- Title
-
Prophylactic Activation of Shh Signaling Attenuates TBI-Induced Seizures in Zebrafish by Modulating Glutamate Excitotoxicity through Eaat2a
- Authors
- Hentig, J., Campbell, L.J., Cloghessy, K., Lee, M., Boggess, W., Hyde, D.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomedicines
|
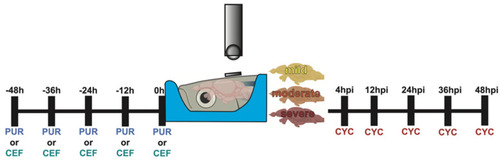
Experimental timeline of Shh modulation. Graphical representation of the dosing schedule of purmorphamine, ceftriaxone, and cyclopamine in relation to the timing of the TBI. |
|
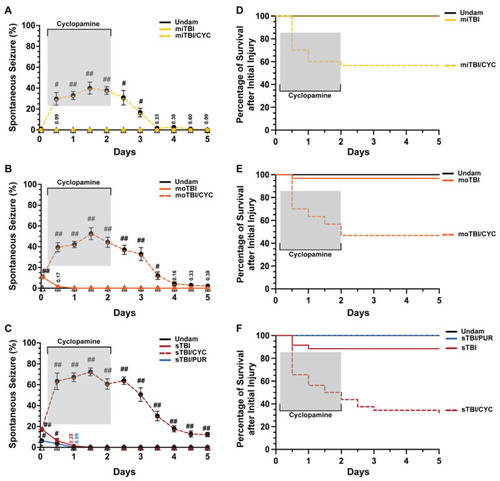
Modulation of Shh alters frequency of TBI-induced PTS events. (A–C) Percentage of fish that displayed spontaneous seizure events spanning the timeframe from within 1 hpi to 5 dpi with and without Shh modulation. (D–F) Percentage of survival across 5 days of fish who initially survived the primary injury across mi-, mo-, and sTBI with and without Shh modulation. Statistical analyses of the repeated-measures data were performed with the Friedman test, n = 100 fish per control/experimental group, grey box denotes period of cyclopamine administration, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01. |
|
CNQX attenuates PTS in Shh-inhibited fish. (A) Percentage of undamaged and sTBI that were Shh inhibited (cyclopamine-treated) and cotreated with either valproic acid (VPA), gabapentin (GABAP), or CNQX that displayed spontaneous seizure events across 5 dpi. (B) Quantification of survival across 5 days of undamaged or sTBI Shh-inhibited fish cotreated with VPA, GABAP, or CNQX. Statistical analysis of the repeated-measures data was performed with the Friedman test, n = 100 fish per control/experimental group, grey box denotes period of cyclopamine/(VPA or GABAP or CNQX) administration, ## p < 0.01. |
|
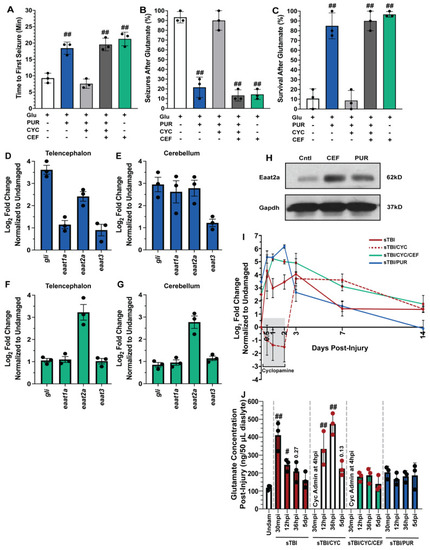
Shh activation combats excitotoxicity and upregulates Eaat2a. Undamaged fish with and without Shh modulation and ceftriaxone treatment were exposed to 5 mM glutamate in fish water (n = 90 fish per control/experimental group). (A) Quantification of time to first seizure, (B) percent of the group to display at least 1 seizure event, and (C) percent of the group that survived for 1 h. (D,E) Expression of Shh component, gli, and excitatory amino acid transporter (eaat) genes by qRT-PCR revealed that purmorphamine increased gli and eaat2a mRNAs in both undamaged telencephalons and cerebellums (n = 3 per control/experimental group, with 5 pooled telencephalons or cerebellums/trial). (F,G) Administration of ceftriaxone increased eaat2a mRNA expression levels without Shh activation in undamaged telencephalons and cerebellums (n = 3 per control/experimental group, with 5 pooled telencephalons or cerebellums/trial). (H) Expression of Eaat2a in the undamaged cerebellum (5 pooled cerebellums per control/experimental group) following