Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240305-3
- Publication
- Schorpp et al., 2023 - Foxn1 is not essential for T-cell development in teleosts
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
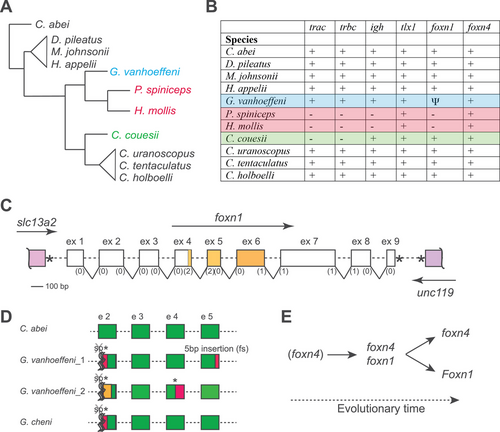
Characteristics of immunogenomes of selected Ceratioidei. (A) Schematic cladogram of phylogenetic relationships among the indicated species (data taken from the study by Swann et al. [24]). (B) Gene content in the indicated species. +, gene present and intact; –, gene missing; Ψ, pseudogenized gene. Further information on tlx1, foxn4, and foxn1 is presented in Supporting information Figs. S2–S4, and Supporting information Data S1–S3. (C) Schematic structure of the foxn1 gene and its syntenic relationship; the exons (but not introns) are drawn to scale with phases of splice sites indicated in brackets. The slc13a2 gene has the same transcriptional orientation as foxn1, whereas the unc119 gene is transcribed in the opposite direction. The * denotes the stop codons. (D) Schematic of mutations observed in foxn1 genes of the indicated specimens (see Supporting information Figs. S5–S7 for details). The splice acceptor sites of exon 2 are mutated, which suggests the presence of aberrant splicing patterns (symbolized by crossed sp, *, and wiggly lines). Specimen G. vanhoeffeni_1 corresponds to specimen UW118701 described in the study by Swann et al. [24]. Exonic sequences shaded in red or orange indicate regions different from wild-type sequences. (E) Scheme highlighting the evolutionary sequence of activities of Foxn1/4 transcription factor-family members supporting thymopoiesis during vertebrate evolution. Primordial thymopoietic activity may have been supported by Foxn4 alone; however, after gene duplication leading to the emergence of Foxn1, co-expression of the two thymopoietic factors established a robust genetic network. This robustness was subsequently abolished in two ways, by loss of an intact foxn1 gene in some species of deep-sea anglerfishes (resulting in foxn4 activity only), and by loss of expression of Foxn4 in the thymic epithelium of mammals (resulting in Foxn1 activity only). |