- Title
-
MicroRNAs show a wide diversity of expression profiles in the developing and mature central nervous system
- Authors
- Kapsimali, M., Kloosterman, W.P., de Bruijn, E., Rosa, F., Plasterk, R.H., and Wilson, S.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Genome Biol.
|
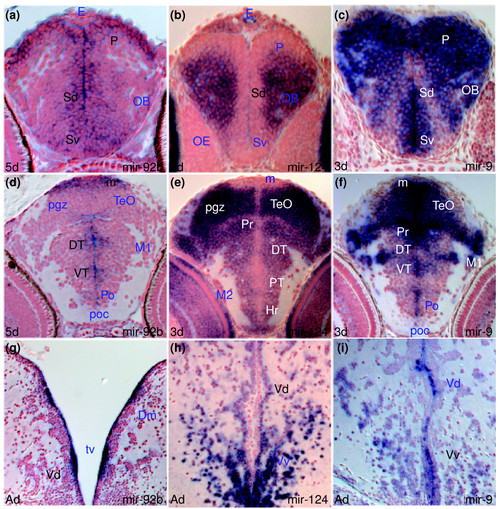
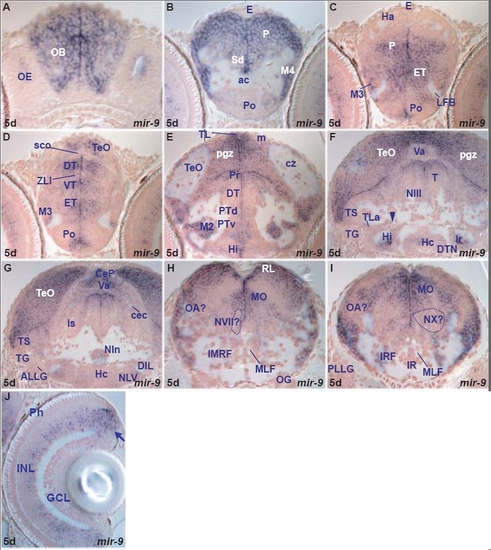
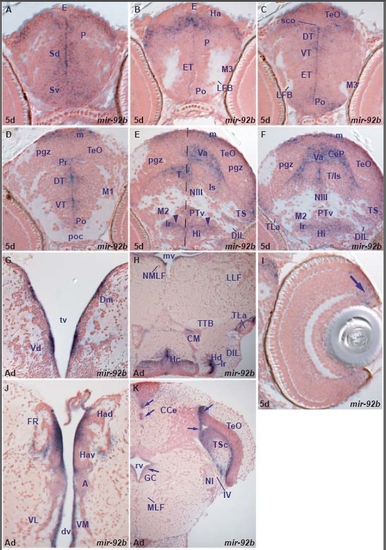
miRNAs expressed in proliferating and/or differentiating cells in the developing and adult zebrafish brain. In this and other figures, unless otherwise mentioned, sections are transverse with dorsal on the top, stage is shown bottom left and miRNA analyzed by in situ hybridization bottom right, in situ staining is in blue and cell nuclei are visualized with nuclear red counterstaining. Abbreviations used in the Results section of the text are denoted in black. For other abbreviations, see Additional data file 26. (a,d,g) miR-92b expression in periventricular and adjacent cells of the telencephalon (a,g), diencephalon and optic tectum (d). (b,e,h) miR-124 expression in differentiating cells in the telencephalon (b,h), diencephalon and optic tectum (e). (c,f,i) miR-9 expression in periventricular/proliferating and differentiating cells of the telencephalon (c,i), diencephalon and optic tectum (f). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
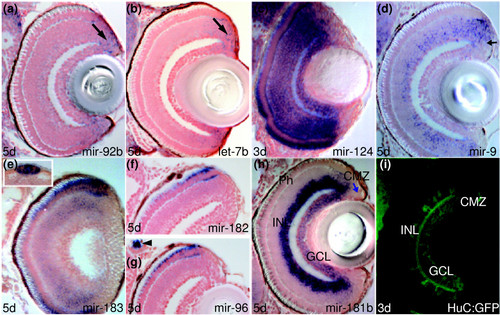
Several miRNAs expressed in discrete retinal cell populations. (a-h) Transverse sections through retinae in situ hybridized with miR-92b, let-7b, miR-124, miR-9, miR-183, miR-182, miR-96 and miR-181b probes. Arrows point at proliferative ciliary marginal zone (CMZ) cells in (a,b,d,h). The inset in (e) shows pineal cells. The arrowhead in (g) indicates miR-96 expression in peripheral sensory neuromasts. (i) Confocal section through the retina of a transgenic line Tg(huC:GFP) immunostained for GFP. Other miRNAs with expression in the retina include miR-454a (Figure C in Additional data file 25), miR-132 (Figure E in Additional data file 25), miR-125b (Figure F in Additional data file 25) and miR-181a (Figure G in Additional data file 13). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
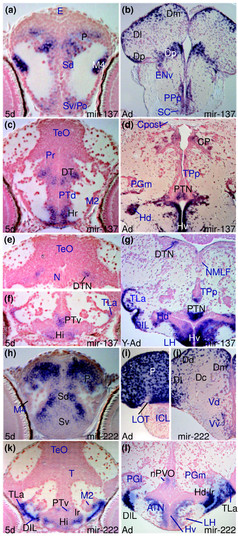
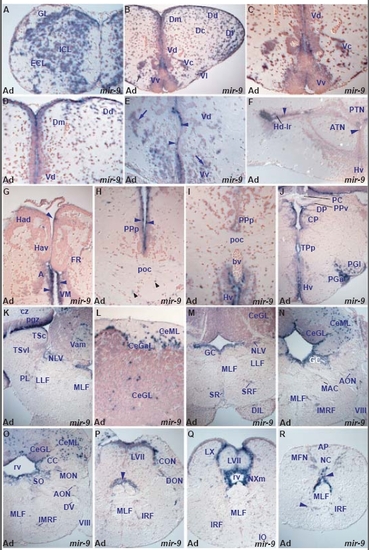
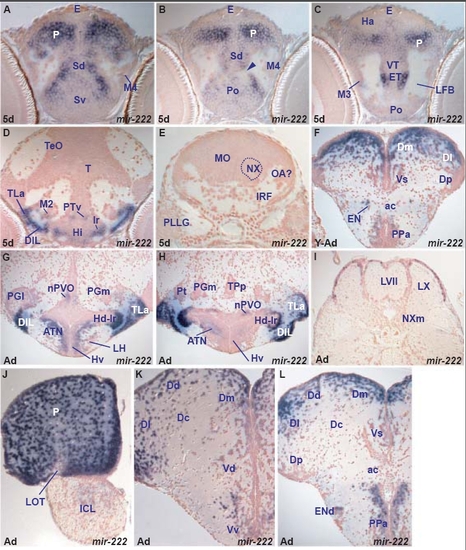
miR-137 and miR-222 expression is conserved between larval and adult brain. (a,c,e,f) miR-137 expression in the larval caudal telencephalon (a), diencephalon (c), dorsal midbrain (e) and hypothalamus (f). (b,d,g) miR-137 expression in adult brain sections at levels corresponding to the embryonic sections shown in (a), (c) and (e/f), respectively. (h,k) miR-222 expression in the larval telencephalic pallium (P) and subpallium (Sd, Sv), hypothalamus (Hi, TLa, DIL, lr) and posterior tuberculum (PTv, M2). (i,j,l) miR-222 expression in corresponding adult nuclei in the pallium (P, Dm, Dl, Dd, Dc), subpallium (Vd, Vv), hypothalamus (ATN, LH, TLa, DIL, Hd-lr) and posterior tuberculum (nPVO, PGl). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
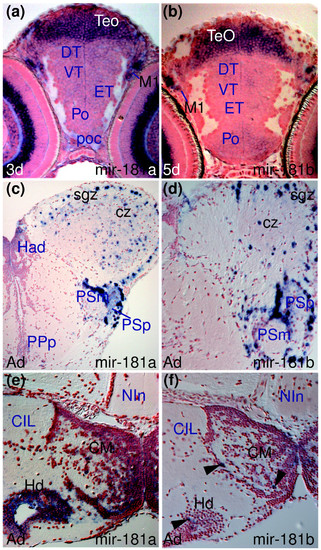
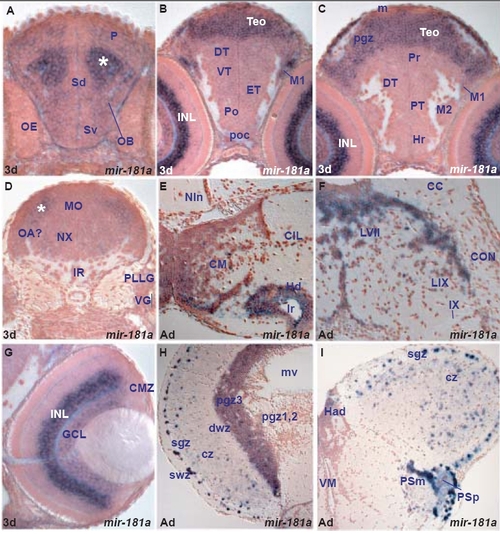
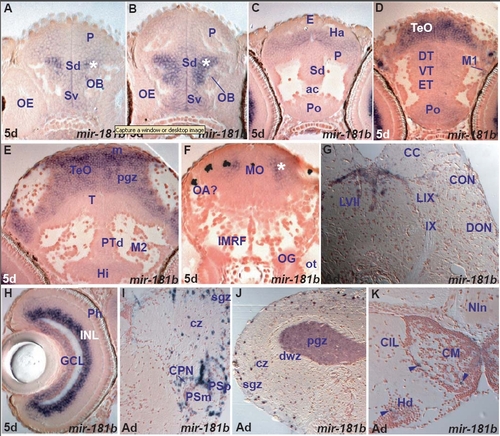
