Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-251016-79
- Publication
- Guerra et al., 2025 - Brain accumulation of lactosylceramide characterizes GALC deficiency in a zebrafish model of Krabbe disease
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
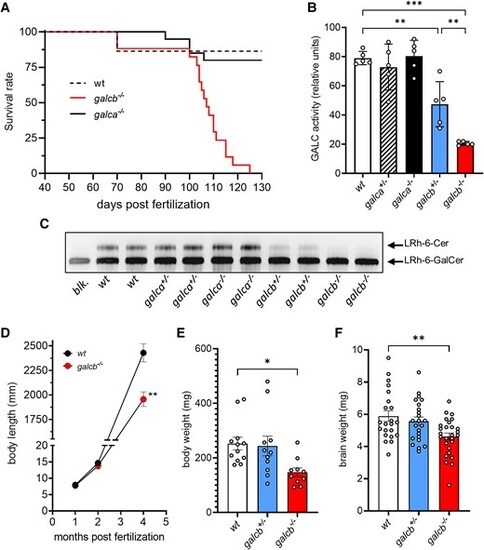
Characterization of galca and galcb knockout zebrafish. (A) Survival analysis of wild-type (WT), galca knockout (KO) and galcb KO zebrafish (n ≥ 17 animals/group). The survival of galca KO mutants and of heterozygous galca+/− and galcb+/− animals (not shown) was not significantly different for WT siblings [Log-rank (Mantel-Coz) test]. (B) GALC enzymatic activity thin-layer chromatography (TLC) assay of the brain extracts of zebrafish mutants at 4 mpf (five animals/group). (C) Representative image of a TLC assay showing the GALC activity of the brain extracts of two animals for each experimental group. (D) Body length of WT and galcb KO zebrafish measured at different times of growth. The rate of growth of galca+/−, galca−/− and galcb+/− animals was not significantly different from WT siblings (not shown). At the end stage of disease (4 months post fertilization), body weight (E) and the weight of harvested brain (F) were measured for the indicated WT, galcb+/−, and galcb−/− animals. Data are the mean ± standard error of the mean. One-way ANOVA (Tukey's multiple comparison test) in B and F; Student's t-test in D: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. |