Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170524-5
- Publication
- Thomas-Jinu et al., 2017 - Non-nuclear Pool of Splicing Factor SFPQ Regulates Axonal Transcripts Required for Normal Motor Development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
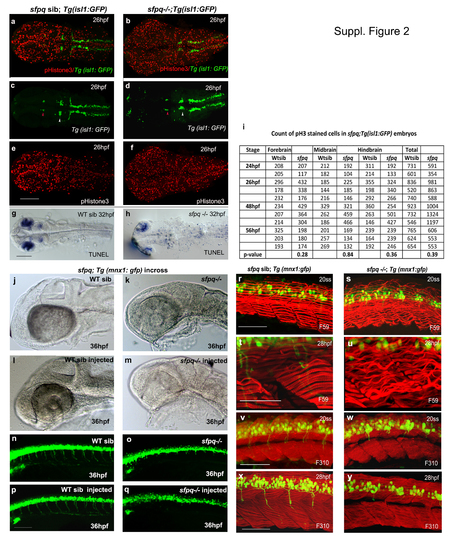
(Related to Figure 2). Cell proliferation and apoptosis in sfpq mutant Dorsal view of zebrafish brain at 26hpf (a-f) and 30hpf (g-h) with anterior to the left. a-f. Cell proliferation in sfpq mutant brain (n=11) analysed using gfp expression in sfpq;Tg:isl1 gfp as a landmark to delineate the domains: nIII neurons (red arrowhead ) as posterior limit of the forebrain and the anterior limit of the midbrain; nV neurons (white arrowhead ) as the posterior limit of the midbrain and the anterior limit of the hindbrain. Cell proliferation in the tail of sfpq mutant was found in par with that of its WT siblings (data not shown). g,h. Increased apoptotis is observed throughout the the sfpq brain (n=4) compared to siblings (n=12). i. Proliferation quantified using phosphor-Histone3 staining, counted in different brain regions of sfpq mutant and siblings. No significant difference was observed in cell count (Student’s t-test, p>0.05). Increased cell proliferation observed in some (n=5 of the 11 counted) may be due to cells getting arrested at G2/M phase of cell cycle. sfpq initial phenotype is independent of cell death j-q. p53 knockdown in sfpq;Tg(mnx1: gfp) embryos. Lateral view of zebrafish brain (jm) and spinal cord (n-q) at 36hpf with anterior to the left. The p53 MO injected sfpq-/- embryos (k, o. n=3) show similar MHB phenotype and axonogenesis defect as the noninjected mutants (m, q. n=5), compared to injected (l, p. n=14) and non-injected siblings (j, n. n=11). Scale bar=100μm. Muscle formation in sfpq mutant r-y. Lateral view of zebrafish muscle, anterior to the left. r-u. Immunostaining for slow muscle with F59 antibody shows proper somatic boundaries and differentiated slow muscle fibres and sarcomeres in the sfpq mutant (20ss: n=6/25; 28hpf: n=9/39). The wavy appearance of slow muscle fibres in the mutant at later stages compared to its WT siblings (c-f), likely due to inactivity. v-y. Immunostaining for fast muscle with F310 antibody shows the integrity of the fast muscle in sfpq mutant (20ss: n=5/22; 28hpf: n=6/24) as normal as in its WT siblings. Scale bar=100μm. |