|
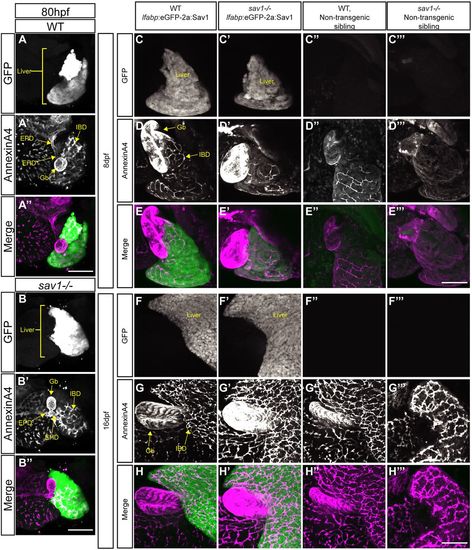
Hepatocyte Hippo signaling is crucial for larval survival and functions non-cell-autonomously to affect the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary system. (A,B,C-C‴,F-F‴) Whole-mount GFP staining in wild-type and sav1−/− larvae. (A′,B′,D-D‴,G-G‴) Annexin A4 staining of gallbladder and intrahepatic biliary cells. Gb, gallbladder; EHD, extrahepatic duct; EPD, extrapancreatic duct; IBD, intrahepatic bile duct. (A″,B″,E-E‴,H-H‴) Merged images with green representing GFP and magenta representing annexin A4. (A-B″) Larvae at 80 hpf (n=3 wild type, lfabp:eGFP-2a:Sav1+ and sav1−/−, lfabp:eGFP-2a:Sav1+). (C-E‴) Larvae at 8 dpf (n=8 wild type, lfabp:eGFP-2a:Sav1+; n=7 sav1−/−, lfabp:eGFP-2a:Sav1+; n=3 wild type, non-transgenic sibling; n=5 sav1−/−, non-transgenic sibling). (F-H‴) Fish at 16 dpf (n=12 wild type, lfabp:eGFP-2a:Sav1+; n=12 sav1−/−, lfabp:eGFP-2a:Sav1+; n=8 wild type, non-transgenic sibling; n=4 sav1−/−, non-transgenic sibling). Scale bars: 100 μm.
|