PUBLICATION
Noise modulation in retinoic acid signaling sharpens segmental boundaries of gene expression in the embryonic zebrafish hindbrain
- Authors
- Sosnik, J., Zheng, L., Rackauckas, C.V., Digman, M., Gratton, E., Nie, Q., Schilling, T.F.
- ID
- ZDB-PUB-160414-14
- Date
- 2016
- Source
- eLIFE 5: e14034 (Journal)
- Registered Authors
- Schilling, Tom, Sosnik, Julian
- Keywords
- Danio rerio, computational biology, developmental biology, hindbrain, morphogen, noise, retinoic acid, rhombomere, stem cells, systems biology, zebrafish
- MeSH Terms
-
- Signal Transduction*
- Rhombencephalon/embryology*
- Tretinoin/metabolism*
- Zebrafish/embryology*
- Gene Expression Regulation, Developmental*
- PubMed
- 27067377 Full text @ Elife
Abstract
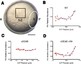
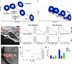
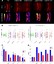
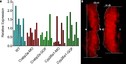
Morphogen gradients induce sharply defined domains of gene expression in a concentration-dependent manner, yet how cells interpret these signals in the face of spatial and temporal noise remains unclear. Using fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) and phasor analysis to measure endogenous retinoic acid (RA) directly in vivo, we have investigated the amplitude of noise in RA signaling, and how modulation of this noise affects patterning of hindbrain segments (rhombomeres) in the zebrafish embryo. We demonstrate that RA forms a noisy gradient during critical stages of hindbrain patterning and that cells use distinct intracellular binding proteins to attenuate noise in RA levels. Increasing noise disrupts sharpening of rhombomere boundaries and proper patterning of the hindbrain. These findings reveal novel cellular mechanisms of noise regulation, which are likely to play important roles in other aspects of physiology and disease.
Genes / Markers
Expression
Phenotype
Mutations / Transgenics
Human Disease / Model
Sequence Targeting Reagents
Fish
Orthology
Engineered Foreign Genes
Mapping