- Title
-
Progenitor-derived glia are required for spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish
- Authors
- Zhou, L., McAdow, A.R., Yamada, H., Burris, B., Klatt Shaw, D., Oonk, K., Poss, K.D., Mokalled, M.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
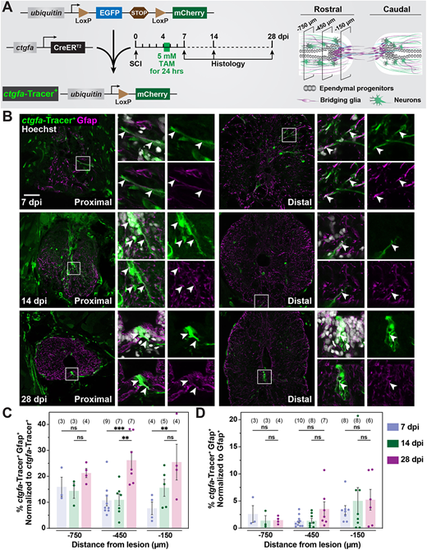
Contribution of ctgfa+ cells to regenerating glia during SC repair. (A) Experimental timeline to evaluate the contribution of ctgfa+ cells after SCI. ctgfa-Tracer animals refer to the compound transgenic line −5.5Kb-ctgfa:CreERT2; ubiquitin:loxP-GFP-STOP-loxP-mCherry. ctgfa-Tracer fish were subjected to complete SC transection and tamoxifen (TAM)-mediated recombination at 4 dpi to enable permanent mCherry labeling in ctgfa+ and ctgfa+-derived cells. SC tissues were collected at 7, 14 and 28 dpi. Schematic of SC tissue illustrates cross-sections at 150, 450 and 750 µm rostral to the lesion that were analyzed for histological examination. The 7 dpi time point was used to assess recombination following TAM treatment. The 14 and 28 dpi time points were used to trace the fates of ctgfa+-derived cells. (B) Immunostaining for mCherry (green), Gfap (magenta), and nuclear Hoechst (gray) at 7, 14 and 28 dpi. mCherry expression, referred to as ctgfa-Tracer+, is used to trace the fates of ctgfa-expressing cells following TAM-inducible recombination. SC sections from TAM-treated ctgfa-Tracer (Cre+) animals are shown. Cross-sections 150 µm (proximal) or 450 µm (distal) rostral from the lesion site are shown. High-magnification insets show select ctgfa-Tracer+ cells in triple-, double- or single-channel views. Arrowheads indicate ctgfa-Tracer+ cells. (C,D) Quantification of ctgfa-Tracer+ and Gfap+ colocalization at 7, 14 and 28 dpi. SC cross-sections 150, 450, and 750 µm rostral to the lesion were analyzed. ctgfa-Tracer+ and Gfap+ fluorescence were quantified. For each section, ctgfa-Tracer+ Gfap+ fluorescence was normalized to total ctgfa-Tracer+ in C and to total Gfap+ in D. Dots indicate individual animals and sample sizes are indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent s.e.m. ***P<0.001; **P<0.01 (two-way ANOVA). ns, not significant (P>0.05). Scale bar: 50 µm. |
|
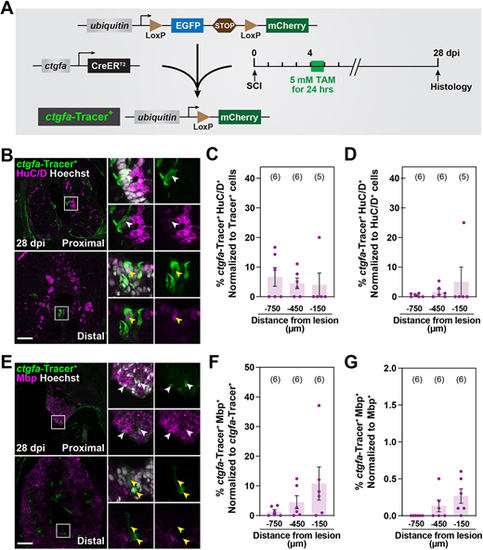
Contribution of ctgfa+ cells to regenerating neurons and oligodendrocytes after SCI. (A) Experimental timeline to evaluate the contribution of ctgfa+ cells after SCI. ctgfa-Tracer animals were subjected to complete SC transection and tamoxifen (TAM)-mediated recombination at 4 dpi to enable permanent mCherry labeling in ctgfa+ and ctgfa+-derived cells. SC tissues were collected at 28 dpi for histological examination. (B) Immunostaining for mCherry (green), HuC/D (magenta) and nuclear Hoechst (gray) at 28 dpi. mCherry expression, referred to as ctgfa-Tracer+, is used to trace the fates of ctgfa-expressing cells following TAM-inducible recombination at 4 dpi. SC sections from TAM-treated