|
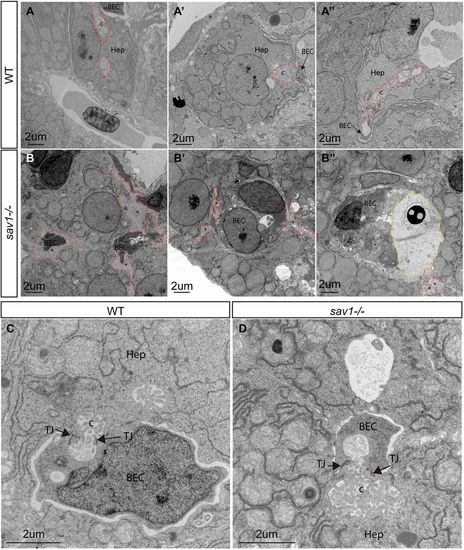
Ultrastructural defects of bile duct canaliculi in sav1−/− larvae. (A-A″) TEM examples of wild-type canaliculi and hepatocyte-biliary epithelial cell junctions. Canaliculi are outlined with dashed red lines. (B-B″) sav1−/− siblings of A-A″ showing examples of hepatocyte-to-biliary cell borders that contain membranous material reminiscent of canaliculi, but lack normal structure (dashed red lines). In B″, a dashed yellow line outlines excessive extracellular space filled with electron-dense material. (C) Higher magnification of wild-type hepatocyte-biliary epithelial cell junction and canaliculi. (D) Example of a rare canaliculi present in sav1−/− larvae showing shorter length and increased diameter. Hep, hepatocyte; BEC, biliary epithelial cell; c, canaliculi; TJ, tight junction. Asterisks indicate abnormal canaliculi or abnormal hepatocyte membrane. n=3 wild type, n=3 sav1−/−. All images are of 10 dpf larvae.
|