- Title
-
Habenula as the experience-dependent controlling switchboard of behavior and attention in social conflict and learning
- Authors
- Okamoto, H., Cherng, B.W., Nakajo, H., Chou, M.Y., Kinoshita, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.
|
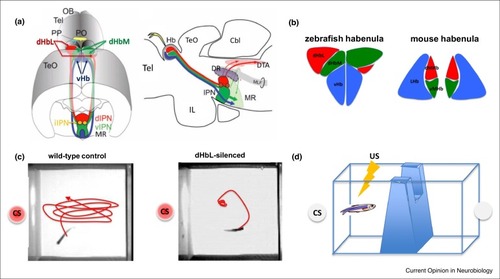
(a) Schematic illustration showing dorsal oblique view (left panel) and lateral view (right panel) of the zebrafish dHb-IPN pathways. OB: olfactory bulb; Tel: telencephalon; P: pineal organ; PP: parapineal organ; TeO: tectum opticum; Cbl: cerebellum; IL: inferior lobe of hypothalamus; MR: median raphe; DR: dorsal raphe; DTA: dorsal tegmentum area; MLF: medial longitudinal fascicle. (b) Comparison between the zebrafish and mouse Hb subnuclear structure. The evolutionarily corresponding structures are labeled with the same colors both in the zebrafish and mouse habenula. dHbL, the lateral subregion of the dorsal habenula; dHbM, the medial subregion of the dorsal habenula; vHb, the ventral habenula; dMHb, the dorsal subregion of the medial habenula; vMHb, the ventral subregion of the medial habenula; LHb, the lateral habenula. (c) The trajectories of the wild-type (left panel) and dHbL silenced (right panel) zebrafish after presentation of the conditioned stimulus (CS, red light). (d) Schematic illustration of the apparatus for active avoidance test. US, unconditioned stimulus (electrical shock). |
|
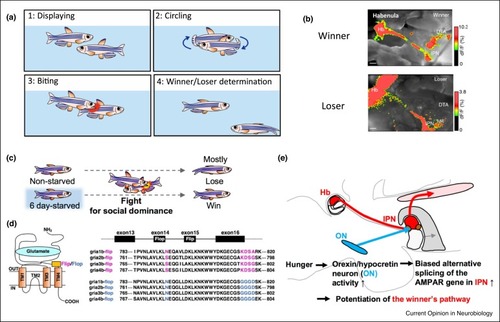
(a) Schematic illustration of dyadic fighting behaviors in male zebrafish. (b) Visualization of excitation propagation pathway (labeled red) from the Hb after electrical stimulation of the Hb by calcium imaging of the Oregon green 488 BAPTA-1AM-impregnated acute brain slices from a winner (upper panel), and a loser (lower panel) fish. (c) Six day-starved zebrafish mostly win the fight for social dominance against non-starved fish. (d) (left panel) Schematic illustration of AMPAR subunit. Flip/flop site is shown. TM, transmembrane domain. (right panel) Amino acid sequence encoded in exon 14 (flop) or exon 15 (flip) of gria1b-4b gene are shown. The distinctive amino acid residues for flip/flop are indicated by pink or blue color. (e) Schematic illustration showing how the IPN input from the hypothalamic orexin/hypocretin neurons potentiates the winner’s pathway. |
|
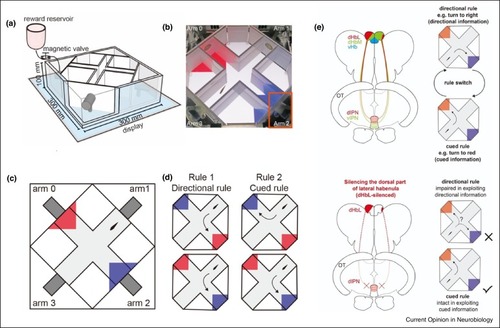
(a) Schematic view of the plus-maze system. (b) Top oblique view of the training space with color blocks displayed at the ends of the arms 0 and 2. Orange inset indicates the location of the food-dispensing unit. (c) Top view of the plus-maze with the displayed color blocks. (d) The illustration of rules. Left panel, two examples of the directional rule, where a fish has to turn left regardless of goal colors. Right panel, two examples of the externally cued rule, where a fish has to turn to the blue goal regardless of turning direction. (e) Specific impairment in the directional rule learning by the dHbL-silenced fish. |
|
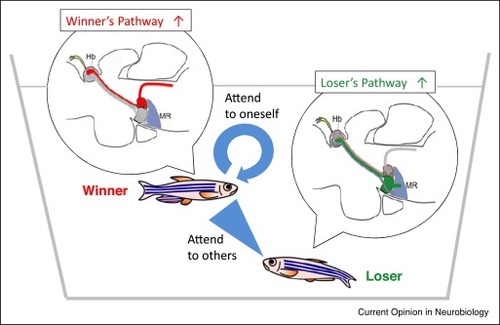
Habenula as the integrated switchboard for controlling behavior and attention in social conflict. Schematic illustration of the concerted control of behavior either as the winner with self-centered (idiotehtic) attention or the loser with others-oriented (allothetic) attention by the two parallel pathways from the dHb to the IPN. |