- Title
-
An optimized base editor with efficient C-to-T base editing in zebrafish
- Authors
- Zhao, Y., Shang, D., Ying, R., Cheng, H., Zhou, R.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Biol.
|
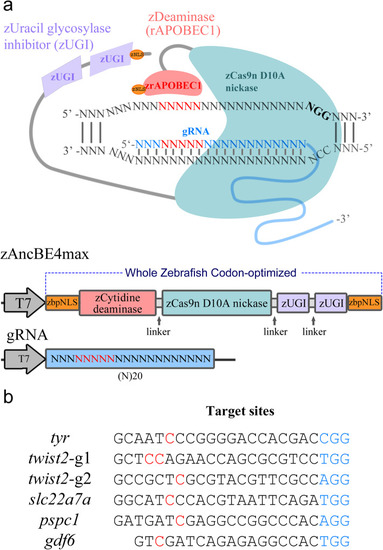
Base editor in zebrafish using a whole zebrafish codon-optimized BE4 system. |
|
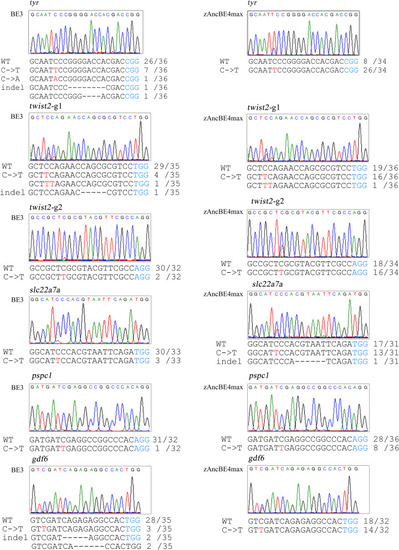
Base C-to-T editing efficiency using zAncBE4max in zebrafish. The zAncBE4max system (right panel) showed higher activity of C-to-T editing than the BE3 system (left panel) at 6 tested sites. Red letter C indicates sites of C-to-T conversion and corresponding overlapped peaks in sequencing chromatogram. PAM region is indicated in blue. Mutant number in sequenced clones is shown on the right of sequences |
|
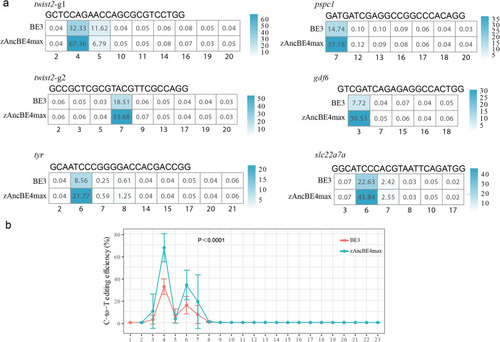
The on-target C-to-T editing efficiency of BE3 and zAncBE4max at 6 target sites. |
|
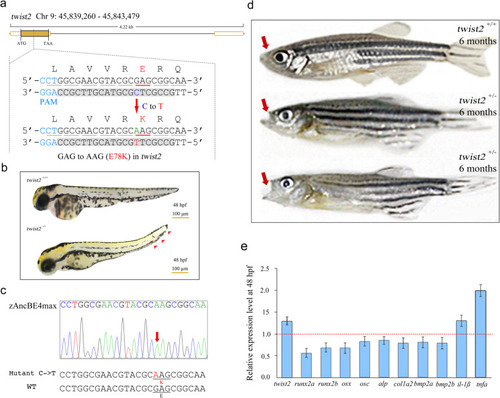
Generation of an AMS zebrafish model using the zAncBE4max system. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|