Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250804-3
- Publication
- Wen et al., 2025 - The Neuroprotective Effects of the Crinoid Natural Compound Rhodoptilometrin in Parkinson's Disease Experimental Models: Implications for ER Stress and Autophagy Modulation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
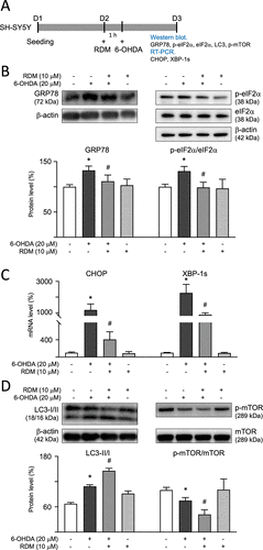
Modulation of ER stress and autophagy signaling in 6-OHDA-treated SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Experimental flowchart. On day 1, cells were plated. On day 2, after a 1 h pretreatment with RDM, cells were subjected to 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity for 16 h. GRP78, p-eIF2α, LC3-I/II, and phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated mTOR were detected using Western blot, while the mRNA levels of CHOP and XBP-1s were measured using RT-PCR. Protein levels of (B) GRP78, p-eIF2α (S51)/eIF2α; (D) LC3-I/II, p-mTOR (S2448); and mTOR were analyzed using β-actin as the internal control. mRNA levels of (C) CHOP and XBP-1s were analyzed using GAPDH as the internal control. The relative protein expression level of control cells is presented as 100% for normalization. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05 compared with the 6-OHDA alone group. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; RDM, rhodoptilometrin; GADPH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; and mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin. |