDM, (+)-rhodoptilometrin |
|
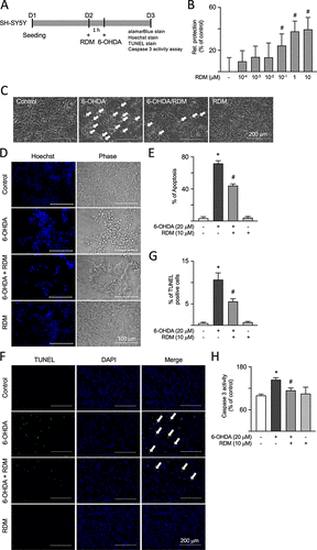
Antiapoptotic effects of RDM in 6-OHDA-treated SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Experimental flowchart. On day 1, cells were plated. On day 2, cells were pretreated with RDM for 1 h and then induced with 6-OHDA for 16 h to cause neurotoxicity. After that, cell viability, cell apoptosis, and caspase 3 activity were assessed using alamarBlue stain, Hoechst and TUNEL stain, and a caspase 3 colorimetric assay kit, respectively. (B) Cell viability was measured using the alamarBlue assay to analyze the neuroprotective activity of various concentrations of RDM (10–4–10 μM). The relative neuroprotection rates (relative protection) were calculated based on cell viability, with the relative cell protection of untreated cells presented as 0%. (C) Phase-contrast images of control, 6-OHDA (20 μM), 6-OHDA (20 μM)/RDM (10 μM), and RDM (10 μM) groups. Cell morphology was observed by using a microscope. Cell death patterns such as shrinkage, floating, and deformation are indicated by white arrows. (D) Microscopic images of the effects of RDM (10 μM) on 6-OHDA-treated SH-SY5Y cells by Hoechst stainings. (E) Cell apoptosis was quantified by measuring the blue fluorescence signals from panel D, indicating condensed or fragmented nuclei. (F) The images of TUNEL staining and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). White arrows indicate cells with TUNEL fluorescence signals. (G) The TUNEL signal was quantified by measuring the green fluorescence signals from panel F. (H) Caspase 3 activity assays with RDM (10 μM) treatment. The relative caspase 3 activity of control cells is presented as 100% for normalization. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05 compared with the 6-OHDA alone group. RDM, rhodoptilometrin; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; and DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
|
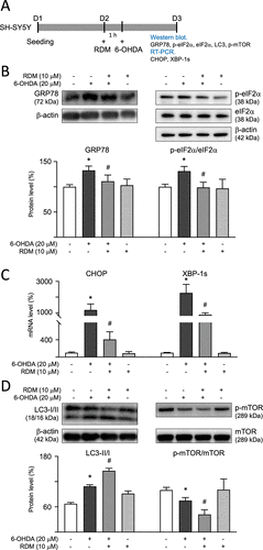
Modulation of ER stress and autophagy signaling in 6-OHDA-treated SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Experimental flowchart. On day 1, cells were plated. On day 2, after a 1 h pretreatment with RDM, cells were subjected to 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity for 16 h. GRP78, p-eIF2α, LC3-I/II, and phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated mTOR were detected using Western blot, while the mRNA levels of CHOP and XBP-1s were measured using RT-PCR. Protein levels of (B) GRP78, p-eIF2α (S51)/eIF2α; (D) LC3-I/II, p-mTOR (S2448); and mTOR were analyzed using β-actin as the internal control. mRNA levels of (C) CHOP and XBP-1s were analyzed using GAPDH as the internal control. The relative protein expression level of control cells is presented as 100% for normalization. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05 compared with the 6-OHDA alone group. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; RDM, rhodoptilometrin; GADPH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; and mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin. |
