Figure 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210915-87
- Publication
- de Vrieze et al., 2021 - Efficient Generation of Knock-In Zebrafish Models for Inherited Disorders Using CRISPR-Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein Complexes
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
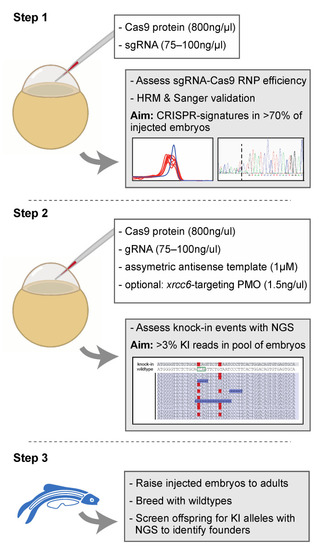
Proposed strategy for the efficient generation of knock-in zebrafish. Step 1 entails the verification of sgRNA-Cas9 efficiency at creating genomic lesions using high resolution melting (HRM) analysis. Step 2 concerns the injection of sgRNA-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes and the asymmetric antisense oligonucleotide template with the variant of interest. Next generation sequencing (NGS) is recommended to determine knock-in efficiency. In the situation of low knock-in efficiency, knockdown of non-homologous end-joining protein Ku70 (by co-delivery of an morpholino antisense oligonucleotide (PMO), targeting xrcc6) may offer a means to improve knock-in efficiency. Finally, injected embryos with sufficient knock-in reads can be raised to adults and screened for founders with the variant of interest in the germline (step 3). The white boxes in step 1 and step 2 described the key components injected into the zebrafish zygote. A detailed protocol can be found in Supplemental Document S1. |