Conserved and divergent expression of miR-181a and miR-181b. (a,b) miR-181a and miR-181b expression in larval tectal (TeO) and migrated pretectal area cells (M1). (c,d) Comparable miR-181a and miR-181b expression in the adult optic tectum (sgz, cz) and pretectal nuclei (PSm, PSp). (e) miR-181a is expressed in more cells than (f) miR-181b (arrowheads) in the adult hypothalamic mamillary body (CM) and dorsal periventricular zone (Hd). |
|
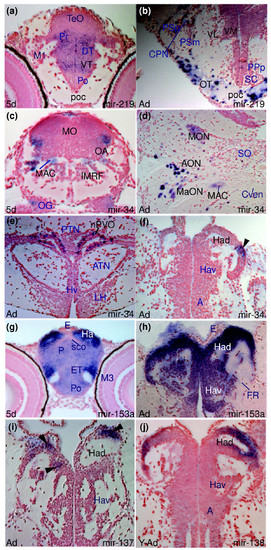
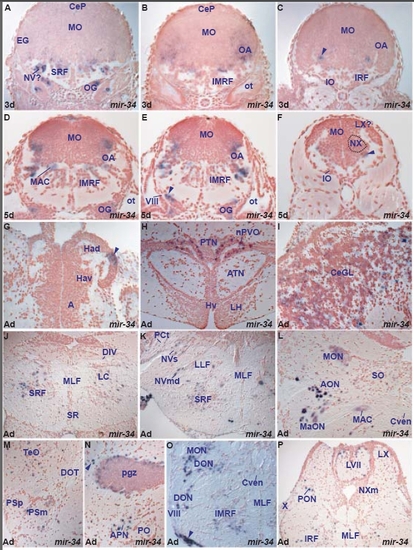
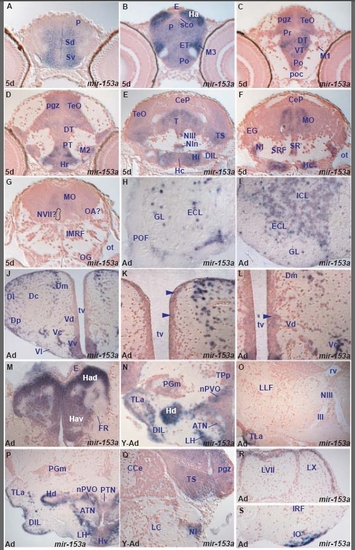
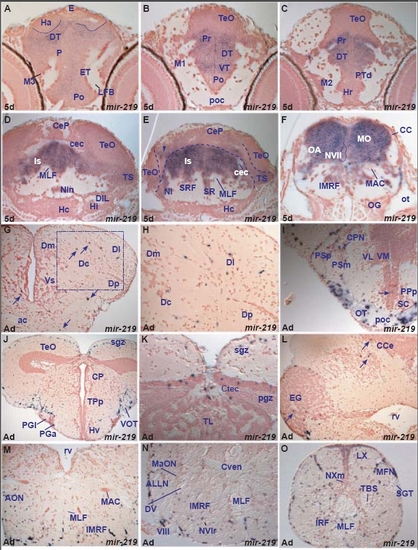
Examples of miRNAs showing differences in expression between larval and adult stages. (a,b) miR-219 expression in the diencephalon at the level of the post-optic commissure (poc) of the larval and adult brain. In the larval brain (a), miR-219 is widely expressed in the ventral (VT) and dorsal (DT) thalamus and periventricular pretectum (Pr) whereas cells of the poc are devoid of expression. In contrast, in the adult (b), miR-219 is expressed in cells in the poc and optic tract (OT) whereas ventrolateral (VL) and ventromedial (VM) thalamic nuclei are devoid of expression. (c-f) miR-34 expression: (c,d) show conserved miR-34 expression in the octaval area (OA, MON, AON, MaON) and Mauthner neuron (MAC) in the larval and adult zebrafish brain, respectively; (e) shows miR-34 in the adult nucleus of the paraventricular organ (nPVO) and the arrow in (f) points to miR-34 expressing cells in the lateral part of the adult left habenula. (g,h) Conserved miR-153a expression throughout the larval (Ha) and adult (Hav, Had) habenulae. (i) miR-137 expression in groups of dorsal habenular cells (Had, arrowheads). (j) miR-138 expression in groups of dorsal habenular cells (Had). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