ctgfa-Tracer (Cre+) animals are shown. Cross-sections 150 µm (proximal) or 450 µm (distal) rostral from the lesion site are shown. High-magnification insets show select ctgfa-Tracer+ cells in triple-, double- or single-channel views. White arrowheads indicate ctgfa-Tracer+ HuC/D+ cells; yellow arrowheads indicate ctgfa-Tracer− HuC/D+ cells. (C,D) Quantification of ctgfa-Tracer+ and HuC/D+ colocalization at 28 dpi. ctgfa-Tracer Hoechst and HuC/D Hoechst were used to quantify the numbers of ctgfa-Tracer+ and HuC/D+ cells. ctgfa-Tracer+ HuC/D+ cells were normalized to the total number of ctgfa-Tracer+ cells in C, and to the total number of HuC/D+ cells in D. (E) Immunostaining for mCherry (green), Mbp (magenta) and nuclear Hoechst (gray) at 28 dpi. SC sections from TAM-treated ctgfa-Tracer (Cre+) animals are shown. Cross-sections 150 µm (proximal) or 450 µm (distal) rostral from the lesion site are shown. High-magnification insets show select ctgfa-Tracer+ cells in triple-, double- or single-channel views. White arrowheads indicate ctgfa-Tracer+ Mbp+ staining; yellow arrowheads indicate ctgfa-Tracer+ Mbp− staining. (F,G) Quantification of ctgfa-Tracer+ and Mbp+ colocalization at 28 dpi. ctgfa-Tracer+ and Mbp+ fluorescence were quantified. ctgfa-Tracer+ Mbp+ cells were normalized to total ctgfa-Tracer+ in F and to total Mbp+ fluorescence in G. For all quantifications, SC cross-sections 150, 450 and 750 µm rostral to the lesion were analyzed. Dots indicate individual animals and sample sizes are indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent s.e.m. Scale bars: 50 µm. |
|
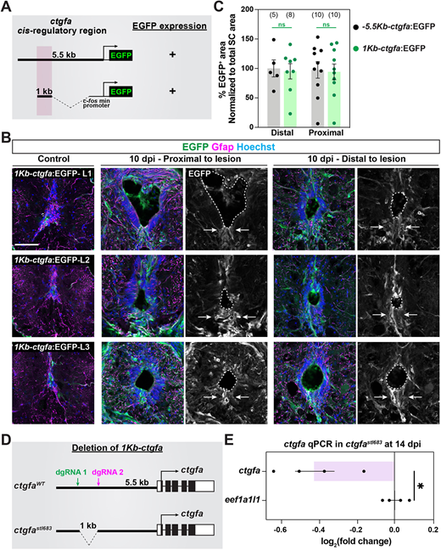
Regulation of ctgfa expression during SC regeneration. (A) A series of transgene constructs were used to identify the cis-regulatory region that drives ctgfa-dependent EGFP expression after SCI. A minimum of three stable lines were generated for each transgene. (B) EGFP and Gfap immunostaining was used to assess reporter expression at 10 dpi and in uninjured control tissues. SC tissues from −5.5Kb-ctgfa:EGFP, −4Kb-ctgfa:EGFP and −3Kb-ctgfa:EGFP transgenic animals are shown. Cross-sections are shown at 150 µm (proximal) and 450 µm (distal) rostral to the lesion. Dashed lines delineate central canal edges. Arrows point to EGFP expression in ventral ependymal progenitors. (C) Quantification of EGFP fluorescence in −5.5Kb-ctgfa:EGFP, −4Kb-ctgfa:EGFP and −3Kb-ctgfa:EGFP transgenic animals. SC cross-sections 150 µm (proximal) and 450 µm (distal) rostral to the lesion were quantified. Dots indicate individual animals and sample sizes are indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent s.e.m. **P<0.01; *P<0.05 (unpaired t-test with Welch's correction). ns, not significant (P>0.05). Scale bar: 50 µm. |
|
