|
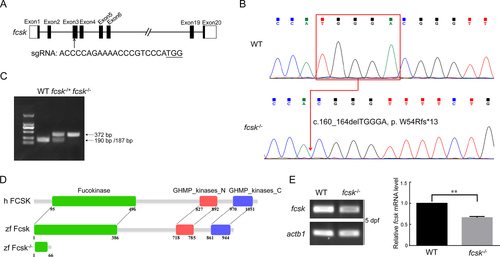
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated fcsk knockout in zebrafish A: CRISPR/Cas9 target sites in fcsk. B: Sanger sequencing confirmed a five-base deletion (c.160_164delTGGGA, p.W54Rfs*13) in F2 generation of fcsk−/− zebrafish. C: fcsk mutation abolished the NcoI cleavage site, preventing digestion of the PCR products in homozygous (fcsk−/−) zebrafish (372 bp). In contrast, PCR products from WT zebrafish were cleaved into 190 bp and 187 bp fragments, while heterozygous (fcsk+/−) zebrafish exhibited digestion of the WT allele, resulting in 372 bp, 190 bp, and 187 bp fragments. D: Protein structure of human FCSK (h FCSK), zebrafish WT Fcsk (zf Fcsk) and mutant Fcsk (zf Fcsk−/−). E: Relative mRNA levels of fcsk in fcsk−/− zebrafish (5 dpf) were detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. dpf: Days post-fertilization. Results are presented as mean±SEM, n=3. **: P<0.01.
|