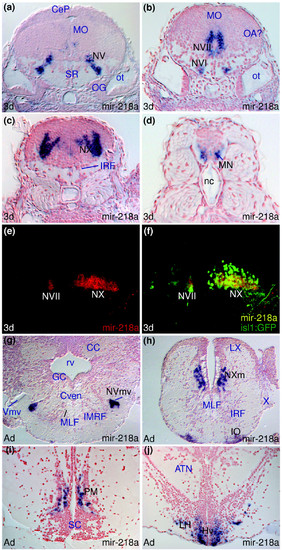
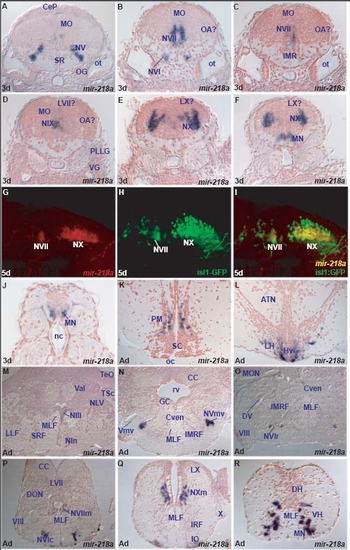
miR-218a is expressed in embryonic cranial and spinal motor-neurons. (a-d,g-h) Larval and adult miR-218a expression in the motor nuclei of the fifth (NV, NVmv), sixth (NVI), seventh (NVII), tenth (NX, NXm) cranial nerves and spinal motor neurons (MN). (e,f) Confocal sagittal sections through the hindbrain of an embryo expressing the Tg(isl1:GFP) transgene with anterior to the left. miR-218a expression is shown in red in (e) and (f) is a superimposition of the miR-218a staining (red) and anti-GFP immunostaining (green). Yellow cells express both miR-218a and GFP in the NVII and NX cranial motor nuclei. (h-j) Additional sites of expression of miR-218a in the adult inferior olive (IO), preoptic magnocellular area (PM) and hypothalamus (Hv, LH). |
|
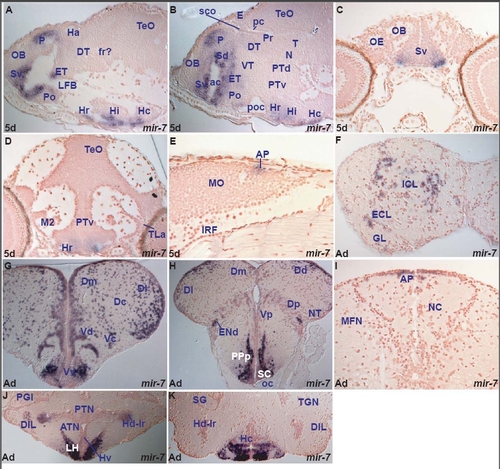
miR-7 expression in the zebrafish brain. miR-7 shows spatially localized expression, largely conserved throughout life. Larval expression is restricted to the forebrain in telencephalic, preoptic, few thalamic, eminentia thalami and ventral hypothalamic cells. In addition, it is expressed in a few cells of the area postrema at the dorsal junction of hindbrain-spinal cord (Table D). miR-7 expression is mainly conserved in telencephalic, hypothalamic nuclei and area postrema between the larval and adult zebrafish brain. However, in the adult, we observe expression in the external and internal cellular layers of the olfactory bulb. Furthermore, in contrast to the larval, the adult thalamus is devoid of miR-7 expression (Table D, I). miR-7 often shares expression in the forebrain with miR-222 but there are also some