Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240216-46
- Publication
- Takada et al., 2023 - Mature mRNA processing that deletes 3' end sequences directs translational activation and embryonic development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
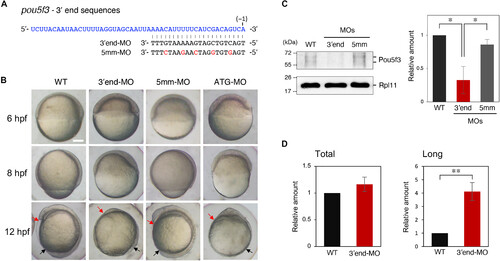
Injection with MO targeting 3′ end sequences of pou5f3 prevents Pou5f3 accumulation and causes severe developmental defects. (A) 3′ end sequences of pou5f3 mRNA that are targeted by 3′end-MO. 5mm-MO contains five mismatches (red). (B) Lateral views of WT and 3′end-MO–, 5mm-MO–, or ATG-MO–injected embryos at 6, 8, and 12 hpf. The 3′end-MO–injected embryos exhibited defective gastrulation (thickened blastoderm and delay in epiboly progression) and shortened anterior-posterior axis (red and black arrows). Similar results were obtained from the three independent experiments. Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Immunoblotting of Pou5f3 in embryos injected with 3′end- or 5mm-MO at 4 hpf (left). The intensities of both Pou5f3 bands were quantified (means ± SD; n = 3) (right). *P < 0.05, Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (D) Levels of total pou5f3 mRNA (Total) and long pou5f3 mRNA (Long) in WT embryos and embryos injected with 3′end-MO at 4 hpf were determined by quantitative RT-PCR (means ± SD; n = 3). **P < 0.01, Student’s t test. |