Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170426-8
- Publication
- Li et al., 2009 - Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
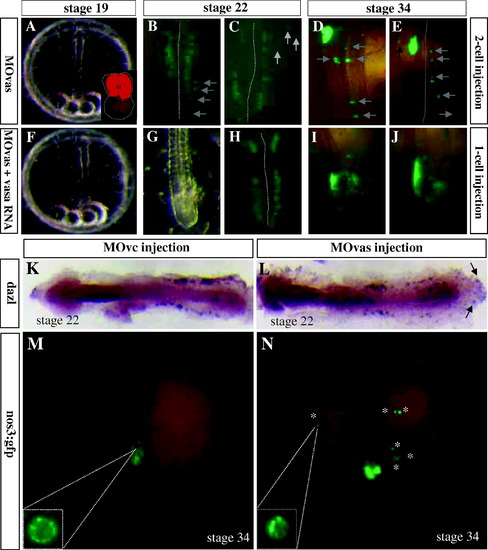
Phenotypic rescue and PGC identity. (A–E) PGCs in embryos injected with MOvas into one of the 2-cells. The insert of (A) shows the MOvas distribution in half of the embryo (asterisk). At stage 19, all PGCs at both sides are aligned normally (B) or nearly so (C). At stage 34, many ectopic PGCs (arrows) are seen in the injected side (D and E). (F–J) vasa RNA can rescue abnormal PGC distribution caused by MOvas. Somatic development appears normal. Many PGCs are seen in the gonad, and ectopic PGCs are usually found close to the gonad, compared to wide distribution of PGCs distantly from the gonad in embryos injected with MOvas only (see Fig. 1F′). (K–N) PGC identity. (K and L) Embryos by stage 22. The germ cell marker dazl RNA is normally expressed in normal and ectopic PGCs (arrows) of MOvc-injected control (K) and MOvas-injected embryos (L). (M and N) Embryos by stage 34. Similar stability and localized perinuclear speckles of the Nanos:GFP fusion protein (green) from injected nos:fgp RNA are seen in both MOvc- and MOvas-injected embryos. Notably, the GFP intensity and nuclear speckle formation are normal also in ectopic PGCs of MOvas-injected embryos (asterisks in N). |
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 126(5-6), Li, M., Hong, N., Xu, H., Yi, M., Li, C., Gui, J., Hong, Y., Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells, 366–381, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.