Figure 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220203-9
- Publication
- Piccolo et al., 2022 - Radiation dose enhancement using gold nanoparticles with a diamond linear accelerator target: a multiple cell type analysis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
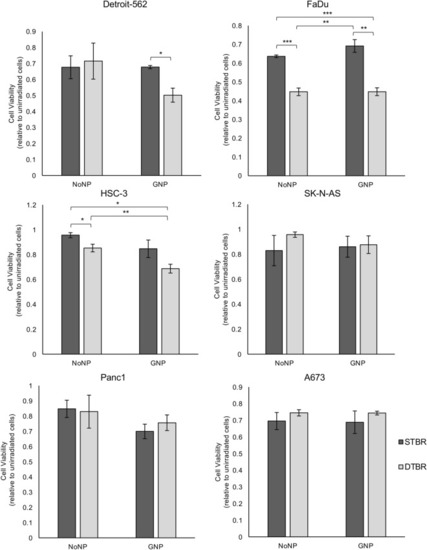
GNP-labeled HNCCs irradiated with the DTB show reduced viability 3 days post-irradiation. The alamarBlue viability assay was used to determine the levels of oxidative phosphorylation in cells irradiated with the STB or DTB and labelled with GNPs or NoNPs, 3 days after radiation. Detroit-562, FaDu, and HSC-3 HNCC lines demonstrated a significant reduction in cell viability following 8 Gy irradiation with the DTB in cells labelled with GNP compared to NoNP-labelled cells with STBR (p = 0.018, p = 0.004, p = 0.003, respectively). NoNP FaDu cells irradiated with the DTB demonstrated decreased viability compared to NoNP and GNP cells with STBR (p = 0.001 and p = 0.003, respectively). Similarly, NoNP HSC-3 cells irradiated with the DTB demonstrated a reduction in viability compared to NoNP cells with STBR (p = 0.049). With DTBR, GNP-labelled HSC-3 cells decreased compared to NoNP cells (p = 0.024). SK-N-AS cells, Panc1 cells, and A673 cells demonstrated no significant differences in viability. Cell viability values are made relative to control cells that were not irradiated and are presented as the fold change means ± standard error of the mean, p* < 0.05, p** < 0.01, p*** < 0.001 for significant decrease in cell viability. Significance between groups was tested using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Tukey multiple comparisons test (n = 3; 10 wells per group/replicate). GNP gold nanoparticles, NoNP no nanoparticles, HNCC head and neck cancer cells, STB(R) standard target beam (radiation), DTB(R) diamond target beam (radiation). |