- Title
-
Fascin 2b Is a Component of Stereocilia that Lengthens Actin-Based Protrusions
- Authors
- Chou, S.W., Hwang, P., Gomez, G., Fernando, C.A., West, M.C., Pollock, L.M., Lin-Jones, J., Burnside, B., and McDermott, B.M.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
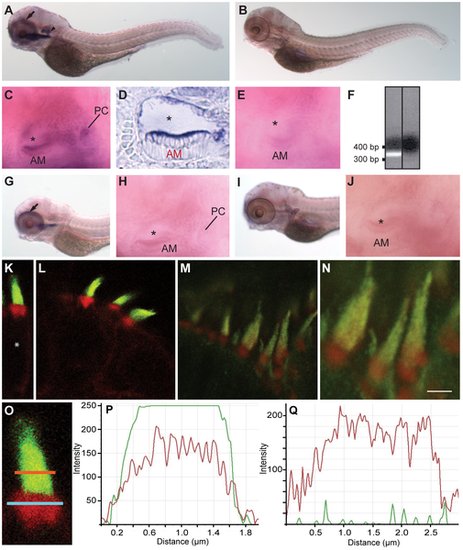
Localization patterns of fascin 2 mRNAs and proteins in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridizations (A–E, G–J) were performed on larvae at 4 dpf. Fascin 2b mRNA is detected in the otocysts (A, arrowhead; C) and the eye (A, arrow). Fascin 2a mRNA is expressed in the eye (G, arrow), but not the otocyst (H). Fascin 2b sense RNA (B,E) and fascin 2a sense RNA (I,J), each labeled, were used as controls. A cryosectioned ear labeled with fascin 2b antisense probe is displayed (D). AM, PC, and asterisk indicate the anterior macula, the posterior crista, and the lumen of the otocyst, respectively (C,D,E,H,J). RT-PCR analysis (F) shows expression of fascin 2b in zebrafish hair cells. Agarose gel confirms the expected product size of the fascin 2b amplicon, left lane (+ hair-cell cDNA); no product is observed without cDNA template, right lane (no template control). Labeling using fascin 2 antiserum reveals strong fluorescent signals (green) in hair bundles of an anterior macula (K,O) and a posterior crista (L) from larvae at 4 dpf and of an adult lagena (M,N). In red, fluorophore-coupled phalloidin labels the filamentous actin of stereocilia and cuticular plates (K–O). Higher magnification of M is displayed (N). Scale bar is 2 μm. Soma is indicated by asterisk (K). An enlarged view of a hair bundle from an anterior macula (O) is shown with regions of interest (ROI) selected for the stereocilia (orange line) and the cuticular plate (blue line). Fluorescence intensity profiles of stereocilia (P), using the orange-line ROI from O, show that the fascin 2b- (green) and phalloidin-associated (red) signals are overlapping. Intensity profiles of the cuticular plate (Q), using the blue-line ROI from O, demonstrate no significant labeling with fascin 2 antiserum (green). Intensity scales are linear, but the units are arbitrary (P,Q). X-axes (P,Q) represent the lengths of the respective orange and blue lines (O). |
|
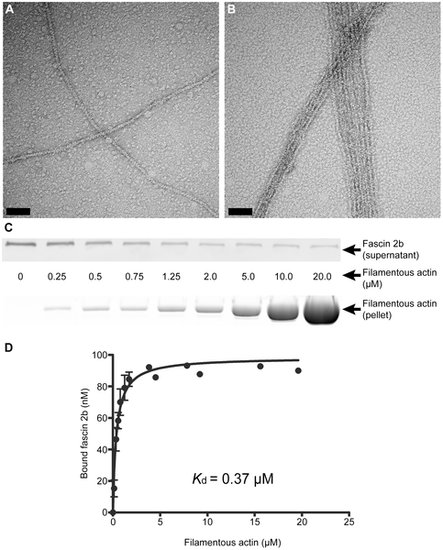
Physical characterization of the interaction between fascin 2b and filamentous actin. Negative staining and electron microscopy reveal actin bundling by recombinant fascin 2b fusion protein. Micrographs display filamentous actin in the absence of MBP-fascin 2b (A) and in the presence of MBP-fascin 2b (B); bundled filaments are observed in B. Scale bars are 100 nm. An immunoblot (C, top), from a cosedimentation experiment, shows the progressive depletion of MBP-fascin 2b from supernatants incubated with increasing concentrations