- Title
-
Identification of a brain center whose activity discriminates a choice behavior in zebrafish
- Authors
- Lau, B.Y., Mathur, P., Gould, G.G., and Guo, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
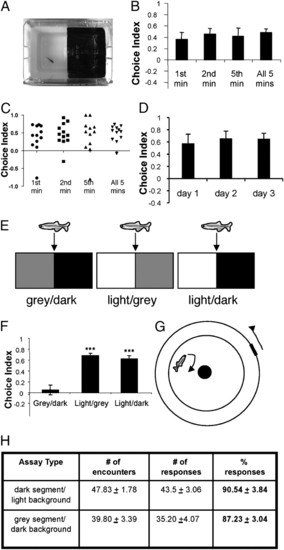
Adult zebrafish display an innate light avoidance behavior. (A) Photograph of the L/D choice chamber. (B) Choice indices in the choice chamber during first, second, fifth, and all 5 min analyzed (a choice index of 1.0 represents 100% time spent on the dark side, and an index of -1.0 represents 100% time spent on the light side) (n = 12 for each group). (C) Scatter plot of B, showing the distribution of choice indices in the tested animals. (D) Choice indices of three trials with a 24-h interval between each trial. The means for choice indices are day 1 (0.58 ± 0.15), day 2 (0.66 ± 0.12), and day 3 (0.65 ± 0.09) (n = 13; P = 0.64, ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test). (E) Schemes of different choice chambers. (F) Choice indices in different choice chambers (L/D, n = 26; light/gray, n = 23; gray/dark, n = 24; F = 28.55, ***P < 0.001 compared with gray/dark, Tukey′s test). (G) Scheme of a visual acuity chamber for testing the ability of zebrafish to discriminate between gray and dark. (H) Comparable visual discrimination of gray segment over dark background (n = 6) vs. dark segment over light background (n = 5), as indicated by comparable % responses (F = 0.36, P = 0.56, Tukey′s test). |
|
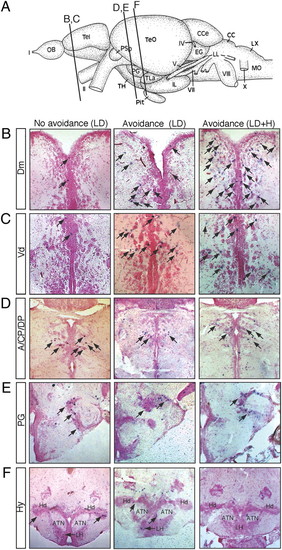
Mapping of c-fos neuronal activity. In all images, c-fos–positive cells are shown in purple (arrows) and brain sections are counterstained with the nuclear fast red. (Left) Brain sections from an animal that was stimulated with the L/D visual stimulus and displayed little avoidance behavior (choice index: -0.04). (Center) Brain sections from an animal that was stimulated with the L/D visual stimulus and displayed avoidance behavior (choice index: 0.40). (Right) Brain sections from animals that were stimulated with the L/D + H and displayed avoidance behavior (choice index: 0.92). (A) Schematic showing the section positions. (B) Dm. (C) Vd. (D) Dorsal thalamus (A, CP, and DP). (E) Preglomerular complex (PG). (F) Hy [anterior tuberal nucleus (ATN), dorsal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hd), and lateral hypothalamic nucleus (LH)]. |
|
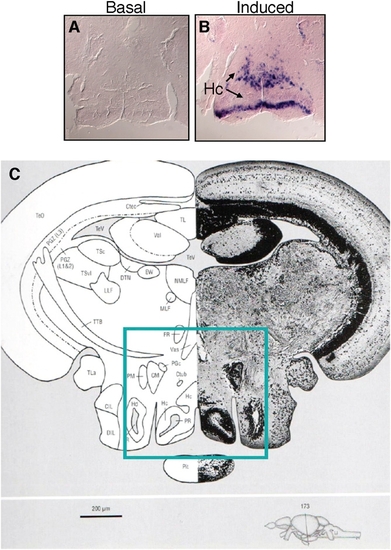
In situ hybridization of c-fos reveals neural activity in basal and induced states. (A) Nominal basal c-fos expression in the brain of adult zebrafish (the hypothalamic region is shown, as boxed in C). (B) Strong and widespread c-fos expression in the brain of zebrafish subjected to intense handling stress (the hypothalamic region is shown, as boxed in C). (C) Section through the diencephalon/midbrain region highlighting the region shown in A and B [corresponding to section 173 in the zebrafish brain atlas (1)]. CIL, central nucleus of the inferior lobe; CM, corpus mamillare; Ctec, commissure tecti; Ctub, commissure of the posterior tuberculum; DIL, diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; EW, Edinger–Westphal nucleus; FR, fasciculus retroflexus; Hc, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd, dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; LLF, lateral longitudinal fascicle; LR, lateral recess of diencephalic ventricle; MLF, medial longitudinal fascicle; NMLF, nucleus of MLF; PGc, caudal preglomerular nucleus; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of the TeO; Pit, pituitary; PR, posterior recess of diencephalic ventricle; TeO, tectum opticum; TeV, tectal ventricle; TL, torus longitudinalis; TLa, torus lateralis; TPM, tractus pretectomamillaris; TSc, central nucleus of torus semicircularis; TSvl, ventrolateral nucleus of torus semicircularis; TTB, tractus tectobulbaris; Val, lateral division of valvula cerebelli; Vas, vascular lacuna of area postrema. |
