Figure 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210915-77
- Publication
- de Vrieze et al., 2021 - Efficient Generation of Knock-In Zebrafish Models for Inherited Disorders Using CRISPR-Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein Complexes
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
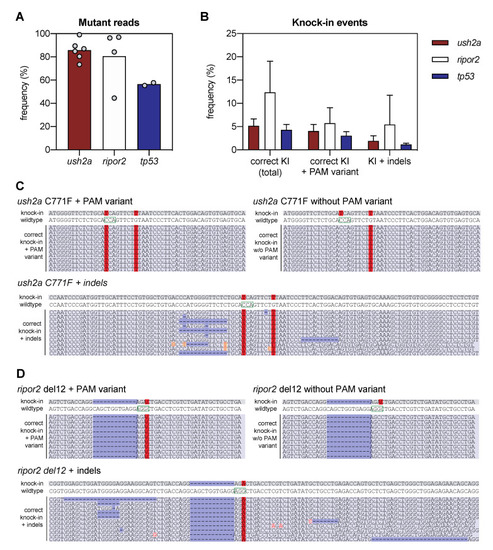
Next-generation sequencing analysis of knock-in efficiency after sgRNA-Cas9 RNP and HDR template delivery. (A) Percentage of mutant reads in the genomic DNA of pooled embryos after injection of sgRNA, Cas9, and asymmetric antisense oligonucleotide templates. Mutant reads are quantified as the percentage of all non-wildtype reads. Data is expressed as mean (bar) and values of individual replicates (scatterplot). (B) Knock-in efficiency after injection of sgRNA, Cas9 and asymmetric antisense oligonucleotide template. Knock-in (KI) reads are quantified as percentage of total reads with correct knock-in with and without the silent variant in the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). The percentage of correct knock-in reads with additional variants is provided as KI + indels. Examples of correct knock-in reads with and without PAM variants and indels are provided for (C) ush2a C771F RNP injected embryos, and (D) ripor2 del12 RNP injected embryos. The correctly-introduced nucleotide substitutions are indicated in red. Unintended nucleotide substitutions are indicated with a red font on orange background. Deletions are indicated in dark blue. The PAM sites are indicated on the wildtype sequences by a green box. |