- Title
-
SBDSR126T rescues survival of sbds-/- zebrafish in a dose-dependent manner independently of Tp53
- Authors
- Oyarbide, U., Shah, A.N., Staton, M., Snyderman, M., Sapra, A., Calo, E., Corey, S.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Life Sci Alliance
|
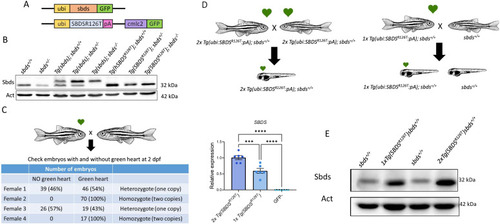
Generation and characterization of the zebrafish transgenic strain expressing |
|
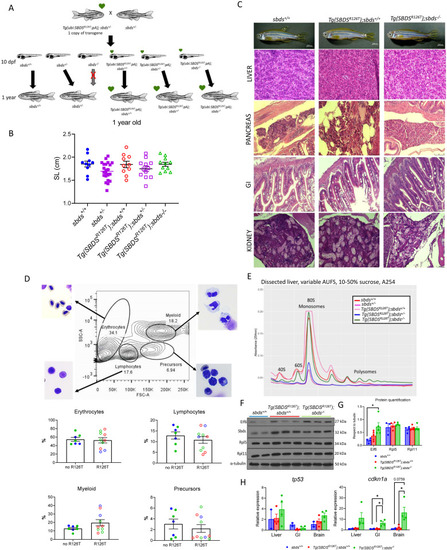
Phenotype and biochemical analysis of adult zebrafish lines expressing the human SBDSR126T. |
|
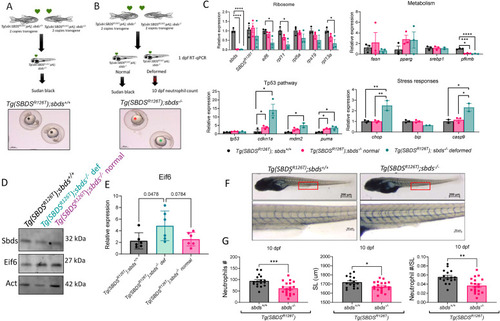
Phenotype of 10 dpf larvae expressing the human SBDSR126T. |
|
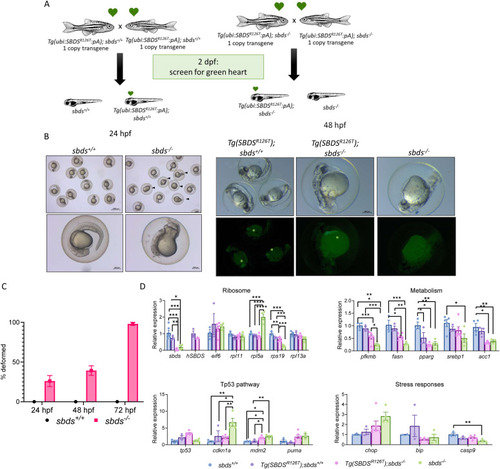
Level of SBDSR126T protein expression affected embryonic development. |
|
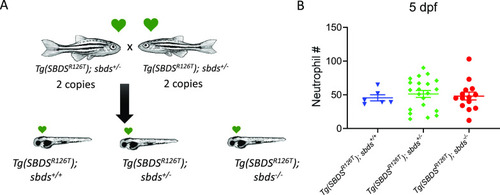
Incrosses of |
|
Two copies of the |
|
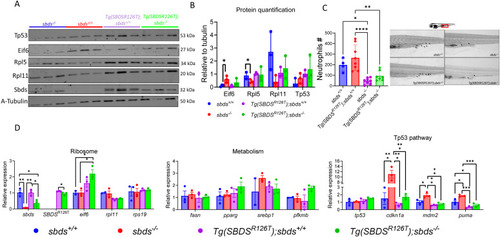
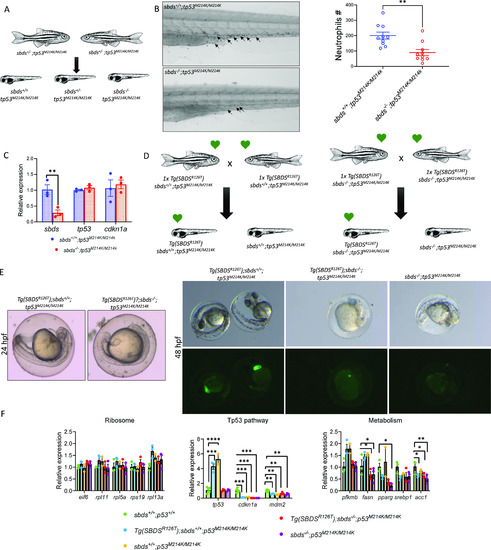
Tp53M214K does not rescue neutropenia or survival in |
|
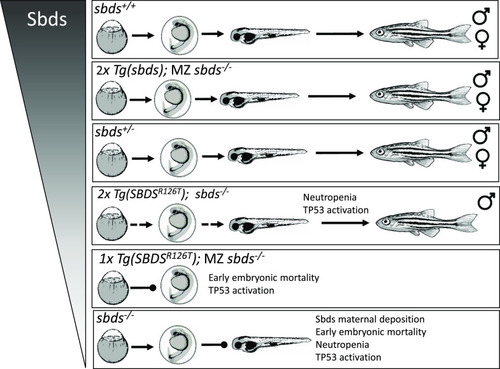
Summary of variable SBDS protein levels on the sbds-null zebrafish. Sbds dose affects survival during development. Note the difference in zebrafish WT sbds rescue |