- Title
-
Interdependence of Bad and Puma during ionizing-radiation-induced apoptosis
- Authors
- Toruno, C., Carbonneau, S., Stewart, R.A., and Jette, C.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
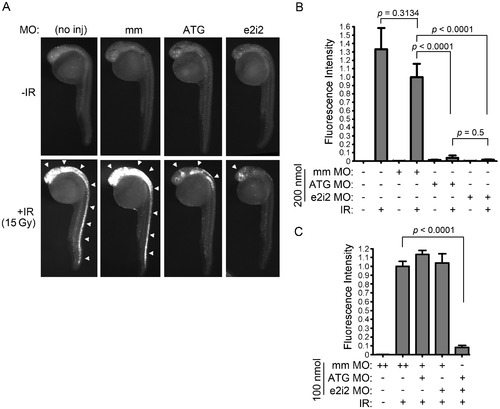
Bad is required for IR-induced apoptosis in zebrafish embryonic neural tissue. (A) Shown are lateral views of 27-hpf embryos (head is top left in each panel) either uninjected or injected with 200 nmol of bad ATG, bad e2i2 or mismatch (mm) MO. Half of each group of embryos were exposed to 15 Gy IR, and all were analyzed by the Casp3 assay. In control embryos (no inj and mm), IR-induced apoptosis occurs predominantly in the brain and all along the spinal cord (white arrowheads), whereas in bad-deficient embryos (ATG and e2i2), residual apoptosis is only observed in the head (arrowheads). (B) Fluorescence intensity, reflecting level of Caspase 3 activity, was measured in the spinal cords of at least 10 embryos from each group in (A) as previously described [34]. The fluorescence intensity in irradiated mismatch-MO-injected embryos was normalized to 1. (C) One-cell stage zebrafish embryos were injected with 100 nmol of bad ATG, bad e2i2 or mm MO as indicated (“++” indicates that 200 nmol was injected to keep total concentration of MO constant between experimental groups) and irradiated and analyzed as in (A-B). Data represent one experiment, and the experiment was independently performed three times with similar results. |
|
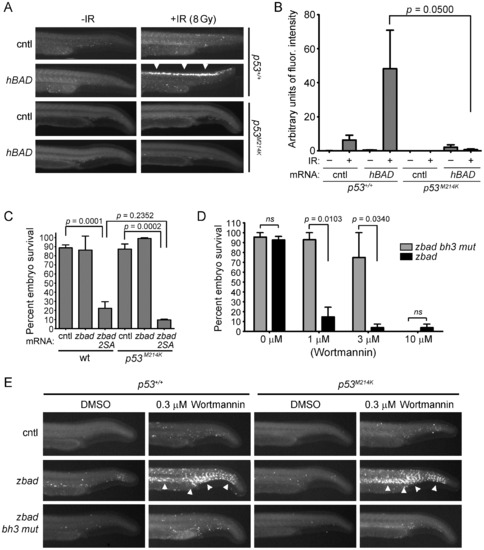
p53 is required for Bad-mediated sensitivity to IR but not wortmannin. (A) Shown are lateral views of representative tails from 27-hpf wild-type or p53 mutant embryos injected with 50 pg of mcherry (cntl) or hBAD mRNA. Embryos were exposed (or not) to 8 Gy IR at 24 hpf and analyzed three hours later by the Casp3 assay. Apoptosis was observed in the spinal cord after hBAD mRNA was injected into wild-type (arrowheads), but not mutant, p53 embryos. (B) Fluorescence intensity was measured in the spinal cords of at least 10 embryos from each group in (A). Data represent one experiment, but the experiment was independently performed three times with similar results. (C) One-cell stage wild-type or p53 mutant embryos were injected with 50 pg of mRNA encoding either mcherry control (cntl) or the constitutively active mutant zbad 2SA. At 8 hpf, embryos were analyzed for survival (defined by a beating heart) as performed previously [34]. Data represent one experiment, but the experiment was independently performed three times with similar results. (D) One-cell stage wild-type embryos were injected with 50 pg of mRNA encoding either zebrafish bad or the apoptotically-inactive zbad bh3 mut. At 8 hpf, embryos were treated with increasing concentrations of wortmannin, or DMSO vehicle alone. At 48 hpf, embryos were examined for survival. At least 10 embryos were analyzed