A distal enhancer element directs glial ctgfa expression after SCI. (A) Sequences within a 1 Kb enhancer element located 3-4 Kb upstream of the ctgfa transcriptional start site were combined with a 96 bp mouse Fos minimal promoter and subcloned upstream of an EGFP-expressing cassette. The clone was co-injected into one-cell-stage wild-type embryos, and three founders were isolated for propagation. (B) EGFP and Gfap immunostaining was used to assess reporter expression at 10 dpi and in uninjured tissue. SC tissues from three independent lines of 1Kb-ctgfa:EGFP transgenic animals (L1, L2 and L3) are shown. Cross-sections are shown at 150 (proximal) and 450 (distal) µm rostral to the lesion. Dashed lines delineate central canal edges. Arrows point to EGFP expression in ventral ependymal progenitors. (C) Quantification of EGFP fluorescence in −5.5Kb-ctgfa:EGFP and 1Kb-ctgfa:EGFP-L1 transgenic animals. SC cross-sections 150 µm (proximal) and 450 µm (distal) rostral to the lesion were quantified. Dots indicate individual animals and sample sizes are indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent s.e.m. ns, not significant (P>0.05; unpaired t-test with Welch's correction). (D) Schematic of wild-type ctgfa locus (ctgfaWT allele) and the targeting strategy adopted to delete sequences within the 1 Kb enhancer element upstream of ctgfa (ctgfastl683 allele). (E) Quantitative RT-PCR for ctgfa in ctgfastl683/ stl683 relative to ctgfaWT. eef1a1l1 was used as a loading control. Relative expression was normalized to eef1a1l1 expression and to expression levels in ctgfaWT siblings. SC tissues from four animals were pooled into a single biological replicate. Four biological replicates were used. Dots represent biological replicate pools. Error bars represent s.e.m. *P<0.05 (unpaired t-test with Welch's correction). Scale bar: 50 µm. |
|
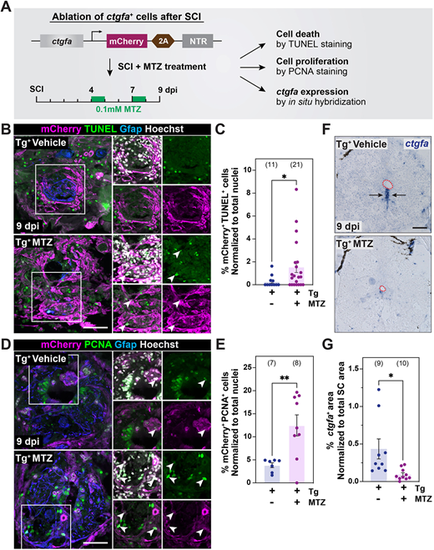
Ablation of ctgfa+ cells during SC regeneration. (A) Experimental timeline to establish a genetic ablation model for ctgfa+ cells after SCI. Transgenic ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals and control siblings were subjected to complete SC transection and metronidazole (MTZ) treatment at 4 and 7 dpi to ablate ctgfa+ cells. TUNEL staining, PCNA staining and ctgfa in situ hybridization were performed to evaluate the extent of cell death and cell proliferation at 9 dpi. (B,C) TUNEL staining in ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals (Tg+) 9 dpi. Tissue sections from vehicle- and MTZ-treated animals are shown. Representative micrographs shown in B are 150 µm rostral to the lesion. The proportion of mCherry+ TUNEL+ cells was normalized to total nuclei number and shown in C. (D,E) PCNA staining in ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals (Tg+) at 9 dpi. Tissue sections from vehicle- and MTZ-treated animals are shown. Representative micrographs shown in D are 450 µm rostral to the lesion. The proportion of mCherry+ PCNA+ cells was normalized to total nuclei number and shown in E. In B,D, arrowheads in high-magnification insets indicate mCherry+ TUNEL+ and mCherry+ PCNA+ cells in