differences (table D, I). A. parasagittal section through the larval fore- and midbrain showing miR-7 expressing cells in the hypothalamus (caudal, Hc, intermediate, Hi and rostral, Hr), preoptic area (Po), eminentia thalami (ET), ventral subpallium (Sv) around the anterior commissure and pallium (P). |
|
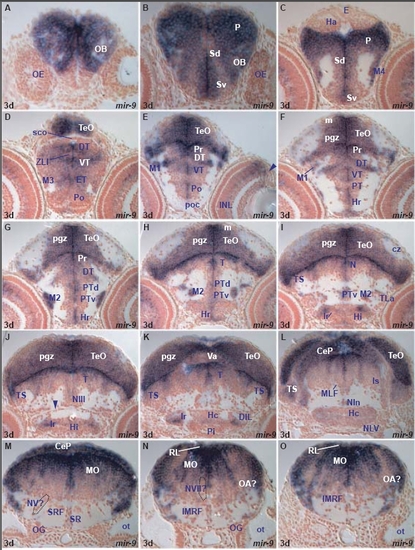
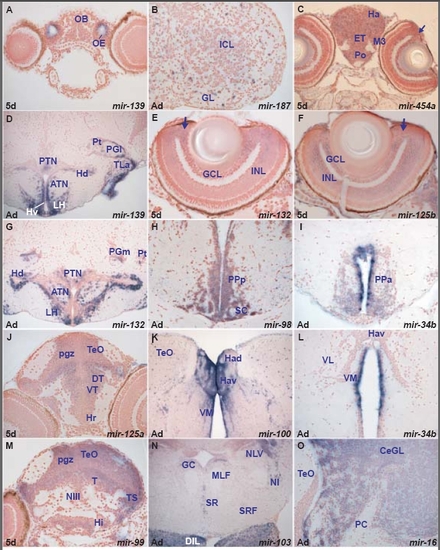
miR-9 expression in the 3dpf zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval rostral telencephalon at the level of the olfactory epithelium (OE) showing miR-9 expressing cells in the olfactory bulb (OB). Expression is absent in cells immediately ventral to the bulb. |
|
miR-9 expression in the 5dpf zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval rostral telencephalon at the level of the olfactory epithelium (OE) showing miR-9 expressing cells in the olfactory bulb (OB). |
|
miR-9 expression in the adult zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the adult olfactory bulb showing miR-9 expressing cells in the internal (ICL), external (ECL) cellular and glomerular (GL) olfactory layers. |
|
miR-34 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval rostral hindbrain at the level of the octaval ganglion (OG) showing miR-34 expressing cells in the ventral medulla oblongata (MO), superior reticular formation (SRF), likely the trigeminal motor nucleus (NV?) and octaval ganglion (OG). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
miR-92b expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-92b expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium, pallium (P) and epiphysis (E). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
