- Title
-
Altered N6-methyladenosine methylation level in spermatozoa messenger RNA of the male partners is related to unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Authors
- Yang, T., Liu, Y., Lin, Z., Chen, F., Zhu, L., Zhang, L., Zhou, B., Li, F., Sun, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Andrology
|
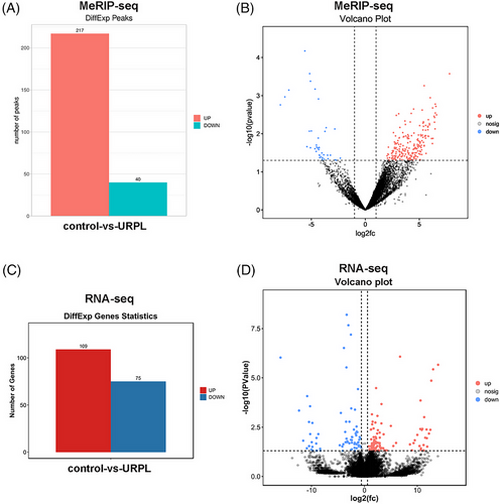
Unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss (URPL) spermatozoa changed N6-methyladenosine (m6A) level and gene expression significantly. Histogram of differentially expressed m6A peaks and expressed genes obtained by methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) (A) and RNA-seq (C) in control and URPL spermatozoa. Volcano plot of changed m6A peaks identified by MeRIP-seq (B) and messenger RNA (mRNA) expression identified by RNA-seq (D) in control and URPL spermatozoa. |
|
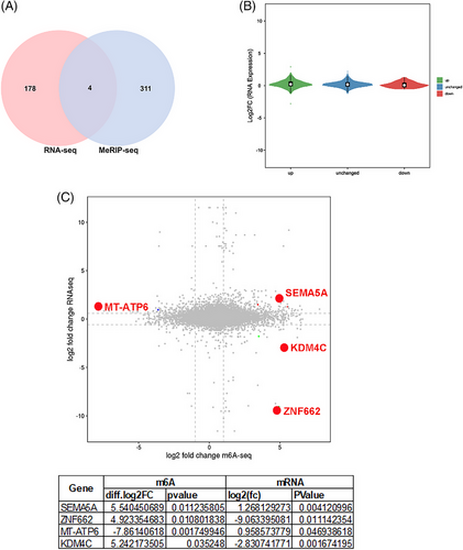
Identification of differential genes in unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss (URPL) spermatozoa by RNA-seq and m6A-seq. (A) Venn diagram shows four significantly co-regulated genes (both N6-methyladenosine [m6A] level and gene expression) in URPL spermatozoa compared to control groups. (B) Violin plot shows the distribution of genes with both m6A methylation level (up, unchanged, and down by X-axis) and gene expression level (Y-axis) in URPL spermatozoa with control groups. (C) The starplot presented the distribution of genes with both differential (hyper or hypo) m6A methylation level (Y-axis) and differential (up or down) gene expression level (X-axis) in URPL spermatozoa compared with control groups. The table shows the detailed data of the four genes |
|
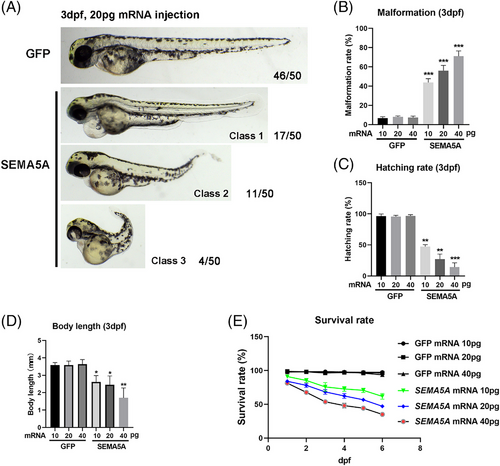
