Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170426-10
- Publication
- Li et al., 2009 - Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
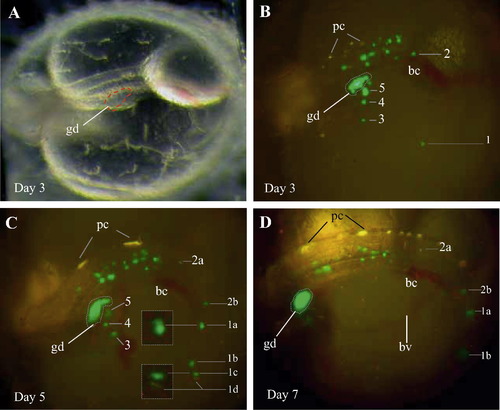
Behavior of vasa-depleted PGCs at ectopic sites. A representative MOvas-injected class II embryo is shown in dorsal lateral views. (A and B) Phenotype and PGC distribution at day 3. (C) Day 5. (D) Day 7. Many PGCs are seen outside the gonad (gd). These ectopic PGCs do not disappear, and undergo cell divisions. Some of these ectopic PGCs are numbered for continuous observation. For example, PGC1 and PGC2 from day 3 (B) to day 5 (C) produce two (2a and 2b) and 4 daughter PGCs (1a–1d). Furthermore, PGCs 1a–1c are seen at cytoplasm division each, as clearly shown in the insert for PGCs 1a and 1c. These ectopic PGCs steadily change their positions, as most evident for numbered PGCs. Cell movement persists until 7 dpf (D), when PGCs 1c and 1d moved down beyond focus and invisible in this particular view. Pigment cells (pc, yellow), blood cells (bc, red) and blood vessel (bv, red color due to blood cells) on the yolk sac are visible. The embryo enlarged by continuous growth. Anterior is to the left. |
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 126(5-6), Li, M., Hong, N., Xu, H., Yi, M., Li, C., Gui, J., Hong, Y., Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells, 366–381, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.