- Title
-
Discriminating Different Cancer Cells Using a Zebrafish in Vivo Assay
- Authors
- Moshal, K.S., Ferri-Lagneau, K.F., Haider, J., Pardhanani, P., and Leung, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Cancers
|
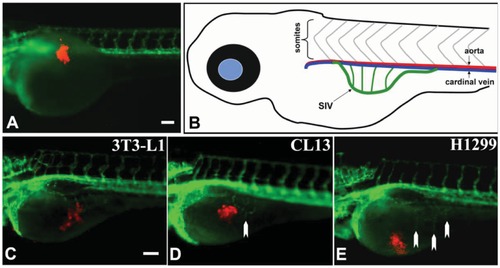
Tumor angiogenesis in transgenic Tg(flk1:GFP) zebrafish embryos. Lateral view of a fluorescent transgenic Tg(flk1:GFP) zebrafish embryo at 1 dpf that was just transplanted with cancer cells labeled with red fluorescent dye (A); (B) shows a sketch depicting the SIV (in green) of a 3 day old zebrafish embryo; Lateral views of transgenic Tg(flk1:GFP) zebrafish embryos at 3 dpf transplanted with 3T3-L1 cells (negative control) (C), CL13 (D) and H1299 (E) cancer cells; White arrows (D, E) indicate newly formed ectopic vessels from the SIV. Scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
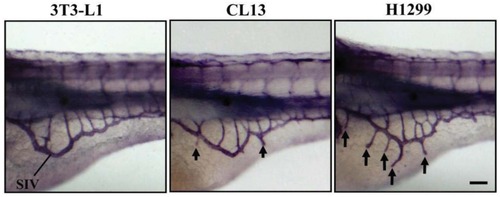
Xenotransplantation-induced neovascularization in the zebrafish embryos. Lateral views of whole-mount alkaline phosphatase stains of zebrafish embryos at 3 dpf were used to evaluate 3T3-L1 control, CL13 and H1299 cancer cell lines for angiogenic potential by measuring newly formed ectopic vessels sprouting from the SIV plexus in the zebrafish/tumor xenograft assay. They show negligible, moderate, and robust angiogenic responses, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. |
|
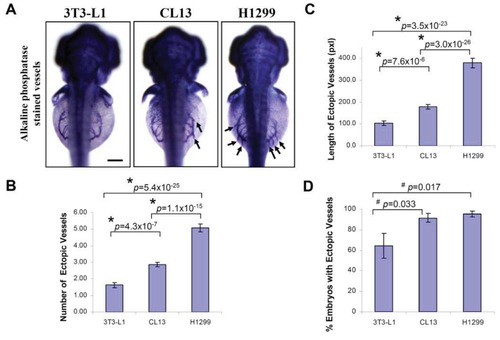
Quantification of angiogenic activity using zebrafish in vivo assay. Cells were injected into zebrafish embryos in order to evaluate the ability of zebrafish/tumor xenograft to quantify their angiogenic potentials. (A) Shown are representative light microscopy images of zebrafish embryos (dorsal view) at 3 dpf subjected to whole-mount alkaline phosphatase staining, 2 days after implantation with 3T3-L1 control, CL13 and H1299 cancer cells, and used to measure the number (B) and the length (C) of newly formed ectopic vessels and the percentage of embryos (D) with ectopic vessels, showing that H1299 and CL13 cancer cells induced differential neovascular response in the zebrafish embryos as compared to the 3T3-L1 control. The error bars represent ± SEM from three independent experiments. p values were determined by the Student′s t-test. Both * (p < 0.01) and # (p < 0.05) indicate statistically significant differences. n represents the number of embryos per group, 3T3-L1 (n = 140); CL13 (n = 198); H1299 (n = 176). Pixel (pxl) corresponds to 0.82 μm. Scale bar = 100 μm. |
|
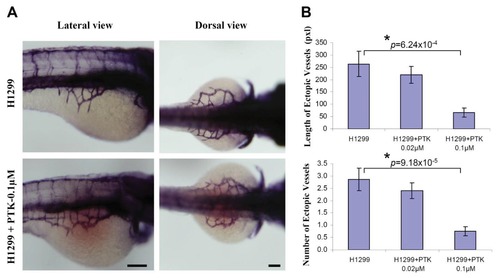
VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition mitigated tumor angiogenesis in embryonic zebrafish. Cells were stained with CM-DiI before implantation using microinjector. Immediately, after H1299 cancer cell implantation, the embryos were systemically exposed to 0.1 μM PTK 787, pharmacological inhibitor of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase through 3 dpf. Shown are the representative whole-mount alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining of the zebrafish embryos implanted with H1299 cancer cells, (A); Quantification of number and length of the ectopic vessel originating from the developing SIV in H1299 cancer cell implanted embryos with or without PTK787 incubation (B). The error bars represent ± SEM. p values were determined by the Student′s t-test. * (p < 0.01) indicate statistically significant difference. n represents the number of embryos per group, H1299 (n = 30); H1299+PTK/0.02 μM (n = 32); H1299+PTK/0.1 μM (n = 29). Pixel (pxl) corresponds to 0.82 μm. Scale bar = 100 μm. |