- Title
-
Macrophage activation drives ovarian failure and masculinization in zebrafish
- Authors
- Bravo, P., Liu, Y., Draper, B.W., Marlow, F.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci Adv
|
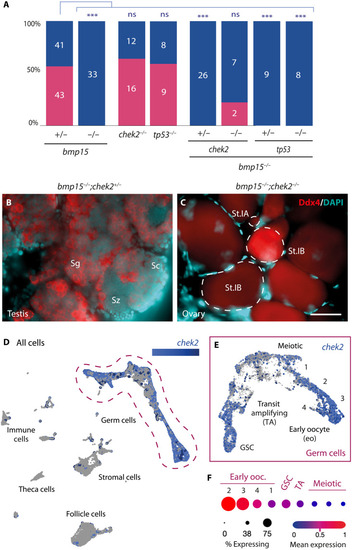
Loss of Chek2 suppresses oocyte death and sex reversal in the absence of Bmp15. ( |
|
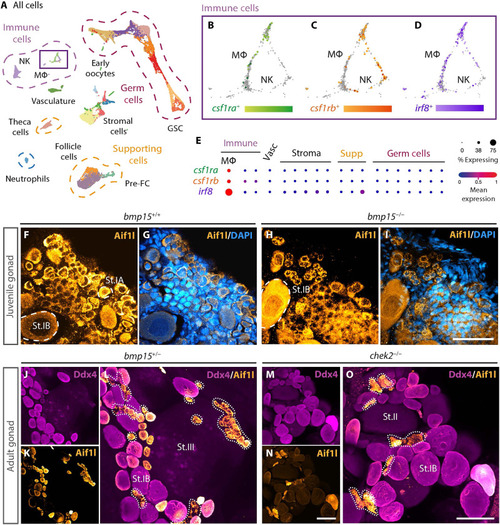
Macrophages are resident ovary cells in juvenile and adult zebrafish ovaries. ( |
|
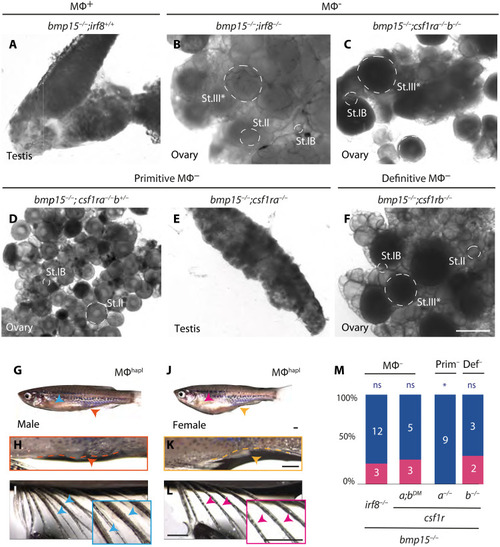
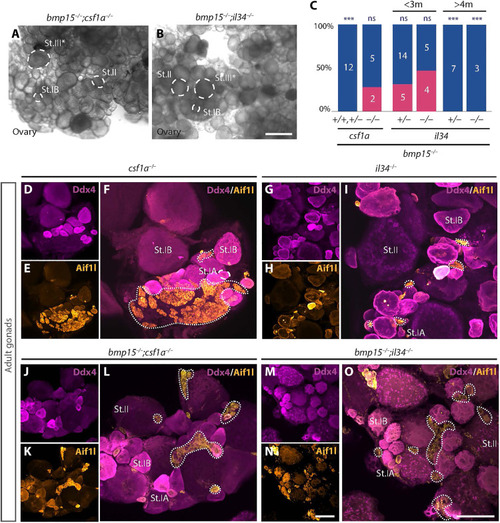
Definitive macrophages are required for ovarian failure and sex reversal of ( |
|
( |
|
( |
|
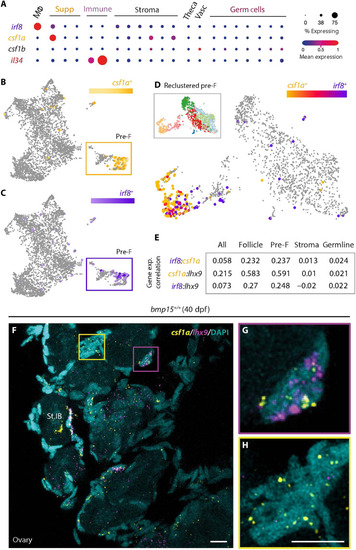
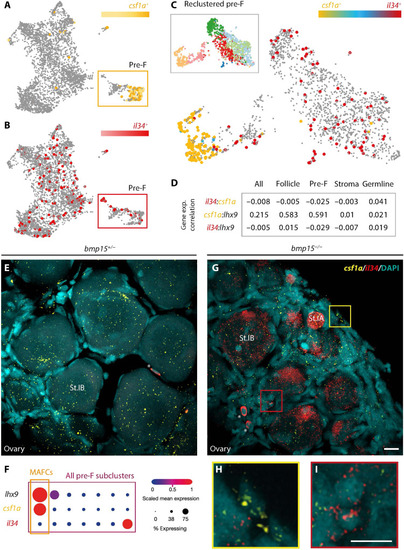
Il34 and Csf1a differentially contribute to ovarian failure and sex reversal and macrophages persist in ( |
|
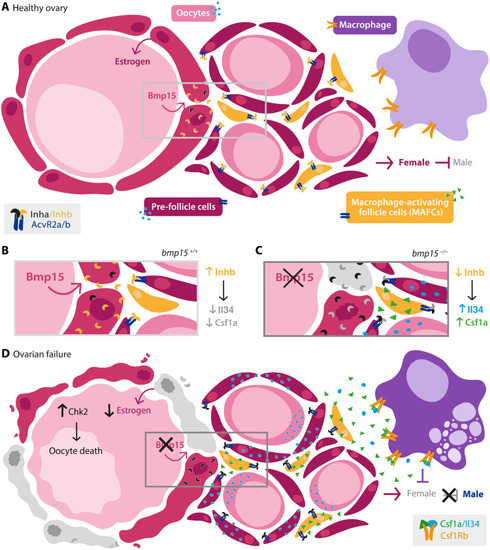
Model of germline-somatic-immune cell axis in healthy ovary and during ovarian failure. Schematic depicts the signals and cellular players in ( |