of actin; molar concentration (C, middle) of actin for each lane is displayed. Image of a gel (C, bottom), after SDS-PAGE and exposure to SYPRO Ruby protein gel stain, shows the actin found in pellets from a cosedimentation experiment. Plotted are the means of specific equilibrium-binding measurements of MBP-fascin 2b to filamentous actin (D). Each point is a mean ± SEM (number of experiments, N = 4) or an average of two experiments (no error bars). |
|
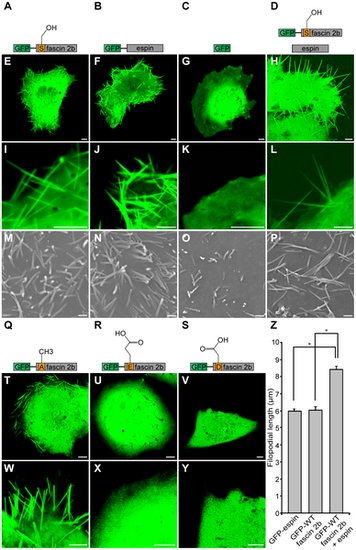
Roles of wild-type or phosphomutant fascin 2b proteins in the formation of long filopodia. Schematics of proteins expressed in COS-7 cells and corresponding confocal micrographs are displayed: GFP-WT fascin 2b (A,E,I), GFP-espin (B,F,J), GFP (C,G,K), GFP-WT fascin 2b and espin (D,H,L), GFP-S38A fascin 2b (Q,T,W), GFP-S38E fascin 2b (R,U,X), or GFP-S38D fascin 2b (S,V,Y). Confocal images are of representative live cells. Filopodia are observable in cells expressing GFP-WT fascin 2b (E,I), GFP-espin (F,J), or GFP-S38A fascin 2b (T,W). None are apparent in cells in which only GFP was introduced, as exhibited by this representative cell (G,K). Cells expressing GFP-S38E fascin 2b (U,X) or GFP-S38D fascin 2b (V,Y) have no filopodia visible by confocal microscopy. Cells that express both GFP-WT fascin 2b and espin have longer cytoplasmic protrusions (H,L,Z) than cells that express GFP-WT fascin 2b or GFP-espin separately (E,F). Scanning electron micrographs of cells expressing GFP-WT fascin 2b (M), GFP-espin (N), or GFP-WT fascin 2b and espin (P) show results similar to those of cells observed using confocal microscopy, except that diminutive filopodia are seen on the surfaces of cells that express the GFP control, as shown in image (O). The mean lengths ± SEM of the cellular protrusions are shown for cells expressing GFP-espin (Nfilopodia = 400), GFP-WT fascin 2b (Nfilopodia = 130), or GFP-WT fascin 2b together with espin (Nfilopodia = 330), and they indicate synergism between fascin 2b and espin (Z). Asterisk indicates P<0.0001 for Student′s t test. Scale bars of confocal images and electron micrographs are 5 μm and 1 μm, respectively. |
|
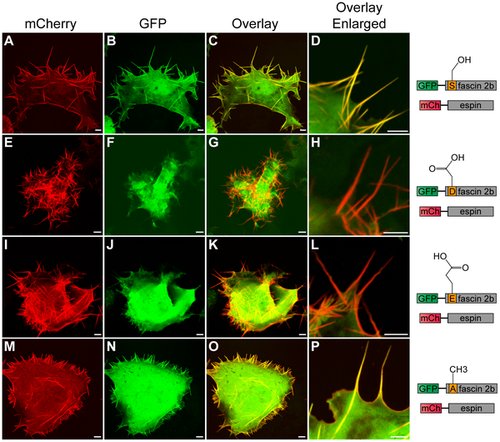
Subcellular localization patterns of wild-type or phosphomutant fascin 2b proteins in live COS-7 cells that coexpress espin. A cell (A–D) coexpressing GFP-WT fascin 2b and mCherry (mCh)-espin displays colocalization of these proteins in filopodia, which are detected as yellow in image overlays (C,D). Images of cells that coexpress mCherry-espin and either GFP-S38D fascin 2b (E–H) or GFP-S38E fascin 2b (I–L) reveal espin-laden protrusions (red) that lack the fascin 2b phosphomutant proteins (G,H,K,L). Micrographs of a cell that expresses both mCherry-espin and GFP-S38A fascin 2b (M–P) show that both proteins reside in filopodia (yellow) (O,P). Scale bars are 5 μm. |