per group in three independent experiments. E) Shown are lateral views of tails from p53 wild-type (left) or mutant (right) embryos after injection with 25 pg of mRNA encoding either mcherry (cntl), zbad, or zbad bh3 mut. Embryos were split into two groups and treated with either 0.3 μM wortmannin or DMSO vehicle beginning at 8 hpf and analyzed at 24 hpf by the Casp3 assay. Wild-type Bad synergizes with wortmannin to induce apoptosis in multiple tissues in a p53-independent manner (arrowheads). |
|
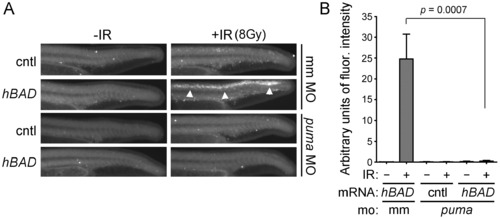
Puma is required for Bad-mediated radiosensitization. (A) Shown are lateral views of representative tails from 27-hpf embryos exposed to 8 Gy IR after injection at the one-cell stage with 50 pg of mRNA encoding mcherry (cntl) or hBAD in addition to either 100 nmol of puma MO or mismatch (mm) control MO. Analysis of Caspase 3 activity shows that hBAD-mediated radiosensitivity (arrowheads) is dependent on puma expression. (B) Fluorescence intensity was measured in the spinal cords of at least 10 embryos from each group in (A). Data represent one experiment, but the experiment was independently performed three times with similar results. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
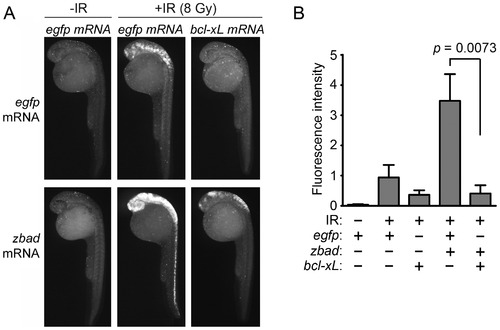
Bad radiosensitizes zebrafish neural tissue through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. (A) Shown are lateral views of 27-hpf wild-type embryos (head is top left in each panel) injected with either 1) 50 pg of egfp mRNA, 2) 25 pg each of egfp and bad, 3) 25 pg each of egfp and zbcl-xL, or 4) 25 pg each of bad and zbcl-xL. At 24 hpf, half of each group was irradiated with 8 Gy IR and analyzed three hours later by the Casp3 assay. (B) Fluorescence intensity was measured in the spinal cords of at least 10 embryos from each group. Data represent one experiment, but the experiment was independently performed three times with similar results. |
|
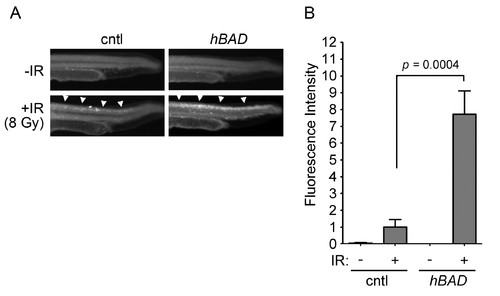
The ability of Bad to radiosensitize zebrafish embryonic neural tissue is conserved between zebrafish and human. Shown are lateral views of representative tails from 27-hpf wild-type embryos injected with 50 pg of mRNA encoding mcherry (cntl) or hBAD. Apoptosis in irradiated embryos is denoted with arrowheads. At 24 hpf, half of each group was irradiated with 8 Gy IR and analyzed three hours later by the Casp3 assay. Fluorescence intensity was measured in the spinal cords of at least 10 embryos from each group. Data represent one experiment, but the experiment was independently performed three times with similar results. |
|
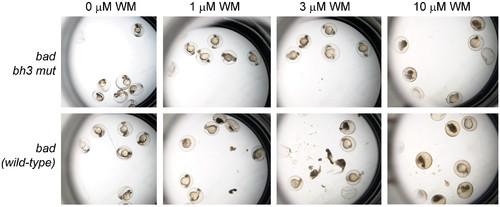
Wild-type Bad synergizes with wortmannin to induced embryonic death. Shown are brightfield views of representative wells from a 12-well plate demonstrating morphological changes observed in the experiment quantified in Figure 2D. WM; wortmannin. |