- Title
-
Joint Action Toxicity of Arsenic (As) and Lead (Pb) Mixtures in Developing Zebrafish
- Authors
- Kiper, K., Freeman, J.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomolecules
|
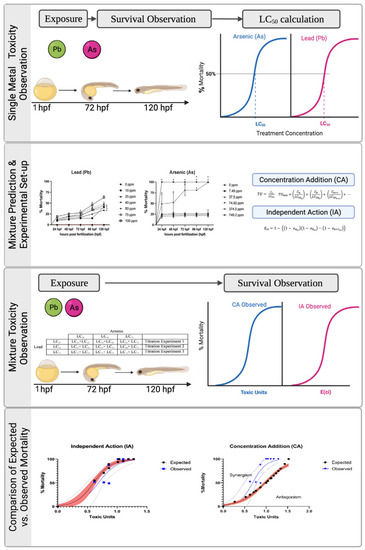
Experimental overview of study. Zebrafish embryos were dosed with a concentration range of each metal to determine lethal concentrations (LC) for benchmark treatment groups in the mixture titration experiments and for predictive mathematical modeling. The expected and observed results were compared among the mathematical models using the prediction deviation ratio and Chi-square test. Type of mixture interaction was determined using regression modeling. |
|
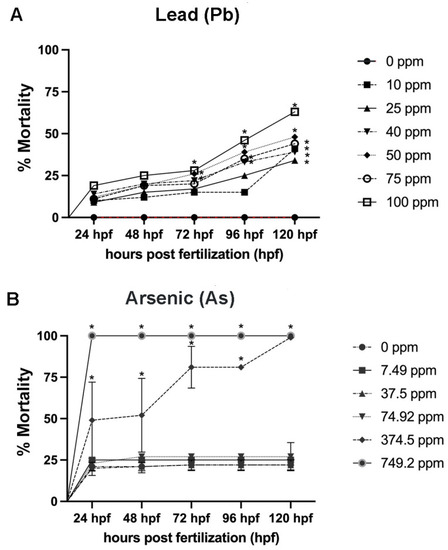
Percent mortality assessed every 24 h from 1–120 h post fertilization (hpf) for Pb and As. Single chemical exposures for Pb (A) and As (B). N = 4 biological replicates for each treatment group with 50 subsamples per each treatment group. Data is presented as mean ± standard deviation. * p < 0.05. |
|
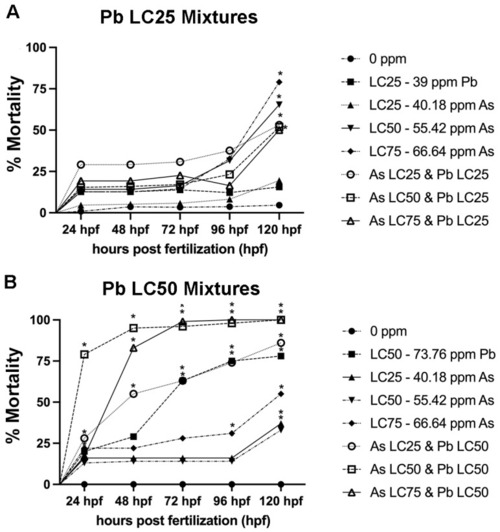
Percent mortality for mixture experiments assessed every 24 h from 1–120 h post fertilization (hpf). Mixture experiments in which Pb was held constant at the 120 hpf-LC25 (39.0 ppm) in experiment 1 (A) and in which Pb was held constant at the 120 hpf-LC50 (73.76 ppm) in experiment 2 (B), while As was varied to include the 120 hpf-LC25, 120 hpf-LC50, and 120 hpf-LC75. N = 3 biological replicates for each treatment group with 50 subsamples per each treatment group. Data is presented as mean ± standard deviation. * p < 0.05. |
|
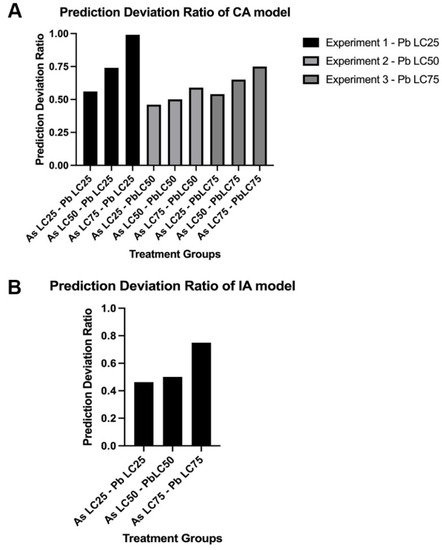
