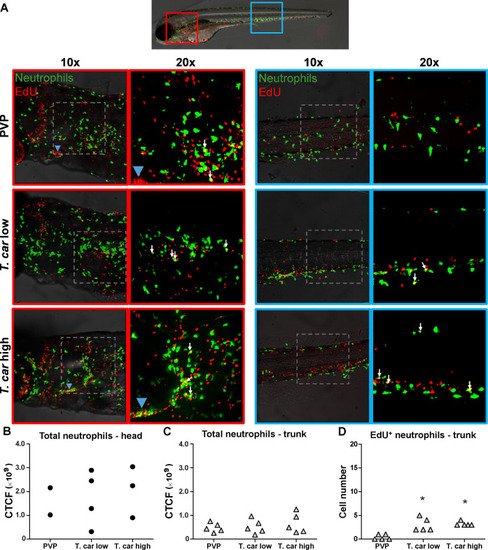
(A) Tg(mpx:GFP) were treated as described in Figure 4 (n = 4–5 larvae per group). Maximum projections of the head (left panels, red boxes) and trunk (right panels, blue boxes) regions of one representative individual in PVP, low- and high-infected zebrafish. Images capture neutrophils (green) and EdU+ nuclei (red). The images acquired at a ×20 magnification show that in all groups, EdU+ nuclei and GFP+ neutrophils only rarely overlapped (white arrows), and was marginally higher in infected than in non-infected PVP controls. Detailed analysis of the separate stacks selected to compose the overlay image of the head region of the high-infected larva (bottom left panel), revealed that none of the neutrophils in the area indicated by the blue arrowhead (thymus) were EdU+ (Video 3). (B–C) Corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) calculated in the head (B) and trunk (C) region of larvae described in A. Symbols indicate individual larvae (n = 4–5 per group from two independent experiments). ** indicates significant differences between CTCF in the head and trunk regions, as assessed by Two-Way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. (D) Tg(mpx:GFP) were treated as described in A and the number of EdU+ neutrophils in the trunk region of PVP, low- and high-infected larvae was calculated. Symbols indicate individual larvae (n = 5 per group from two independent experiments). * indicates significant differences to the PVP control as assessed by One-Way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test.
|

