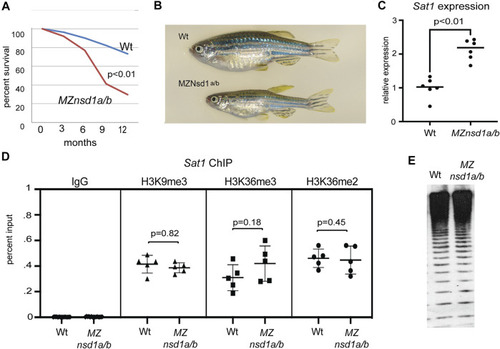
FIGURE 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220402-17
- Publication
- Calvird et al., 2022 - Uncovering Regulators of Heterochromatin Mediated Silencing Using a Zebrafish Transgenic Reporter
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
Combined homozygous deletion of |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Protruding-mouth to Adult |