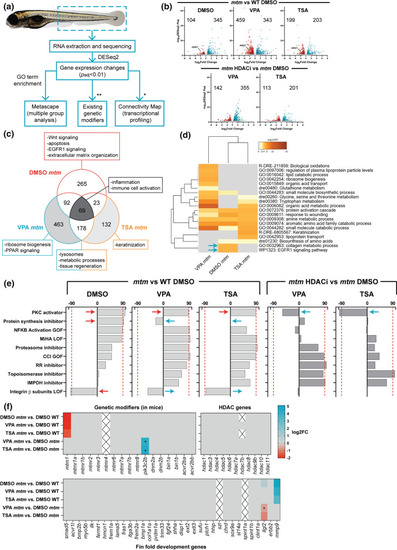
Fig. 2
|
Comparative transcriptomics in mtm mutants treated with HDAC inhibitors. a Schematic outlining the analyses performed (*genes needed to be converted to human orthologs; **zebrafish orthologs of genetic modifiers identified previously in Mtm1-/y mice). b Volcano plots showing differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between groups of interest (adjusted p value < 0.01, log2FC > 0.585). c Venn diagram highlighting DEGs that are shared or unique to each group and their associated GO enrichment terms. d Heat map visualization of GO terms enriched in mtm groups vs WT DMSO controls. Gray indicates lack of significance. e Connectivity scores generated by comparing the top DEGs (up to 300) from each group with the perturbagen-induced gene signature profiles in Connectivity Map. Scores > 90 indicate a high degree of similarity between queried gene lists and experimentally determined transcriptional responses to chemical or genetic perturbagens. The transcriptional signature of mtm mutants closely emulates that of human cell lines treated with protein kinase C (PKC) activators. f Heat maps showing expression changes in hypothetical modifier genes. Zebrafish orthologs of known genetic modifiers of Mtm1 in mice (*padj = 0.017, 0.015), HDAC genes, and genes involved in larval zebrafish fin fold development (*padj = 0.065) were considered. Gray indicates genes did not meet cut-offs and crossed boxes show genes that were not detected. Overall, none of these modifiers alone may account for the observed rescue |