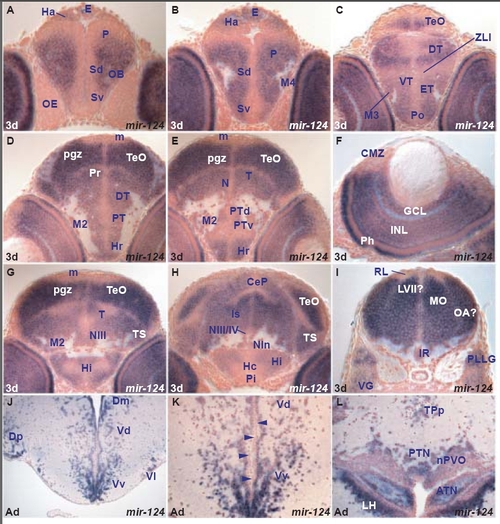
miR-124 expression in the zebrafish brain A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon and rostral epithalamus showing miR-124 expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium, pallium (P), olfactory bulb (OB) and habenula (Ha). Expression is absent from ventricular and periventricular cells. |
|
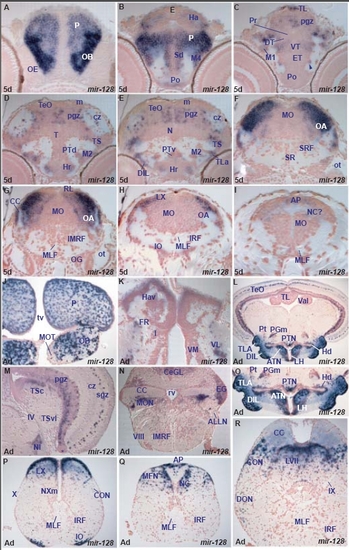
miR-128 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the rostral larval telencephalon showing miR-128 expressing cells in the olfactory bulb (OB) and pallium (P). |
|
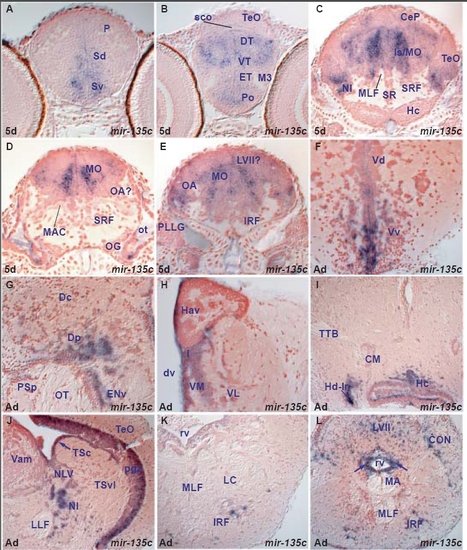
miR-135c expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-135c expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium. |
|
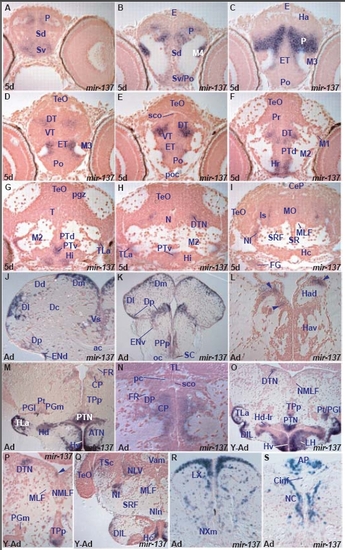
miR-137 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-137 expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium and pallium (P). |
|
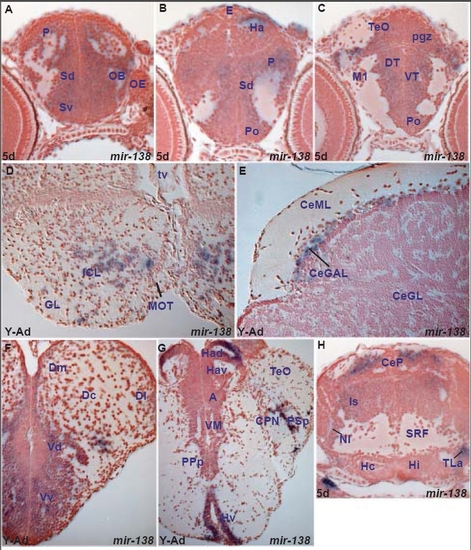
miR-138 expression in the zebrafish brain A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-138 expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium, pallium (P) and olfactory bulb (OB). |
|
miR-153a expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-153a in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium and pallium (P). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
miR-181a expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-181a expressing cells throughout the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium, pallium (P) and olfactory bulb (OB). The asterisk marks the strongly expressing miR-181a cell group in the central pallium, close to OB and Sd. |
|
