- Title
-
Modelling 3D Tumour Microenvironment In Vivo: A Tool to Predict Cancer Fate
- Authors
- Marines, J., Lorenzini, F., Kissa, K., Fontenille, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Curr. Iss. Mol. Biol.
|
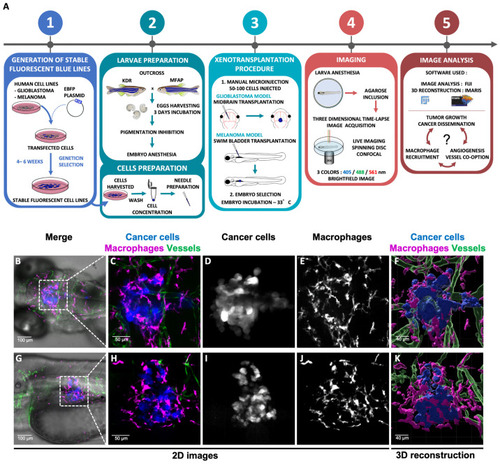
Experimental workflow and 3D glioblastoma and melanoma TME reconstruction. ( |
|
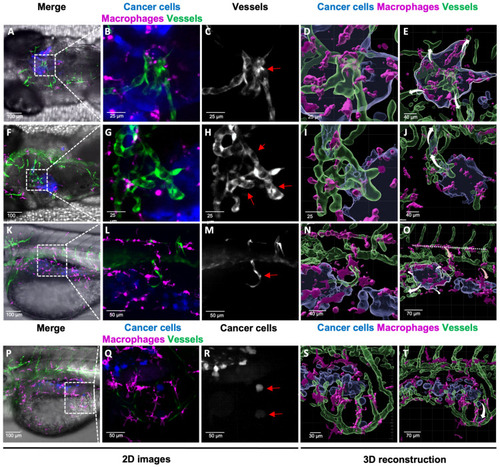
Analysis of 3D TME reconstruction and vessel dynamics: a predictive tool for tumour fate. ( |