- Title
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts influence Wnt/PCP signaling in gastric cancer cells by cytoneme-based dissemination of ROR2
- Authors
- Rogers, S., Zhang, C., Anagnostidis, V., Liddle, C., Fishel, M.L., Gielen, F., Scholpp, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
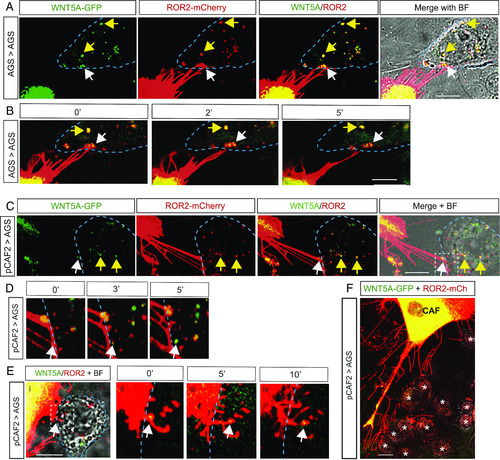
CAFs form extensive filopodial contacts with AGS cells and have up-regulated ROR2 expression on cytoneme tips. ( |
|
ROR2 and WNT5A complexes are transported from producing pCAF2 cells to receiving AGS cells. ( |
|
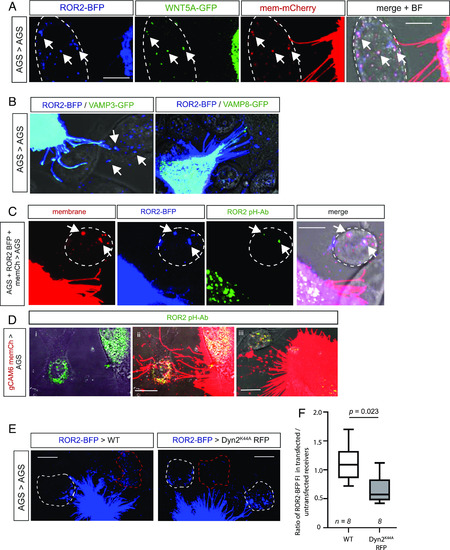
WNT5A/ROR2 complexes are endocytosed by receiving cells and exist in a conformation that enables signaling. ( |
|
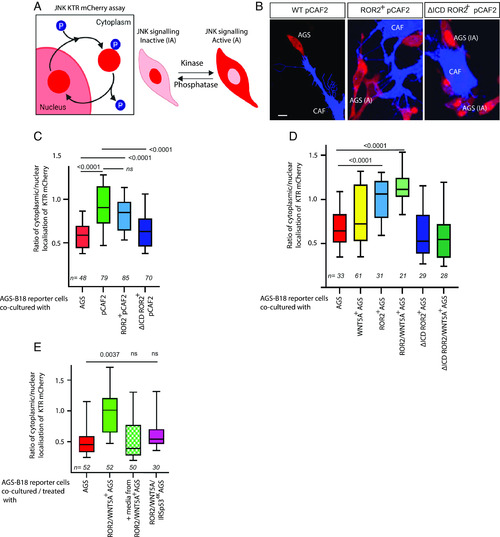
ROR2 induces JNK signaling in receiving AGS cells. ( |
|
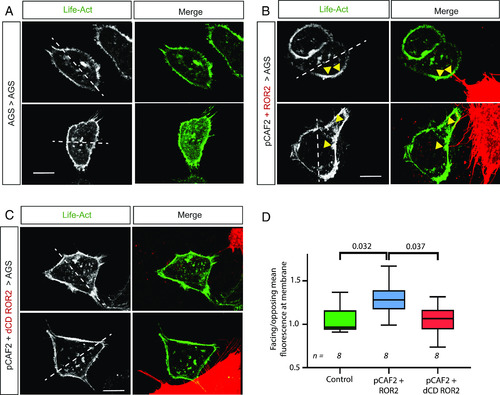
ROR2 induces actin polarization in receiving AGS cells. AGS cells were transfected with LifeAct GFP and cultured either ( |
|
ROR2 induces polarized migration and invasion in 3D models. ( |