Figure 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210625-11
- Publication
- Leyden et al., 2021 - A distributed saccade-associated network encodes high velocity conjugate and monocular eye movements in the zebrafish hindbrain
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
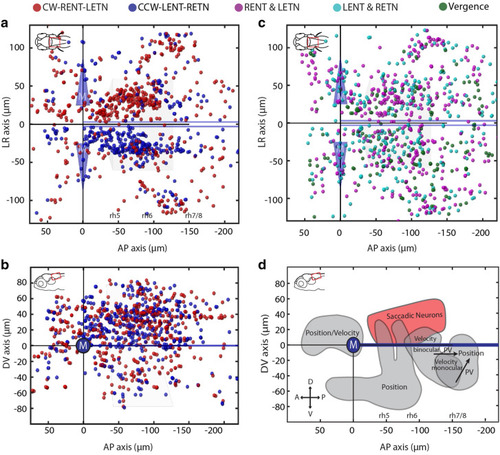
Anatomical distribution of putative burst neurons in the zebrafish hindbrain. Each colored ball represents an identified saccade-associated neuron. ( |