Comparison of prediction deviation ratio (PDR) of mixtures for the CA and IA models. For the CA model (A), each exposure scenario in each experiment was evaluated for PDR values that approached 1. The IA model (B) is limited to evaluating metal mixtures at the same LC percentage for approaching 1. N = 3 biological replicates for each treatment group with 50 subsamples per each treatment group. |
|
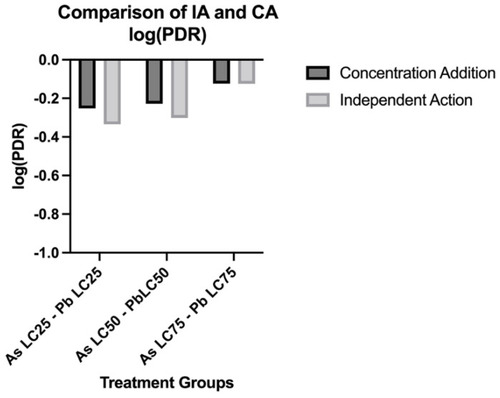
Comparison of predicted lethality using the Independent Action (IA) and Concentration Addition (CA) models. The log of the prediction deviation ratios (PDR) of mixtures for the CA and IA models. N = 3 biological replicates for each treatment group with 50 subsamples per each treatment group. |
|
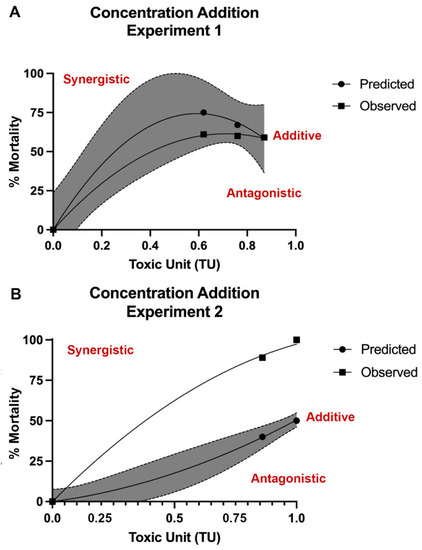
Observed and predicted mortality using the concentration addition (CA) model. Developing zebrafish were exposed to the metal mixtures from 1 to 120 h post fertilization (hpf) and mortality recorded. Results were compared to predicted mortality based on CA models when the Pb LC25 (39.0 ppm, mg/L) concentration was held constant (A) or when the Pb LC50 (73.76 ppm) concentration was held constant (B). Similarity of predicted and observed curves indicates additive interaction (within in shaded region) (A), where upper deviation from predicted curve suggests synergistic response (B). N = 3 biological replicates per treatment group with 50 subsamples per biological replicate. |
|
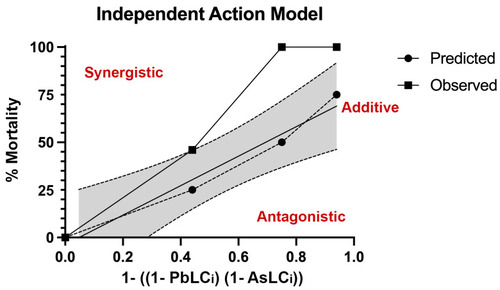
Observed and predicted mortality using the independent action (IA) model. Developing zebrafish were exposed to the metal mixtures from 1 to 120 h post fertilization (hpf) and mortality recorded. Results were compared to predicted mortality based on the IA model, where the predicted LC of each metal is equal. The upper deviation of the observed curve compared to the predicted curve suggests a synergistic response. N = 3 biological replicates per treatment group with 50 subsamples per biological replicate. |