Figure 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221226-215
- Publication
- Lee et al., 2022 - Anp32a Promotes Neuronal Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury of Zebrafish Embryos
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
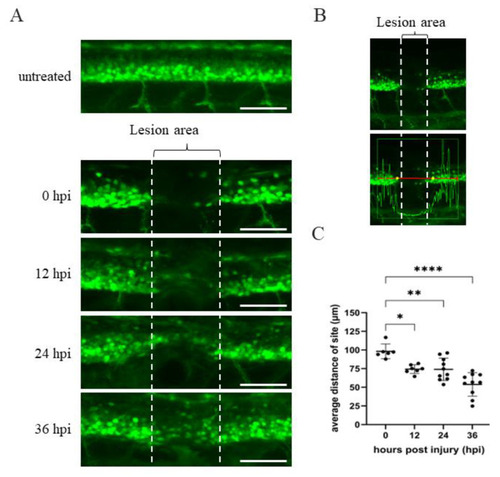
Time course of spinal cord regeneration of Tg(mnx1:GFP) transgenic zebrafish larvae after SCI. (A) Spinal cord located at the 17–20th segment of Tg(mnx1:GFP) embryos at 48 hpf was crushed, causing SCI. Complete loss of motoneuronal connections in the lesion area around the SCI (indicated by two broken lines) occurred at 0 hpi. Then, spinal cord regeneration from 12 to 36 hpi was shown, compared to uninjured spinal cord. (B) Image of SCI-Tg(mnx1:GFP) larvae at 0 hpi used to quantify the length of lesion site (in μm) using Zen 2010b Sp1 software. The box in the lower panel shows a red line 300 μm in length. This indicates the detection area with fluorescent cells located at either side of the SCI site, as marked by the vertical white broken line. While the GFP signal within the box could be detected, its intensity dropped at the SCI site. Indeed, the yellow dots mark the place where the strength of the green fluorescence signal dropped off at both sides of the SCI. The length of yellow dots relative to that of the vertical broken white line was measured. Observed by the naked eye, the length of yellow dots was longer than that of SCI site (white broken line). (C) Statistical analysis of the distance (in μm) between the two yellow dots versus temporal regenerative response (in hpi) in SCI-Tg(mnx1:GFP) embryos. Each dataset was obtained from three independent experiments and represented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA was used to perform statistical analysis (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001; ns: not significant). Scale bar: 100 μm. |