Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150715-1
- Publication
- Xiong et al., 2015 - Multibow: Digital Spectral Barcodes for Cell Tracing
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
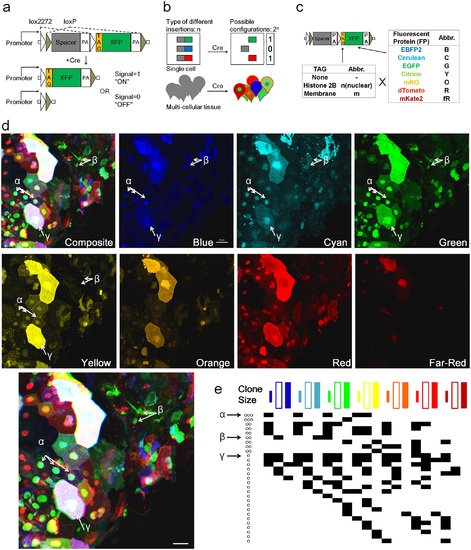
Design and test of Multibow in zebrafish. a. Modified “Brainbow [1]” cassette that allows a binary ON/OFF switch. b. Multibow Strategy. Each cell harbors multiple different ON/OFF cassettes to generate random color “digital” barcodes upon Cre-mediated recombination. c. Table of Multibow Tags and Fluorescent Proteins (FPs). d. Diversity of color codes. Image is a densely labeled region along the trunk of a 40hpf hsp70:cerulean-cre embryo injected with all 21 Multibow constructs and heat-shocked at 10hpf for 1 hour. The color and tag diversity generates barcodes for cell clones that appear random and diverse. Intensity differences further help distinguish cells from neighbors visually. The Composite image is made from the green, yellow (turned to blue) and red panels. 3 different clones are highlighted by α, β, γ and corresponding arrows. Scale bar: 10µm. See also S3 Table. e. Partial table of clones of different color codes found in d.. The colored square labels of the top row indicate nuclear, membrane and cytoplasmic, respectively. A black square in the table indicates this clone being positive for the corresponding color. Distinct "barcodes" form for different clones. The α, β, γ clones are indicated by arrows. The number of annotated cells labels (~30) represents a large fraction of cells found in the image in d, which contains ~50 cells. The fact that most of these cells have a color code distinct from any other cell (except clones that have the same color) show that Multibow label is highly random. |