Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170523-38
- Publication
- Thomas-Jinu et al., 2017 - Non-nuclear Pool of Splicing Factor SFPQ Regulates Axonal Transcripts Required for Normal Motor Development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
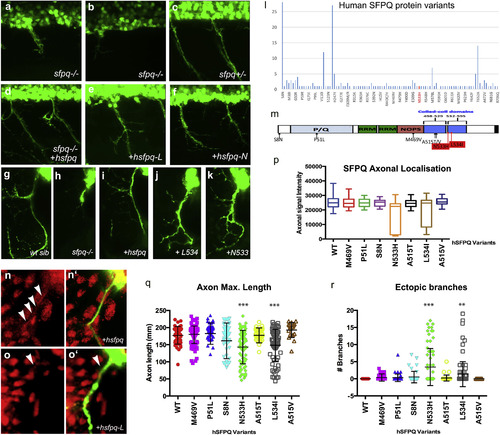
Human Mutations Affect SFPQ Localization and Motor Development in the Zebrafish (A–K) Lateral (A–F) and transverse (G–K, N, and O) views of the spinal cord in sfpq−/− mutant (A, B, and H), siblings (C and G), and homozygous mutant rescued by wild-type human Sfpq (D and I) or L534 (E, J, and O) or N533 (F and K) mutant human Sfpq. (L) Distribution of SFPQ variants in all exome-sequenced human individuals. In red, the position of the variants only found in fALS patients. (M) Schematic of the wild-type hSFPQ protein and the seven variants cloned and tested in double-blind rescue experiments in the Tg(mnx1:GFP) background. S8N (c.23G>A) is present in 4 SALS and 24 ExAC samples, showing a modest enrichment in SALS (p = 0.029, two-tailed Fisher’s test). P51L (c.152C>T) is private to a single SALS patient and absent from all controls. M469V (c.1405A>G) is in a single SALS patient and twice in ExAC (p = 0.071). A515V (c.1544C>T) and A515T (c.1543G>A) are in two and one ExAC normal individuals, respectively, and are located in the coiled-coil domain close to the two FALS variants we identified. (N and O) Close-up of the motor axon and its environment, stained for SFPQ in red and GFP in green in the sfpq−/−; Tg(mnx1:GFP) rescued by injection of the human (N and N′) or L-mutated form (O and O′). Arrowheads show localization of SFPQ in motor axons. (P) Quantification of the α-SFPQ red fluorescent signal in motor axons on confocal stacks, for five pairs of motor axons per 48 hpf embryo stained with SFPQ antibody. Measurement was done in no less than 30 (maximum, 46) embryos per variant injected. Injection is done in sfpq+/−;Tg(mnx1:GFP) incross progeny. The embryos showing poor signal intensity were genotyped and were all homozygous mutants. (Q) Quantification of the length of ventral motor axons. Measures were made for five segments per 48 hpf embryo (five somites anterior to the cloaca) on confocal stacks, using FIJI Single Neurite Tracer in no less than 28 (maximum, 41) embryos per variant injected. Injection is done in sfpq+/−;Tg(mnx1:GFP) incross progeny. The embryos showing shorter axon length were genotyped and were all homozygous mutants. Asterisks indicate highly significant reduction in axon lengths compared to wild-type (pairwise ANOVA, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001). The two significantly different variants show same difference when comparing pairwise to the other variants. All other variants are not significantly different from wild-type. (R) Quantification of ectopic ventral motor branching. Measures were made for five segments per 48 hpf embryo (five somites anterior to the cloaca) on confocal stacks using FIJI Single Neurite tracer in no less than 28 (maximum, 41) embryos per variant injected. Injection is done in sfpq+/−;Tg(mnx1:GFP) incross progeny. The embryos showing excessive branching were genotyped and were all homozygous mutants. Asterisks indicate significance (pairwise ANOVA, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001 and ∗∗p < 0.001) compared to wild-type. The two significantly different variants show same difference when comparing pairwise to the other variants. All other variants are not significantly different from wild-type. |