Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220817-32
- Publication
- Braems et al., 2022 - HNRNPK alleviates RNA toxicity by counteracting DNA damage in C9orf72 ALS
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
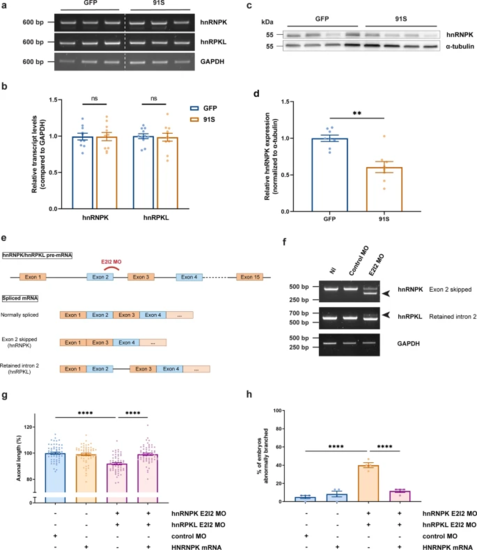
C9orf72 repeat RNA induces hnRNPK deficiency, which affects motor neuron health in zebrafish embryos. a RT-PCR analysis of HNRNPK zebrafish orthologues hnRNPK and hnRPKL in 30 hpf GFP and 91S mRNA-injected zebrafish embryos. b Relative quantification of hnRNPK and hnRPKL transcript levels in 30 hpf GFP and 91S mRNA-injected zebrafish embryos (N = 10 experiments). Data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated with ratio paired t test. c Western blot detecting endogenous hnRNPK protein levels in 6 hpf GFP and 91S mRNA-injected zebrafish embryos. A-tubulin was used as a loading control. d Relative quantification of hnRNPK protein levels in 6 hpf GFP and 91S mRNA-injected zebrafish embryos, normalized to α-tubulin levels (N = 8 experiments). Data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated with ratio paired t test; **P < 0.01. e Schematic presentation of splice-blocking morpholino targeting the exon 2-intron 2 (E2I2) junction in zebrafish hnRNPK and hnRPKL pre-mRNA. Outcome of the differentially spliced transcripts is shown. f Validation of MO-mediated knockdown by RT-PCR analysis. HnRNPK and hnRPKL splice variants in 30 hpf non-injected (NI), standard morpholino (control MO) and hnRNPK or hnRPKL targeting morpholino (E2I2 MO)-injected embryos are shown. Arrowheads indicate the alternative splice product induced by E2I2 splice-blocking MO. Exon 2 of hnRNPK is skipped and results in a shorter transcript. In hnRPKL, retention of intron 2 results in a higher weight band. GAPDH was used as reference gene. g, h Effect of morpholino-mediated knockdown of hnRNPK and hnRPKL on axonal length (g) and branching (h) (N = 4 experiments). E2I2 splice-blocking morpholinos were injected at 0.15 mM for hnRNPK and 0.25 mM for hnRPKL. Standard morpholino 0.25 mM. g, h Data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated with Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison test (g) or one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (h); ****P < 0.0001 |