SEMA5A-overexpressed zebrafish embryo model showed significant developmental abnormality. (A) Morphogenesis of live control (injection with GFP messenger RNA [mRNA]) and SEMA5A-overexpressed (injection with SEMA5A mRNA) embryos at 3dpf; SEMA5A morphants at approximately 3dpf are displayed according to increasing levels of severity of axial development (classified 1–3, respectively). Dose-dependent effect of SEMA5A overexpression on zebrafish embryo malformation (B), hatching rates (C), body length (D), and survival rates (E) at 3 dpf. Values significantly different from the control are indicated by asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001). |
|
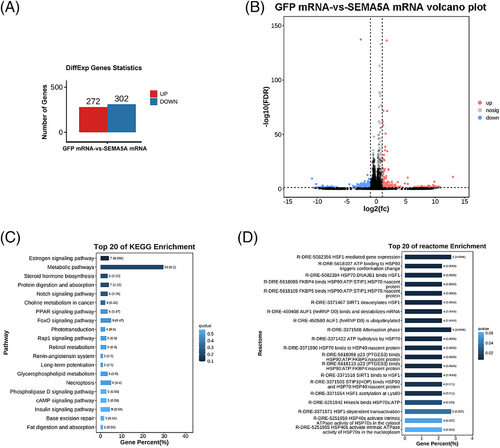
Transcriptomic alteration of SEMA5A overexpression in zebrafish early embryos. Statistical bar chart (A) and volcano plot (B) of differentially expressed genes are depicted. The top 20 enriched KEGG (C) and Reactome (D) pathways. |
|
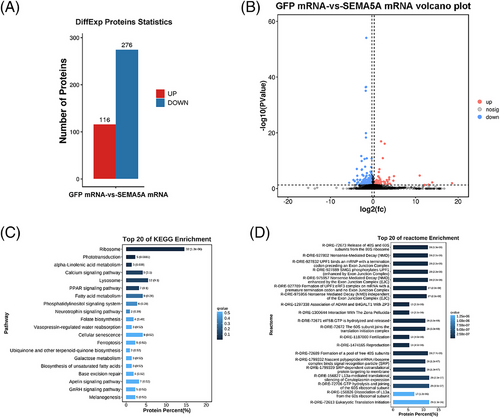
Proteomic alteration of SEMA5A overexpression in zebrafish early embryos (4.5 hpf). Statistical bar chart (A) and volcano plot (B) of differentially expressed proteins are depicted. The top 20 enriched KEGG (C) and Reactome (D) pathways. |
|
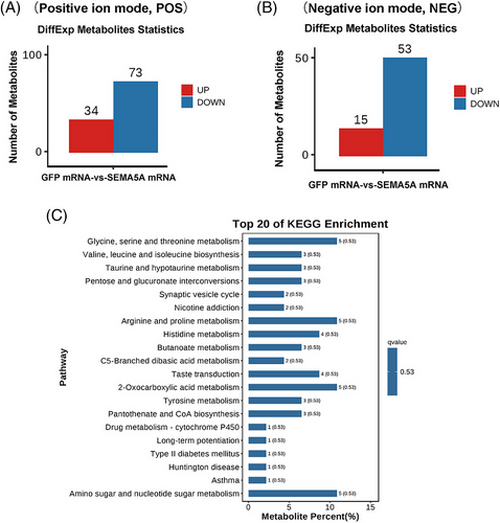
Metabolomic alteration of SEMA5A overexpression in zebrafish early embryos (4.5 hpf). (A, B) Statistical bar chart of differentially expressed metabolites are depicted (POS mode and NEG mode). (C) The top 20 enriched KEGG pathways. |
|
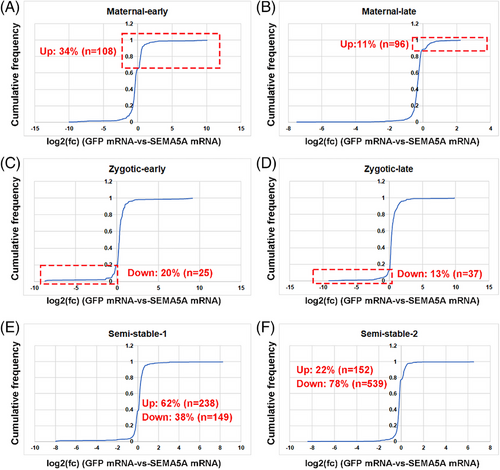
SEMA5A overexpression disturbs zebrafish zygotic genome activation (ZGA). Cumulative distribution of the log2 fold changes of RNA expression at 4.5 hpf for the six gene groups (maternal-early, maternal-late, zygotic-early, zygotic-late, semi-stable 1 and semi-stable 2) between control (GFP injection)and SEMA5A overexpression (A–F). |