|
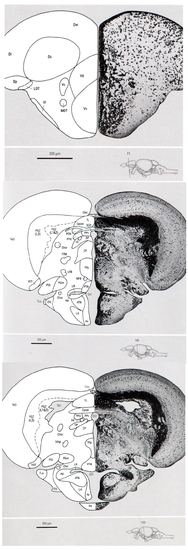
Sections from the adult zebrafish brain atlas (1) highlighting the regions shown in Fig. 4 B–F (boxed areas). (1) Section through the telencephalic region [corresponding to section 71 in the zebrafish brain atlas (1)]. D, dorsal telencephalic area; Dc, central zone of D; Dl, lateral zone of D; Dm, medial zone of D; Dp, posterior zone of D; LOT, lateral olfactory tract; MOT, medial olfactory tract; V, ventral telencephalic area; Vc, central nucleus of V; Vd, dorsal nucleus of V; Vl, lateral nucleus of V; Vv, ventral nucleus of V. (2–3) Sections through the diencephalon/midbrain region [corresponding to sections 149 and 153 in the zebrafish brain atlas (1), respectively]. ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; Chor, commissura horizontalis; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; Cpost, commissura posterior; Ctec, commissura tecti; DIL, diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; DiV, diencephalic ventricle; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; FR, fasciculus retroflexus; Hd, dorsal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus; Hv, ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; LFB, lateral forebrain bundle; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; LR, lateral recess of diencephalic ventricle; MFB, medial forebrain bundle; PCN, paracommissural nucleus; PGl, lateral preglomerular nucleus; PGm, medial preglomerular nucleus; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of the TeO; PPd, periventricular pretectal nucleus dorsal part; PPv, periventricular pretectal nucleus ventral part; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; Sco, subcommissural organ; TeO, tectum opticum; TL, torus longitudinalis; TLa, torus lateralis; TPM, tractus pretectomammillaris; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; VOT, ventrolateral optic tract. |
|
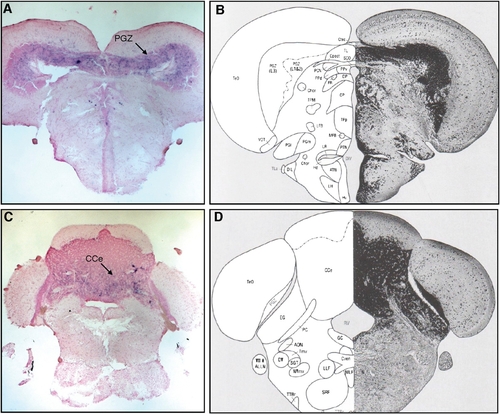
Activity of c-fos in the mid- and hind-brain regions. (A) Section through the midbrain region showing the c-fos–positive cells in the TeO periventricular zone (PGZ). (B) Corresponding brain section from the adult zebrafish brain atlas (1). (C) Section through the hind-brain region showing the c-fos–positive cells in the cerebellar region, corpus cerebelli (CCe). (D) Corresponding brain section from the the adult zebrafish brain atlas (1). |
|
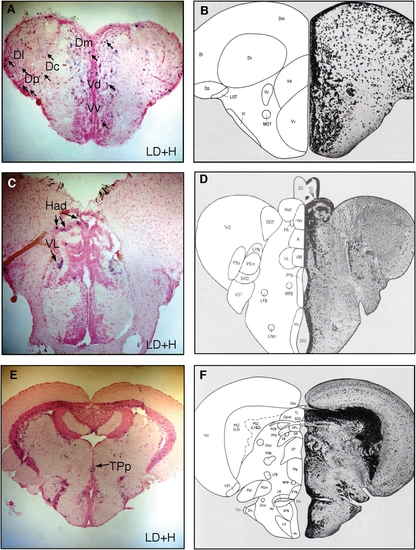
Activity of c-fos in brain regions from animals subjected to both L/D and L/D + H. Sections through the telencephalic region (A) and diencephalic/ midbrain regions (C and E) showing the c-fos–positive cells in regions, including the Dc (central zone of dorsal Tel), Dl (lateral zone of dorsal Tel), Dm (medial zone of dorsal Tel), Dp (posterior zone of dorsal Tel), Vd (dorsal nucleus of ventral Tel), Vv (ventral zone of ventral Tel), Had (dorsal habenula nucleus), VL (ventrolateral thalamic nucleus), and TPp (periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum). (B, DF) Corresponding brain section from the adult zebrafish brain atlas (1). |