|
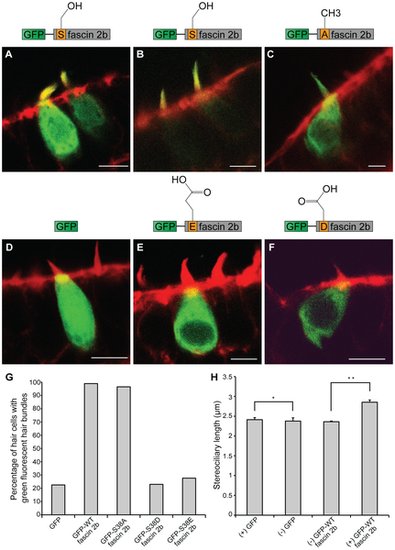
Localization patterns of wild-type or phosphomutant fascin 2b fusion proteins in hair cells, and the effect of GFP-WT fascin 2b expression on stereociliary length. Representative confocal images of transgenic hair cells in the anterior maculae of zebrafish at 4 dpf are displayed. Hair cells expressing GFP-WT fascin 2b (A,B), GFP-S38A fascin 2b (C), GFP (D), GFP-S38E fascin 2b (E), or GFP-S38D fascin 2b (F) are labeled with fluorophore-coupled phalloidin (red). The fusion proteins and GFP appear green. When high levels of GFP-WT fascin 2b are expressed in hair cells (number of cells, N = 192), the fusion protein localizes to the stereocilia and the somata (A), but when low levels are expressed, it localizes specifically to the hair bundles (B). GFP-S38A fascin 2b (N = 86) (C) localizes with a pattern that is similar to that of GFP-WT fascin 2b (A). In contrast, cells expressing GFP (N = 71) (D), GFP-S38E fascin 2b (N = 94) (E), or GFP-S38D fascin 2b (N = 74) (F) generally exhibit greatly reduced levels of GFP fluorescence in their hair bundles. Scale bars are 5 μm. Graph displays the percentage of transgenic hair cells with GFP fluorescence in their bundles for each expressed fluorescent protein (G). As represented by graph (H), cells that express GFP-WT fascin 2b ((+) GFP-WT fascin 2b, N = 132) have an increased mean hair-bundle length when compared to that of non-transgenic hair cells ((-) GFP WT-fascin 2b) in transgenic animals that mosaically express the transgene. The means of the bundle lengths of cells that lack expression of the fluorescent proteins ((-) GFP WT-fascin 2b, N = 480; (-) GFP, N = 45) and that of those that express GFP ((+) GFP, N = 148) are similar, indicating that there is no substantial experimental variation of the controls within and between the two groups. The means of the bundle lengths ± SEM are plotted. Single and double asterisks indicate P = 0.8653 and P = 0.0001, respectively, for Student′s t tests. |
|
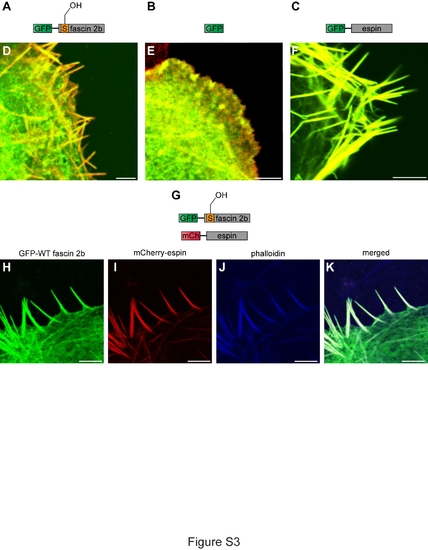
Localization of fascin 2b and espin proteins in fixed COS-7 cells. Schematics of the proteins expressed in cells are portrayed: GFP-WT fascin 2b (A), GFP (B), GFP-espin (C), and GFP-WT fascin 2b and mCherry-espin (G). To visualize actin-based filopodia, cells were labeled with Alexa 568 phalloidin (red)(D-F) or Alexa 633 phalloidin (blue) (J,K). Merged images show localization of GFP-WT fascin 2b (green) (D) or GFP-espin (green) (F) to filopodia where they overlap with actin (yellow). No filopodia are detectable in a fixed cell that expresses only GFP (green) (E). Coexpression of GFP-WT fascin 2b (H) and mCherry-espin (I) shows that both proteins colocalize (white) (K) to phalloidin-labeled filopodia (J) in a fixed COS-7 cell. Scale bars are 5 μm. |