- Title
-
Lipid droplet biology and evolution illuminated by the characterization of a novel Perilipin in teleost fish
- Authors
- Granneman, J.G., Kimler, V.A., Zhang, H., Ye, X., Luo, X., Postlethwait, J.H., Thummel, R.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
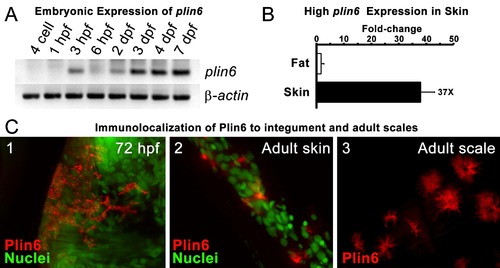
Plin6 is expressed in early zebrafish development and in adult skin. Plin6 expression is shown in two independent samples from each tissue. The full-length Plin6 (55 kDa) and the immunoreactive degradation product of Plin6 (40 kDa) is found only in skin tissue. Background bands are abundant in liver and muscle tissue, but do not correspond to the molecular weight of Plin6. The blot was stripped and probed for β-actin, to serve as a loading control. However, since β-actin is not expressed in muscle tissue, the blot was again stripped and probed for Gapdh. |
|
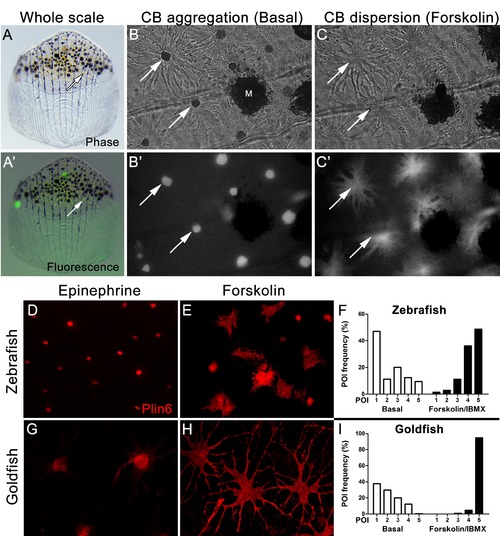
Carotenoid pigment aggregation and dispersion in adult zebrafish xanthophores correlates to Plin6 expression. (A) An isolated scale containing melanophores (black) and xanthophores (gold, arrow). (A’) Fluorescent and brightfield overlay showing xanthophore auto-fluorescence (the two large fluorescent spots are auto-fluorescent debris). (B) Higher magnification image showing many star-shaped xanthophores (arrows) in a basal state of pigment aggregation. A few melanophores (M) can also be visualized. (B’) The fluorescence image of B showing the auto-fluorescence in xanthophores. (C) Following a 1 hr incubation in forskolin, pigment is dispersed. (C’) The fluorescence image shows the pigment dispersion. (D–E) Plin6 is immunolocalized to xanthophores in isolated scales from zebrafish in both aggregated (D; Epinephrine) and dispersed states (E; Forskolin). (F) Quantification of the percentage of xanthophores at each Pigmentary Organelle Index (POI) normalized to 100% (p<0.0001). (G–H) Plin6 is immunolocalized to xanthophores in isolated scales from goldfish in both aggregated (G) and dispersed states (H). (I) Quantification of the percentage of xanthophores at each Pigmentary Organelle Index (POI) normalized to 100% (p<0.0001). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
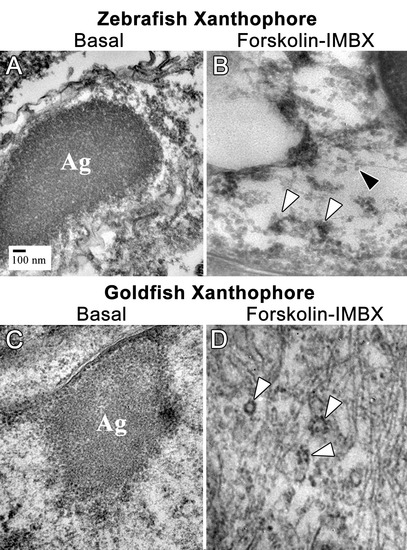
Thin section transmission electron microscopy (TSTEM) of zebrafish and goldfish xanthophores. (A) A zebrafish xanthophore with aggregated CB (Ag). (B) TSTEM of a zebrafish xanthophore following forskolin-IBMX treatment shows clusters of dispersed CD (white arrowheads) and individual CD (black arrowhead). (C) TSTEM of a goldfish xanthophore with aggregated DB (Ag). ( |
|
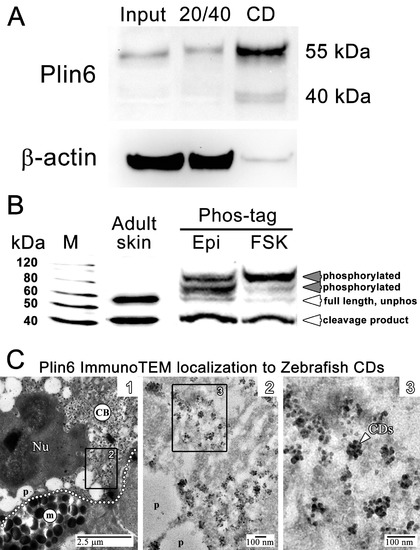
