Figure 1
|
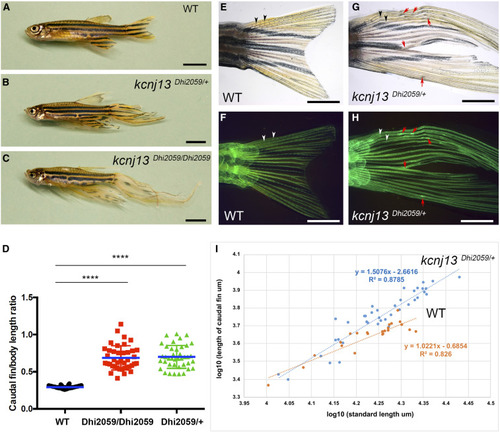
Fins are elongated in the adult zebrafish mutant Dhi2059. (A) WT fish with normal-sized fins. (B and C) Both one- and two-copy transallelic mutants of Dhi2059 possessed elongated paired and median fins. Bars, 50 mm in (A–C). (D) The lengths of caudal fins in Dhi2059 mutants are significantly longer compared to WT siblings. Fish were generated by |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |