- Title
-
The Contribution of the Zebrafish Model to the Understanding of Polycomb Repression in Vertebrates
- Authors
- Hanot, M., Raby, L., Völkel, P., Le Bourhis, X., Angrand, P.O.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
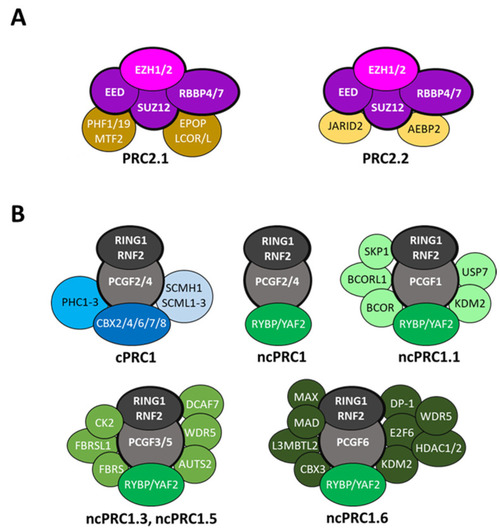
The mammalian Polycomb repressive complexes. (A) PRC2 is composed of four core subunits, EZH1/2, EED, SUZ12 and RBBP4/7, and is classified as two distinct complexes, PRC2.1 and PRC2.2 based on the auxiliary proteins associated. (B) The core PRC1 complex is composed of RING1 or RNF2 associated with one of the six PCGF proteins. Canonical PRC1 (cPRC1) includes PCGF2 or BMI1 (PCGF4), one of the chromobox proteins (CBX2, CBX4, CBX6-8), a polyhomeotic protein (PHC1/2/3) and eventually an SCM protein (SCMH1 or SCML1/2/3). In contrast, non-canonical PRC1 (ncPRC1) can include all PCGF proteins (PCGF1/2/3/4/5/6) associated with RYBP or YAF2. The identity of the PCGF subunit imposes the nature of the auxiliary proteins present in the assembly, thus defining diverse distinct ncPRC1 complexes. |
|
Deposition of the Polycomb-associated histone marks. Targeting of the PRC2 complex through the action of auxiliary proteins (white circles) leads to methylation at H3K27 (purple dashed arrow). This post-translational modification is recognized by the CBX subunit (blue) of the cPRC1 complex, which in turn ubiquitinylates H2AK119 (black dashed arrow). The ncPRC1 complexes containing RYBP/YAF2 (green) are recruited to chromatin, irrespective of H3K27me3, by the means of auxiliary subunits (blue arrow). Within all PRC complexes, some auxiliary proteins are involved in the stimulation of the catalytic activity (red arrows). |