Plin6 is localized to carotenoid droplets and is phosphorylated under conditions that disperse pigment. (A) Western blot analysis of Plin6 expression from three fractions of skin homogenate separated by a sucrose gradient; total protein homogenate in 40% sucrose prior to centrifugation (Input), the protein fraction at the interface of the 20% and 40% sucrose layers following centrifugation (20/40), and the purified CD fraction that floated above the 20% sucrose following centrifugation (CD). (B) Western blot analysis of Plin6 expression from untreated skin (adult skin), and from scales treated with epinephrine (Epi) or forskolin-IBMX (FSK) to inhibit or stimulate PKA activity, respectively. Proteins from treated scales were resolved using polyacrylamide gels containing Phos-tag, which retards the electrophoretic mobility of phosphorylated proteins. Plin6 is largely unphosphorylated (Unphos, white arrowheads) under conditions that promote aggregation (Epi) and highly phosphorylated (Phos, grey arrowheads) under conditions that promote dispersion (FSK). (C) Plin6 immunoTEM in zebrafish scales. (C-1) A dotted white line demarks the rough boundary between a xanthophore (top) and melanophore (bottom). The carotenoid body (CB) with clusters of CD puncta is located in a field adjacent to the nucleus (Nu) of the xanthophore. Pterinosomes (p) within the xanthophore are also present, as well as a field of melanosomes (m) within the adjacent melanophore. (C-2) Higher magnification of the boxed inset shown in C-1. (C-3) Higher magnification of the boxed inset shown in C-2 show Plin6 immunoreactivity targeted to clusters of CDs (arrowhead). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
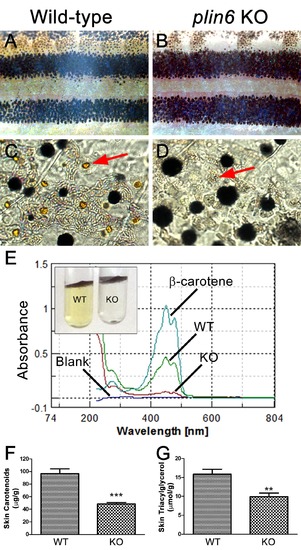
Reduced carotenoid concentration in plin6 knockout zebrafish. Brightfield images of the flank and isolated scales from adult wild-type (A, C) and plin6 mutants (B, D) show a reduction in yellow carotenoid pigmentation in mutant tissue (red arrows in C, D). (E) Extraction of carotenoid pigment from wild-type and plin6 mutant integument (inset) and the corresponding absorbances of carotenoids from a β-carotene standard, wild-type skin (WT), and plin6 mutant skin (KO). (F) Quantification of skin carotenoid levels from wild-type (WT) and plin6 mutant skin (KO). N = 4; *** = p<0.001. (G) Quantification of skin triacylglycerol levels from wild-type (WT) and plin6 mutant skin carotenoid droplets (KO). N = 3; ** = p<0.02. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
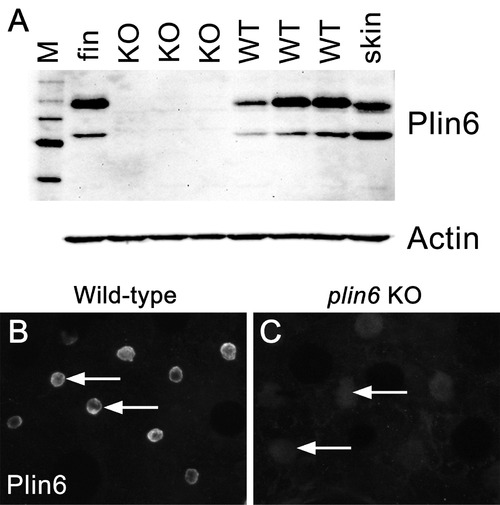