triple-, double- or single-channel views. (F,G) ctgfa in situ hybridization in ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals (Tg+) at 9 dpi. Tissue sections from vehicle- and MTZ-treated animals are shown. Representative micrographs shown in F are 450 µm rostral to the lesion. Dashed red lines delineate central canal edges. Quantification of ctgfa+ expression domains is shown in G. For all quantifications, dots represent individual animals and animal numbers are indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent s.e.m. **P<0.01; *P<0.05 (unpaired t-test with Welch's correction). Scale bars: 100 µm. |
|
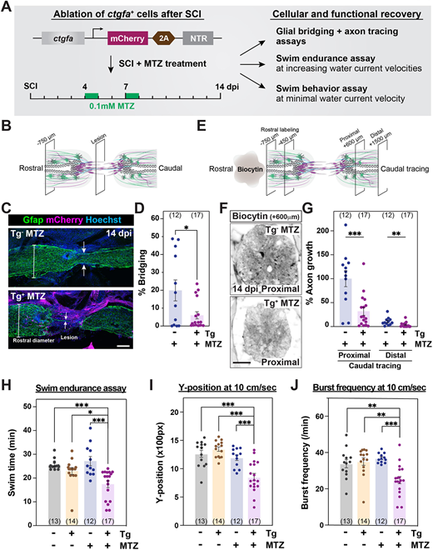
ctgfa+ cells are required for SC regeneration. (A) Experimental timeline to evaluate the requirement of ctgfa+ cells after SCI. Transgenic ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals and control siblings were subjected to complete SC transection and metronidazole (MTZ) treatment at 4 and 7 dpi to ablate ctgfa+ cells. Swim assays were performed and SC tissues were collected at 14 dpi to assess regeneration. (B-D) Glial bridging in ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals (Tg+) and wild-type siblings (Tg−) at 14 dpi. Tg+ and Tg− animals were treated with MTZ. Representative immunohistochemistry shows the Gfap+ bridge at the lesion site in C. Percentage bridging represents the cross-sectional area of the glial bridge at the lesion site relative to the intact SC 750 µm rostral to the lesion in D. (E-G) Anterograde axon tracing in ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals (Tg+) and wild-type siblings (Tg−) at 14 dpi. Biocytin axon tracer was applied rostrally and analyzed at 600 µm (proximal) and 1500 µm (distal) caudal to the lesion (E). Representative images show the extent of biocytin labeling 600 µm (proximal) caudal to the lesion in F. Axon growth was first normalized to the extent of biocytin at 450 and 750 µm rostral to the lesion, and then to labeling in Tg− controls at the proximal level in G. (H) Swim endurance assay for ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals and wild-type siblings at 14 dpi. This behavioral test was used to assess the capacity of ctgfa-ablated animals to swim in an enclosed swim tunnel under increasing water current velocities. The time at exhaustion for each fish is shown. (I,J) Swim behavior assays were used to assess the performance of ctgfa:mCherry-2A-NTR animals and wild-type siblings at minimal water current velocity at 14 dpi. Average Y-position in the tunnel (I) and burst frequency (J) were quantified at 10 cm/s water current velocity. For all quantifications, dots represent individual animals and animal numbers are indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent s.e.m. ***P<0.001; **P<0.01; *P<0.05 (unpaired t-test with Welch's correction for D and G; one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons for H-J). Scale bars: 100 µm. |