either purmorphamine or ceftriaxone treatment was assessed by immunoblot, using GAPDH as a loading control (H, top and lower bands, respectively). Eaat2a protein expression was increased following either purmorphamine or ceftriaxone treatment compared to controls. (I) Expression of eaat2a by qRT-PCR in sTBI fish with either Shh signaling activated, inhibited, or inhibited and cotreated with ceftriaxone at 12 hpi to 14 dpi (n = 3 per control/experimental group, with 5 pooled cerebellums/group). (J) Microdialysis was performed to quantify extracellular glutamate levels in undamaged and sTBI fish with and without Shh modulation and ceftriaxone treatment at 30 min post-injury, 12 and 36 hpi, and 5 dpi (n = 3 per control/experimental group). In panels A-C, the plus sign (+) denotes application of the reagent and the minus sign (-) denotes the absence of the reagent. Grey box denotes period of cyclopamine administration. Statistical analyses were performed with a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison post hoc test, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01. |
|
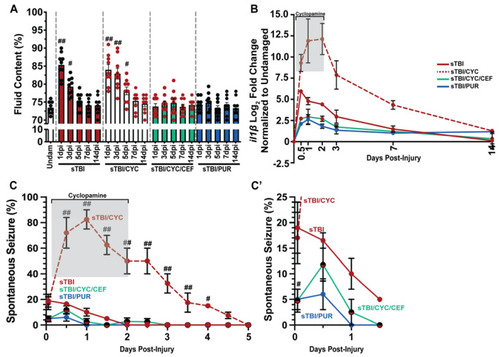
Prophylactic Shh activation attenuates TBI-induced edema, neuroinflammation, and PTS. (A) Histogram quantifying brain edema in undamaged and sTBI fish with and without Shh modulation and ceftriaxone treatment across 1 to 14 dpi (n = 9 fish per control/experimental group). (B) Expression of il1β by qRT-PCR in the cerebellum of sTBI fish with and without Shh modulation and ceftriaxone treatment compared undamaged fish (n = 3 per control/experimental group, with 5 pooled cerebellums/trial). (C) Percentage of fish that displayed spontaneous seizure events spanning the timeframe of from within 1 hpi to 5 dpi with and without Shh modulation and ceftriaxone treatment (n = 100 fish per control/experimental group). (C’) Expanded view of early post-traumatic seizure percentage. Grey box denotes period of cyclopamine administration. Statistical analyses were performed with either a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test (A), a two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison post hoc test (B), or the Friedman test of the repeated-measures data (C), # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01. |
|
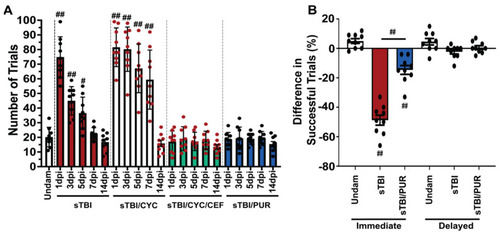
Cognitive impairments are attenuated by prophylactic Shh activation. (A) Histogram quantifying the number of trials required for associative learning assay of undamaged and either untreated or Shh-modulated sTBI fish at 1, 3, 5, 7 and 14 dpi (n = 9 fish per control/experimental group). (B) Quantification of immediate and delayed recall of undamaged, sTBI, and sTBI/PUR fish (n = 9 fish per control/experimental group). Statistical analyses were performed with a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01. |