The absence of Plin6 expression in plin6 mutants. (A) Western blot analysis of Plin6 expression in whole skin homogenates comparing three plin6 homozygotes to their wild-type siblings. Homogenates of tail fin and whole skin taken from other wild-type stocks are used as positive controls for Plin6 expression and β-actin is used as a loading control. (B–C) Plin6 immunolocalization to CB in xanthophores from isolated wild-type (B) and plin6 mutant scales (C) shows an absence of immunolocalized Plin6 in mutant scales. |
|
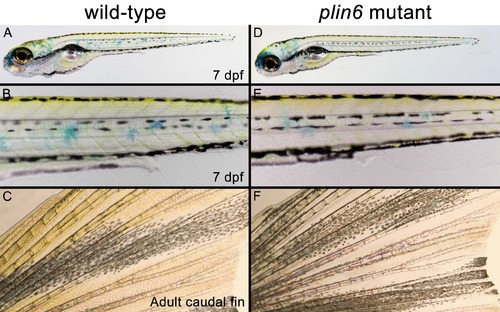
Developing and adult plin6 mutant fish show no obvious defects. Wild-type (A–C) and plin6 mutant fish (D–F) are shown. At seven dpf, no discernable defects are observed in plin6 mutants, including the normal development of the melanophore stripe patterning, eye development, swim bladder formation, heart development, and body axis development (all commonly observed developmental defects in fish). Xanthophores are also present (yellow). Some surface xanthophores take up the methylene blue present in the embryo media. Adult caudal fins (C, F) show normal fin morphology in plin6 mutants. A slight reduction of carotenoid (yellow) pigmentation can now be observed in the mutants. |
|
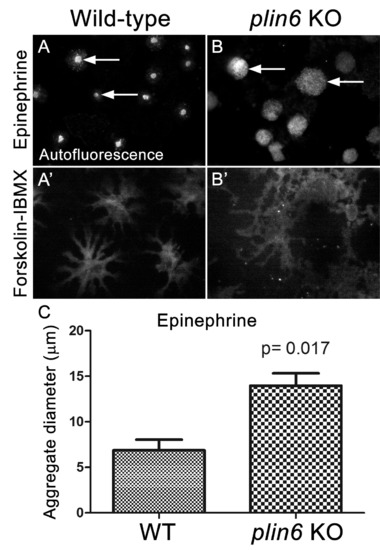
Loss of Plin6 function impairs CB aggregation in adult zebrafish xanthophores. (A–A’) An isolated scale from a wild-type animal showing xanthophore carotenoid body auto-fluorescence. 1 hr incubation in Epinephrine (A) or forskolin-IBMX (A’) induced CB aggregation and dispersion, respectively. (B–B’) An isolated scale from a plin6 mutant animal showing xanthophore carotenoid body auto-fluorescence. 1 hr incubation in Epinephrine (B) failed to induce tight CB aggregation (arrows). However, incubation in forskolin-IBMX (B’) induced CB dispersion. (E) Quantification of the aggregate diameter of wild-type and plin6 mutant xanthophores from measurements of Epinephrine-treated scales (N = 3; p=0.017). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
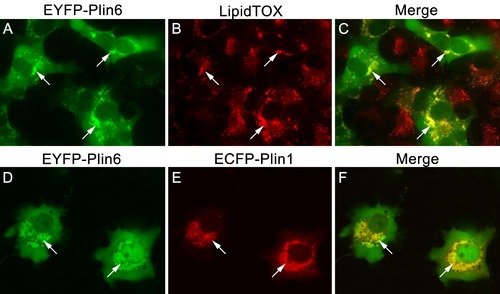
CD and LD are analogous structures. (A) Expression of EYFP-Plin6 fusion protein in COS7 cells that have been induced to create lipid droplets. Strong expression is observed near the nuclei (arrows). (B) Lipidtox staining of intracellular lipid droplets (arrows). (C) Overlay of A and B, showing co-labeling of EYFP-Plin6 fusion and LipidTOX stained lipid droplets (arrows). (D) Expression of EYFP-Plin6 fusion protein in COS7 cells (arrows). (E) Mouse Plin1-ECFP fusion expression in the same cells shown in panel A (arrows). (F) Overlay of panels A and B, showing co-expression of zebrafish EYFP-Plin6 and mouse Plin1-ECFP (arrows). |