|
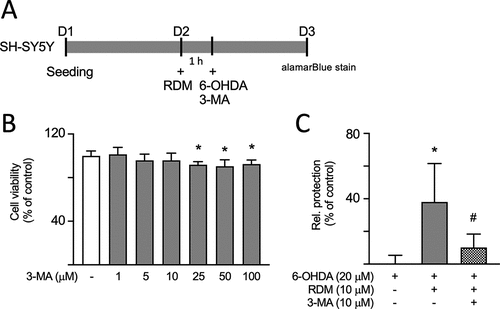
Impact of inhibiting autophagy on the neuroprotective activities of RDM in SH-SY5Y cells treated with 6-OHDA. (A) Experimental flowchart. On day 1, cells were plated. On day 2, cells were pretreated with RDM for 1 h followed by treatment with 3-methyladenine (3-MA), an autophagy inhibitor. The cells were then subjected to 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity for 16 h. Cell viability was assessed using alamarBlue staining. (B) 3-MA cytotoxicity on SH-SY5Y cells using alamarBlue assay. Cells were treated with 3-MA at concentrations ranging from 1 to 100 μM for 16 h. The relative viability of control cells is presented as 100% for normalization. (C) Assessment of neuroprotective activity with 3-MA (10 μM) and RDM (10 μM) treatment. The relative neuroprotection (relative protection) was calculated based on cell viability, with the relative cell protection of untreated cells presented as 0%. *p < 0.05 compared with control group; #p < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA alone group. RDM, rhodoptilometrin. |
|
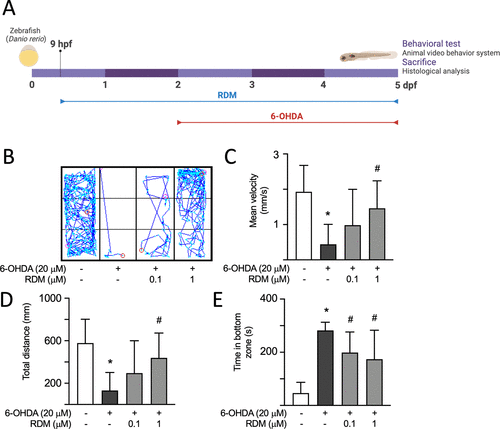
Effect of RDM on locomotor activity in 6-OHDA-induced zebrafish PD model. (A) Experimental flowchart. RDM (0.1 and 1 μM) was continuously administered to zebrafish embryos from 9 h postfertilization (hpf) to 5 days postfertilization (dpf). During this period, 250 μM 6-OHDA was added from 2 to 5 dpf. The swimming patterns of the zebrafish were recorded using an Animal Video Behavior System, and their locomotor activity was analyzed. After the zebrafish were euthanized, their heads were collected for biochemical analysis. Representative images and quantitative analysis of the effects of RDM on swimming patterns (B), mean velocity (C), total distance traveled (D), and time spent in the bottom zone (E) in the 6-OHDA-induced zebrafish PD model. The relative level of control zebrafish is presented as 100% for normalization. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05 compared with the 6-OHDA alone group. PD, Parkinson’s disease; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; and RDM, rhodoptilometrin. |
|
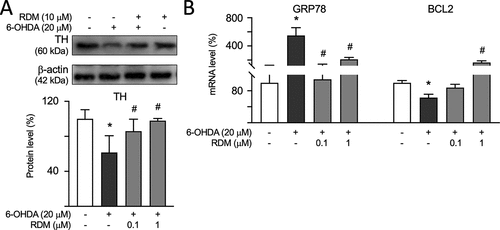
Effect of RDM on dopaminergic-specific marker TH, GRP78, and BCL2 expression in 6-OHDA-induced zebrafish PD models. The zebrafish heads were collected, and TH levels were measured using Western blot, while mRNA levels of GRP78 and BCL2 were measured using RT-PCR. The protein level of (A) TH was analyzed using β-actin as the internal control. mRNA levels of (B) GRP78 and BCL2 were analyzed by using GAPDH as the internal control. The relative protein expression level of control zebrafish is presented as 100% for normalization. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05 compared with the 6-OHDA alone group. 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; RDM, rhodoptilometrin; RT-PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction; and TH, tyrosine hydroxylase. |