miR-181b expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-181b expressing cells throughout the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium, pallium (P) and olfactory bulb (OB). The asterisk marks the strongly expressing miR-181b cell group in the central pallium, close to the OB and Sd. |
|
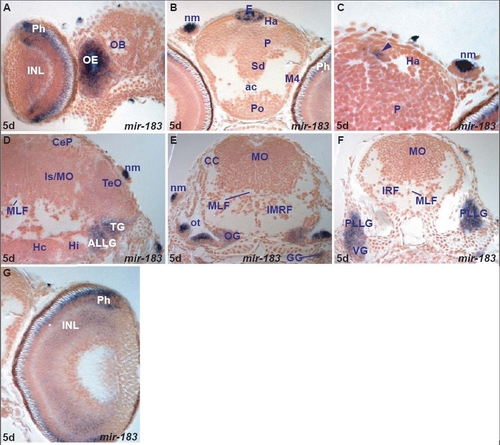
miR-183 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval rostral brain and retina showing miR-183 expressing cells in the olfactory epithelium (OE), retinal photoreceptor (Ph) and inner nuclear (INL) layers. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
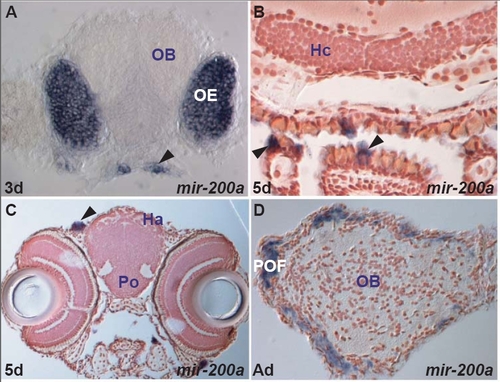
miR-200a expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the rostral part of the larval head showing miR-200a expressing cells in the olfactory epithelium (OE) and the taste buds (arrowhead). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
miR-218a expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval hindbrain at the level of the octaval ganglion (OG) showing miR-218a expression in the trigeminal motor nucleus (NV). |
|
miR-219 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval caudal telencephalon and rostral diencephalon showing miR-219 weakly expressing cells in the rostral preoptic area (Po), eminentia thalami (ET), pallium (P), dorsal thalamus (DT) and habenula (Ha). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
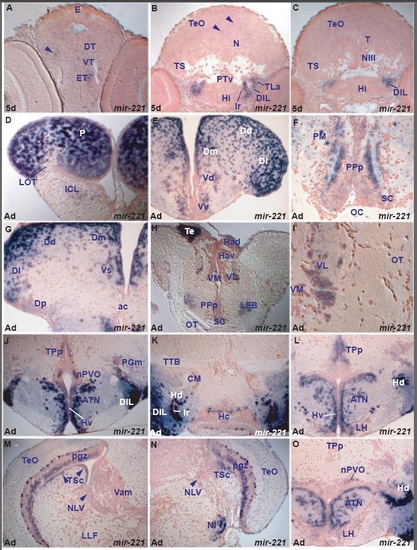
miR-221 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval diencephalon showing weakly miR-221 expressing cells in the eminentia thalami (ET) and thalamic area (arrowhead, dorsal thalamus-DT, ventral thalamus-VT). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
