- Title
-
Nephroprotective Role of Zhibai Dihuang Wan in Aristolochic Acid-Intoxicated Zebrafish
- Authors
- Lu, P.H., Lee, H.Y., Liou, Y.L., Tung, S.F., Kuo, K.L., Chen, Y.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomed Res. Int.
|
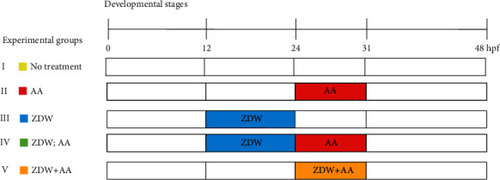
Schematic representation of experimental protocols performed in this study. Five groups (I-V) were applied in the treatment experiments based on combinations of different exposure onsets: (I) no treatment group, water only; (II) AA group, exposed to AA from 24 to 31 hpf; (III) ZDW group, exposed to ZDW from 12 to 24 hpf; (IV) ZDW, AA group (defined as pretreatment), exposed to ZDW from 12 to 24 hpf, withdrawn ZDW and followed by exposure with AA from 24 to 31 hpf; (V) ZDW+AA group (defined as cotreatment), coexposure with AA and ZDW from 24 to 31 hpf. |
|
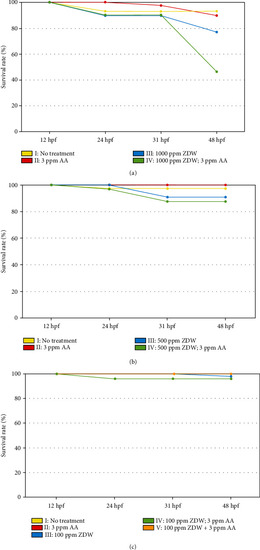
ZDW dose titration and survival rate analysis in this study. For ZDW dose titration, wild-type (WT; AB strain) embryos were collected, randomly divided into 50 per experimental group, and exposed to either water (no treatment, control: 0 ppm) or water containing ZDW (1000, 500, and 100 ppm, (a)–(c)) and/or 3 ppm AA. All embryos were cultivated in 6-well cell culture plates, and survival rates were determined at 12, 24, 31, and 48 hpf. The |
|
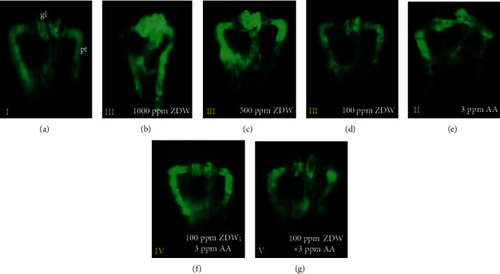
Kidney phenotypes of zebrafish embryos after prevention of ZDW. Morphological changes of Tg( |
|
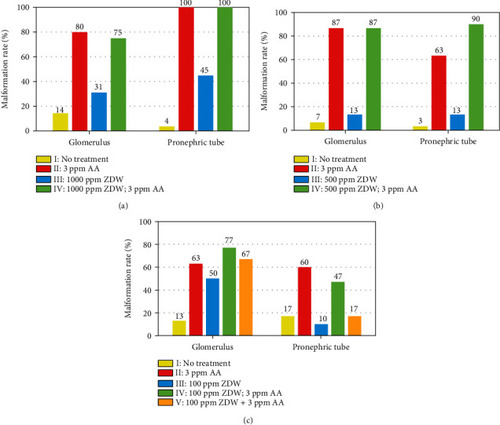
Malformation rates of kidney-defective phenotypes of zebrafish embryos after prevention of ZDW. Malformation rates of Tg( |
|
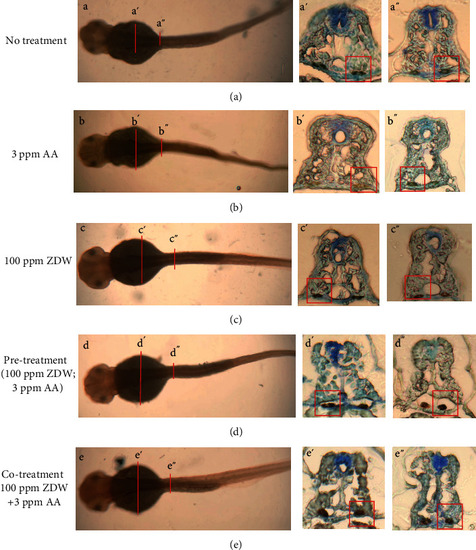
ZDW pretreatment attenuated AA-induced defective pronephric ducts. Immunohistochemical staining of the basolateral marker Na+/K+-ATPase alpha1 subunit ( |
|
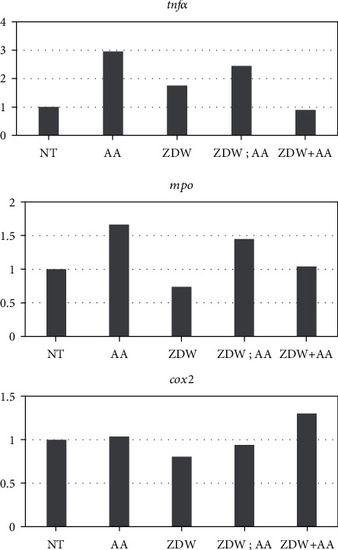
Quantitative gene expression was analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The total RNA was extracted at the 48 hpf, and the relative expression levels of the indicated genes were determined by qRT-PCR. The gene expression results of the indicated genes between no treatment control (NT) and different experimental groups. The data in triplicate were normalized for zebrafish |