miR-222 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing miR-222 expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium and pallium (P). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
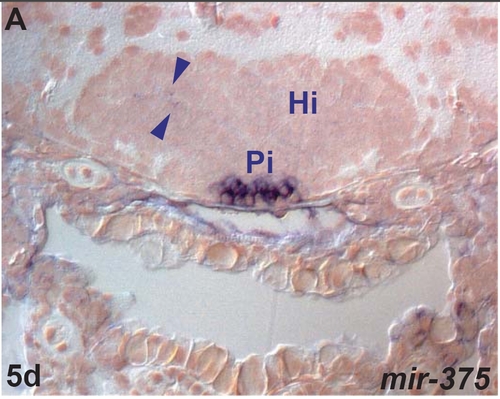
miR-375 expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the embryonic intermediate hypothalamus (Hi) showing weak miR-375 expression in the hypothalamus (arrowheads) and strong expression in the pituitary (Pi). |
|
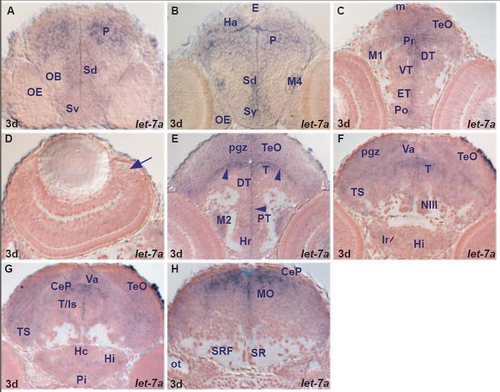
let-7a expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing let-7a expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium and pallium (P). |
|
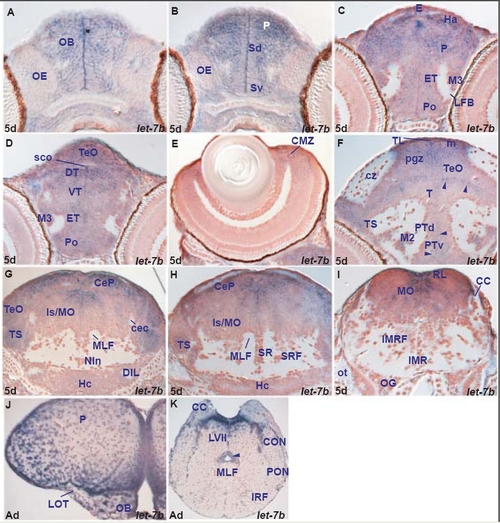
let-7b expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval rostral telencephalon showing let-7b expressing cells in the olfactory bulb (OB). |
|
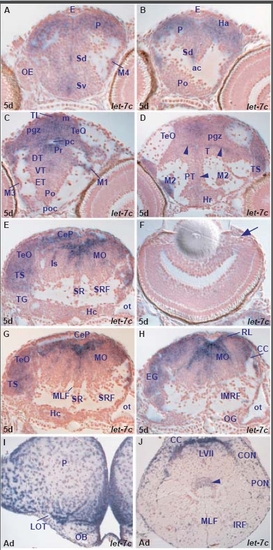
let-7c expression in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval telencephalon showing let-7c expressing cells in the ventral (Sv) and dorsal (Sd) subpallium and pallium (P). |
|
Other miRNAs expressed in the zebrafish brain. A. transverse section through the larval rostral telencephalon showing miR-139 expressing cells in the olfactory epithelium (OE). miR-139 is widely expressed in differentiated cells in the zebrafish brain (see also panel D). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
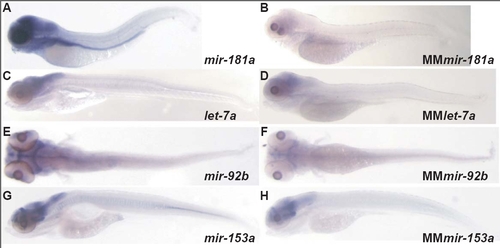
Mismatch test for let-7a, miR-92b, miR-153a and miR-181a. A,C,E,G: show in situ hybridization signal for full matching LNA probes miR-181a, let-7a, miR-92b and miR-153a, respectively. |